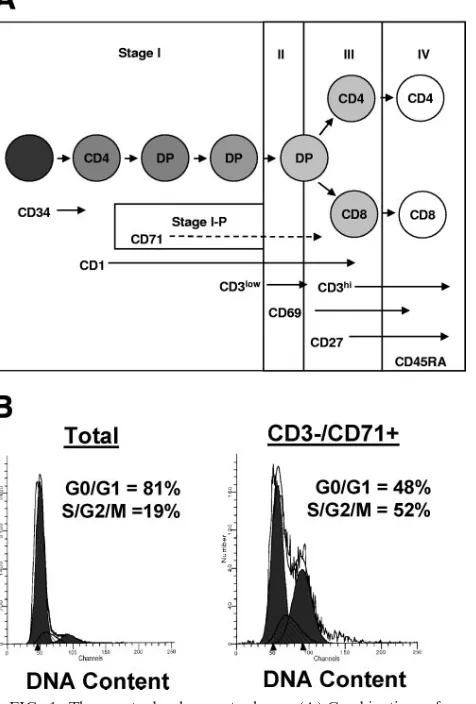
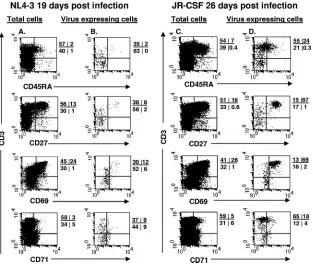
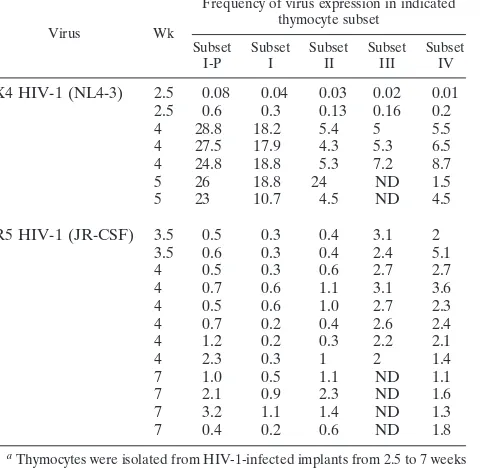
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Persistence and Production in T-Cell Development
Full text
Figure

Related documents
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA IN CHILDREN & ASSESSMENT OF SEVERITY OF ASTHMA AND ITS CORRELATION WITH SERUM IgE
Because of the general relatedness of lentiviruses, it is con- ceivable that additional lentivirus genes are also required for HIV replication but exist in a surrogate or
Direct Immunofluorescence study: Linear deposition of IgA along the basement membrane zone is seen. There may also
CVB3 infection of female mice results in preferential Th2 cell responses, but in vivo treatment of fe- males with androgens can shift the dominant CD4 1 T-cell response toward the
the N protein in neurons infected with CVS-B2c and CVS-N2c differed (Fig. 2) despite the identical amino acid sequences of this protein in the variants (16), the differences in
HTLV-1 envelope-dependent entry, we examined the inhibi- tory effect of mature gp46 and gp21 proteins, which were purified from an HTLV-1-infected cell line (12, 26), on syncy-
Accumulation of mutant virus in organs of infected turnip deter- mined by dot blot analysis of total viral DNA isolated from tissues at 26 days postinfection of plants infected
Given the rarity of naturally occurring mutations which result in enhanced initiation of translation and previous evi- dence that domain 3 is essential for IRES activity of FMDV
