Active Learning of Causal Networks with Intervention Experiments and Optimal Designs
Full text
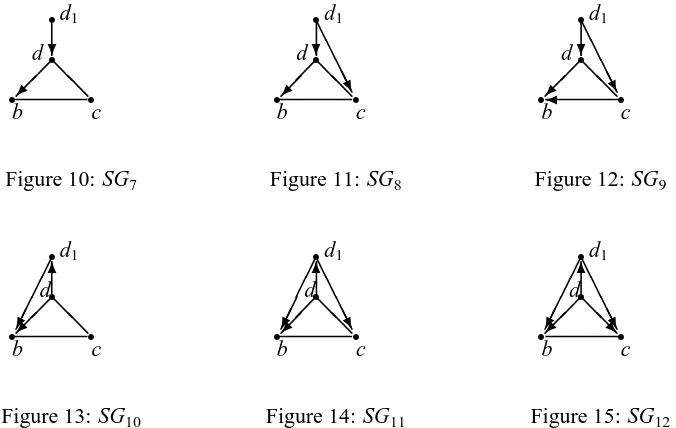
Figure
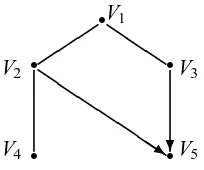
![Figure 2: The equivalence class [G].](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/9833521.1969546/4.612.111.510.128.255/figure-the-equivalence-class-g.webp)
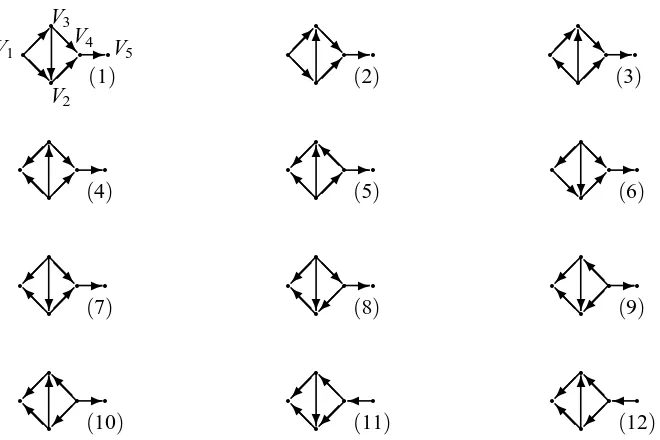
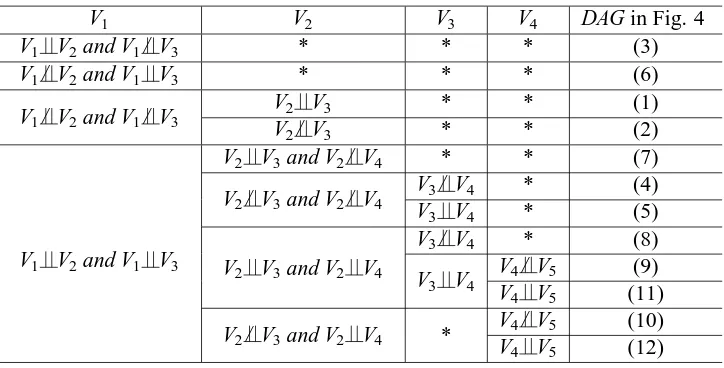
Related documents
Our comparison studies between the augmented BGG model with Basel I bank regulation and the one with Basel II bank regulation suggest that, in the presence of credit market
Examples of predicates with modal, modality and phase verbs: 1a) Der Konsul musste diese Ida in Schtz nehmen. 1b) Konzul morade uzeti Idu u zańtitu. 2a) Unsere Tony soll
ВИСНОВКИ В дисертаційній роботі наведене теоретичне узагальнення та вирішення наукового завдання кріохірургічного лікування хворих
Olympia, Sun Aquarius, Moon Sagittarius; Seattle, Sun Capricorn, Moon Leo Spokane, Sun Sagittarius, Moon Pisces; Tacoma, Sun Gemini, Moon Leo Yakima, Sun Aquarius,
Insurers issuing out-of-state group policies may engage in rating practices that state law prohibits for policies issued directly in the state, except that the small
4 UCLA Wil Stanley Zach Hendrickson Gabi Garcia Fernandez Davide Gardini Cyrus Fa’alogo Miki Jauhiainen Felipe de Brito Ferreira Concordia Irvine Wil Stanley Taylor Richards Gabi
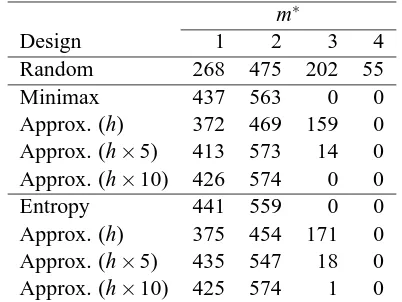
We define a solution to the optimization problem as a set of values given to the decision variables (i.e., the input parameters to the simulation model, also called factors)..