Understanding Differences in Perceived Peer Review Helpfulness using Natural Language Processing
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Income tax in the third quarter was NOK 195.8 million, up from NOK 49.7 million in second quarter 2011 due to higher exploration expenses related to drilling operations on the
This design helped in examining the relationship HRM practices have with Organisational growth of Saipem Contracting Nigeria Limited in terms of technological transfer to Nigerian
Following the Tunisian uprisings in 2011, cooperation between Tunisia and the EU, and particularly Italy, regarding irregular migration increased as thousands of Tunisians
14 • Visits to residential & commercial buildings to observe planning & services 9 • Evolving simple two- dimension house plan to scale 17 • Interior presentations
Klauer (1991) further derived the uniformly most powerful unbiased (UMPU) test and the uniformly most accurate confidence interval based on the exact distribution of the
Our approach addresses the DG problem in CC-FG-SBIR by embedding the query sketch in our universal embedding space, and using this embedding as the descriptor of the new domain
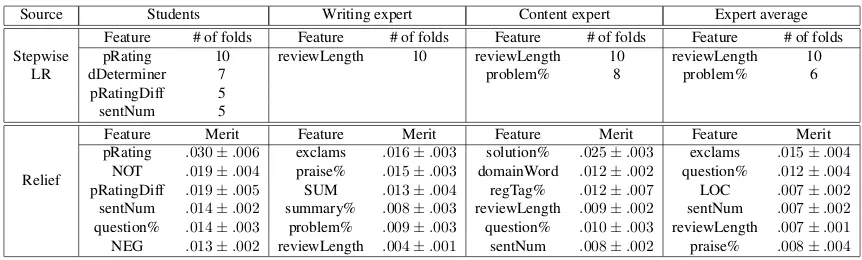
In addition to the user-specific model of Section 2.2.2, we evaluate four user-agnostic models: (1) a baseline model that trains a linear logistic regres- sor on features extracted
To summarize, the core contributions of my thesis are twofold: the additions to the framework for non-parametric inference, namely the kernel Kalman rule and the sub- space