Screw Intramedullary Nailing for Fractures of the Humeral Shaft
Full text
Figure

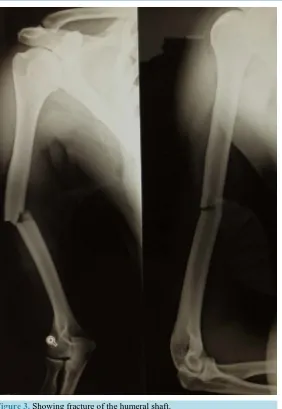

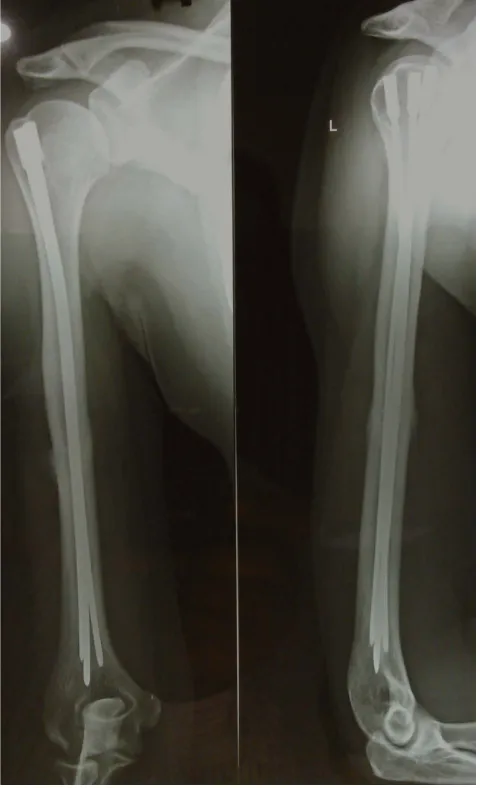
Related documents
occidentalis link plant showed a significant (P < 0.05) phytoextraction potential for all the five metal considered in this study when the waste dump soil was used in six
The present study aimed to examine the different types of stressors experienced by adults of different ages in everyday life, their coping strategies, and positive/negative
A comparative study of the fracture union between long and short proximal femoral intramedullary nails antirotation in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures in
Stainless Steel Flexible Intramedullary Fixation of Unstable Femoral Shaft Fractures in Children.. External fixation or flexible intramedullary nailing for femoral
This study consisted of 20 patients with traumatic humeral shaft fractures, treated with closed ante-grade intramedullary titanium elastic nailing were included in the
Conclusions: Unreamed intramedullary nailing, if it can be implemented with closed technique and with double lock screw at the distal side, provides satisfactory results in the
Conclusions: Gentle progressive reaming, correct entry point, minimal damage to rotator cuff, properly embedding the tip of the nail, good apposition of fracture fragments,
Many authors compared the intramedullary nail (IMN), which involved gamma nail, intramedullary hip screw (IMHS), and PFN, with sliding hip screw (SHS)