Metal ion–binding properties of the L aspartic acid and tartaric acid, a coparative investigation How can be increased the dosage of mineral absorption in the body
Full text
Figure

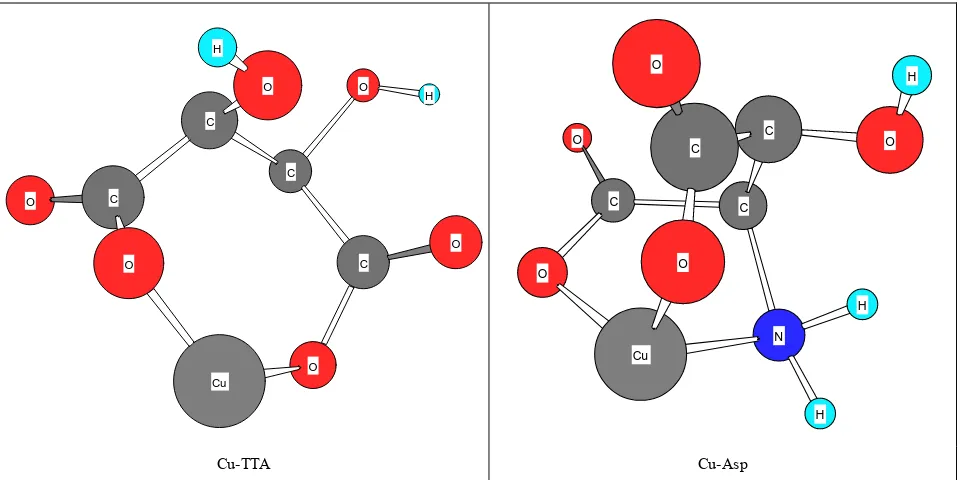
Related documents
Methods: QBC939 cells were divided into D group (cells without treatment), Dz group (cells transfected with negative control), Dm group (cells transfected with miR-181a
This paper reports on a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) sensor, which consists of a planar antenna, millimeter-wave monolithic integrated circuits (MMIC), and a phase
Its frequency of M O O cm is greatly shifted from the gas phase frequency (3756 and 3652 cm indicating a strong perturbation by the surface field. This strength of adsorption
There was no evidence for a minimum size for sexual maturity; in contrast to the three other genotypes of females examined, the immature N’ N’ fish of any age group were not
Transverse relaxation rates of P19 cells under various conditions of extracellular iron supplementation.. Cellular iron handling in P19 cells in response to
RT-PCR analysis of effects of BAI on the gene expression of IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 in IL-1 E - and TNF- D -activated HMC-1 cells. HMC-1 cells were treated
Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and activity of daily living among oldest-old in China: based on Chinese Longitudinal Health Longevity Survey.. This
The results re- vealed that (i) the lowland areas have events with relatively larger variability in rain depth and rain rate as compared to events in the mountain areas, (ii)