Analysis of three strategies to increase screening coverage for cervical cancer in the general population of women aged 60 to 70 years: the CRICERVA study
Full text
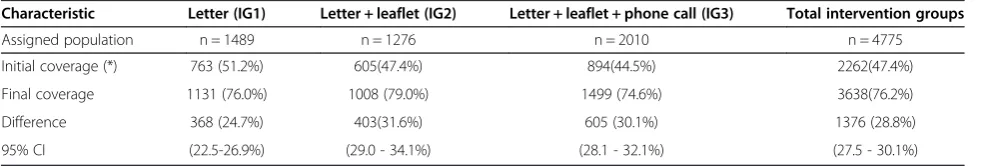
Figure


Related documents
redundant information so that the length of the final block equal to block size of the scheme..
The main purpose of the experimental modal analysis is to determine dynamic properties, such as the natural frequency, damping ratio, and mode shape of the
This study aimed to analyze the prevalence of complications associated with cochlear implantation in Misrata central hospital,
of their partner's wish for a child early in the relationship than young parents, while young couples agreed implicitly more often on having children.. This probably implies
Throughout the book, she then elaborates on the different themes, introducing the reader to how they have been discussed within the field, and bringing up numerous examples of
Wu, “Global existence and blow-up problems for quasilinear parabolic equations with nonlinear boundary conditions,” SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, vol. Wang, “The
Detrended Correspondence Analysis (DCA) for the proportional abundance (%) of bird species in the three habitats (inside aggregates, edges and outside aggregates), in
First, at the national level, in each of the years 2005, 2010, 2014, and 2016, after controlling for other factors, significant inequalities persisted in Rwanda by poverty and