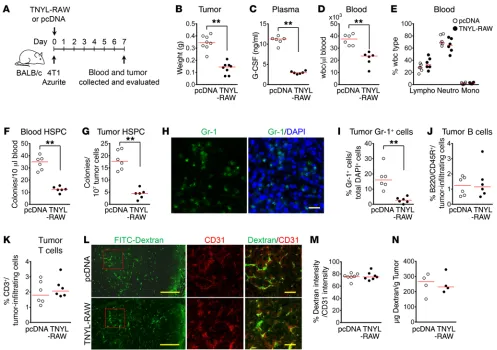
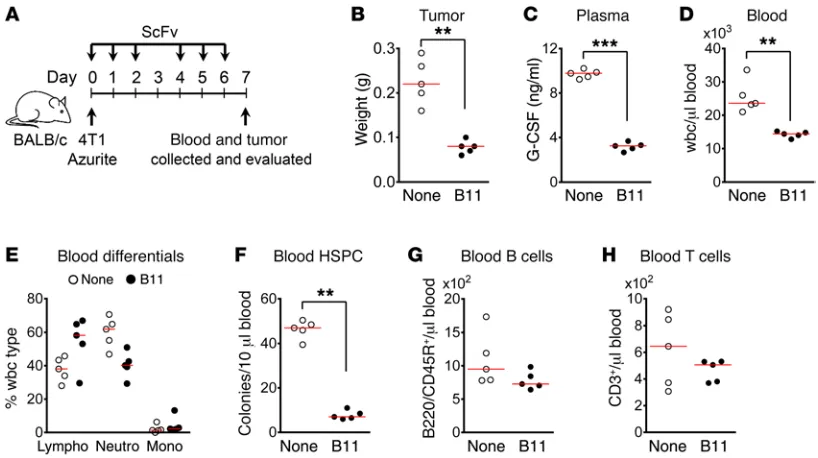
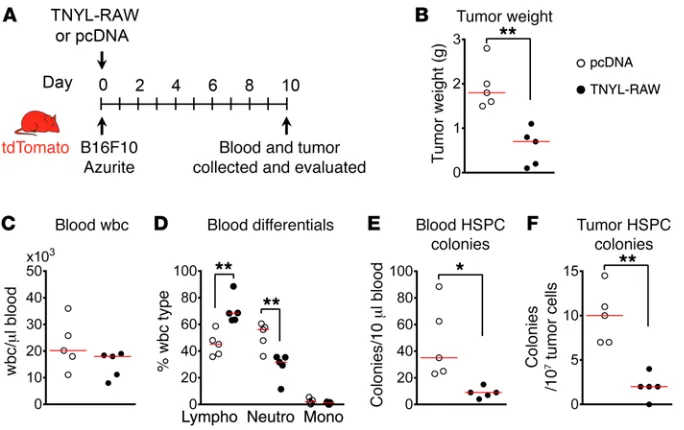
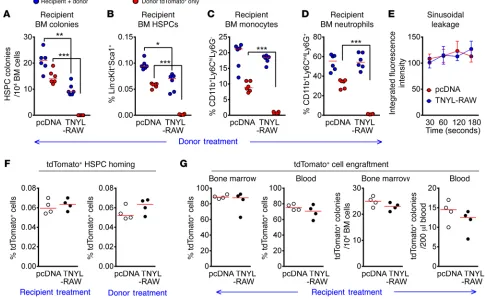
Sinusoidal ephrin receptor EPHB4 controls hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization from bone marrow
Full text
Figure



Related documents
cardiogenic shock or congestive heart failure in the setting of acute myocardial infarction. Gutovitz AL, Sobel BE, Roberts R: Progressive nature of myocardial injury in
Hence the re ranking concept arises to re rank the retrieved images based on the text surrounding the image and metadata and visual feature.. A number of methods
To further support the risk analysis re- lated to the dispersion of uranium and thorium from solid phases to the environment, crystallographic structure of uranium-thorium
The growth rate decreased with increasing salinities and showed a maximum in a mesohaline medium, while the photosynthetic rate and the chlorophyll a content increased under
Migraine is associated with an increased risk of deep white matter lesions, subclinical posterior circulation infarcts and brain iron accumulation: the population- based MRI
µ M in the mix of the assay. Total binding evaluation was accomplished using de-ionized water. A cryopreserved membrane expressing 5HT 6 receptor at 37°C was used
With these certificates publishers of maps, atlases or other cartographic products will avoid potential mistakes and inaccuracies and will also provide users with
As regards the variations found in our study, the most common type (Type I, 45%) formed the esoph- ageal hiatus from muscular contributions arising solely from the right crus (Fig..