Predicting frequent asthma exacerbations using blood eosinophil count and other patient data routinely available in clinical practice
Full text
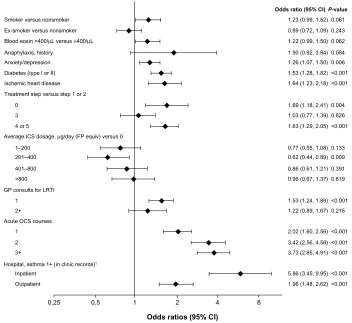
Figure




Related documents
Outsourcing data storage increases the attack surface area. 1.When data is distributed it is stored at more locations increasing the risk of unauthorised
5 In 1997, the Copyright Office issued a comprehensive review of the copyright licensing regimes governing the retransmission of over- the-air radio and television
Extravascular lung water index measurement in critically ill children does not correlate with a chest x-ray score of pulmonary edema [published correction appears in Crit
When the athlete is evaluated initially in the office or emergency department after a concussion, a thorough history, including signs and symptoms as well as details of any previous
The first 47 medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency cases de- tected by the New England Newborn Screening Program were classified according to initial and
Zane: So I literally wasted my years growing up, um, you know, I got to know a few good people here and there, but education-wise, I just (sigh) I just fooled around with my
Evidence of pathogenesis shows a close association between chronic cerebrospinal venous inhibitions (CCSVI) to MS supporting the pathogenetic theory (Table 1) [42-49]. It is
Third, the category of the lung nodule image is finally determined with a probabilistic estimation based on the combination of the nodule structure and surrounding anatomical