The orthotic and therapeutic effects following daily community applied functional electrical stimulation in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial
Full text
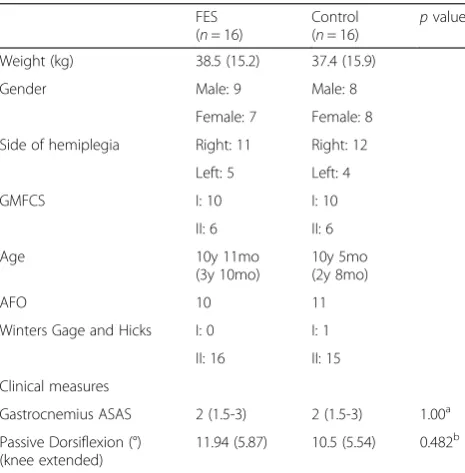
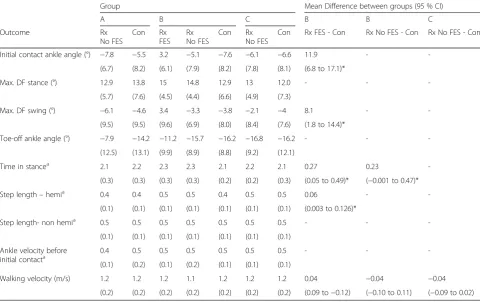
Figure


Related documents
These nations emphasized trade considerations' 2 rather than foreign policy 3 or national security con- cerns.' 4 The United States therefore adopted unilateral
In this paper, we initiate the basic theory of hybrid random differential equations of mixed perturbations of second type involving two nonlinearities and prove the basic result such
The findings here suggest the possibility that a significant portion of the observed positive coefficients in larger firms and firms with foreign ownership can be accounted for by
Overall, a higher percentage of Public Program students in our sample are equipped with a wider variety of technological devices and software than are students enrolled in
Serious toxicity following NSAID overdose is rare, however identi- fication and treatment of patients with massive ingestions at risk of significant effects such as
In the MDF manufacturing industry, safety officers will conduct the safety meeting in section vice per every three months. Those meetings contain important information
Pediatrics 2003; 111:836 – 843; physical activity, strength training, aerobics, dancing, walking, seasonal activity, inactivity, television, videos, computer games, video games,