Irrigated small-grain residue management effects on soil chemical and physical properties and nutrient cycling
Full text
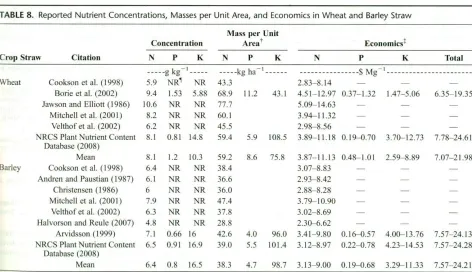
Figure



Related documents
From the study findings, the amount or volume of credit needed (5.58), relationship with the microfinance provider (2.88), problematic extent of protocols including
This article presents ALOCS, a distributed data repository that adopts the key-value model, but allows a set of pairs to be grouped in a single structure, called bucket, whose
Four supplemental rules are needed to prevent second-tier holding companies from exploiting their narrow banks’ safety net subsidies. First, narrow banks should
The effect of multiple infusions of infliximab (INF), a chimeric anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody, on the concentration of hexosaminidase (HEX) activity in a synovial
In 70% of patients with metastatic tumor in the neck as a first symptom of the disease the primary side of cancer is located in nasopharynx, palatine tonsil or hypopharynx.. Having
Some of the challenges in making a comparison between WRF-ACASA simulations and the observations are that (1) the observation heights were frequently different than the simulated
CDS are color coded to indicate genes common between phylogenetic bins (green = identified in all four bins; black = only present in corresponding bin; purple = identified in FlavI
These variables and parameters include the profiles of snow temperature, density, grain size, stickiness, and liquid water content, the characteristics of the substratum (e.g.