organic papers
Acta Cryst.(2006). E62, o2003–o2004 doi:10.1107/S160053680601436X Bu¨yu¨kgu¨ngo¨r and Odabas¸og˘lu C
14H10ClNO2
o2003
Acta Crystallographica Section EStructure Reports Online
ISSN 1600-5368
3-(4-Chloroanilino)isobenzofuran-1(3
H
)-one
Orhan Bu¨yu¨kgu¨ngo¨raand Mustafa Odabas¸og˘lub*
a
Department of Physics, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, TR-55139 Kurupelit Samsun, Turkey, andbDepartment of
Chemistry, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, TR-55139 Kurupelit Samsun, Turkey
Correspondence e-mail: muodabas@omu.edu.tr
Key indicators
Single-crystal X-ray study T= 296 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.005 A˚ Rfactor = 0.055 wRfactor = 0.139
Data-to-parameter ratio = 14.5
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
Received 10 April 2006 Accepted 20 April 2006 3-Substituted phthalides. Part IV.
#2006 International Union of Crystallography
All rights reserved
The structure of the title compound, C14H10ClNO2, is stabilized by N—H O, C—H and – interactions. The phthalide part of the molecule is planar and the dihedral angle between the phthalide group and the benzene ring is 75.58 (15).
Comment
Phthalides are known to show diverse biological activities as hormones, pheromones and antibiotics (Aoki et al., 1973; Kubota & Tatsuno, 1971; Tsi & Tan, 1997). As part of our ongoing research on 3-substituted phthalides, the title compound, (I), has been synthesized and its crystal structure is reported here.
[image:1.610.254.410.347.464.2] [image:1.610.209.461.582.704.2]The molecule of (I) is built up from a phthalide unit connected to a chlorophenyl ring through an amino group (Fig. 1). The phthalide part (atoms C1–C8) is essentially planar, the largest deviation from the mean plane being 0.014 (3) A˚ for atom C1. The dihedral angle between thep -chlorophenyl ring and the mean plane of the phthalide group is 5.58 (15).
Figure 1
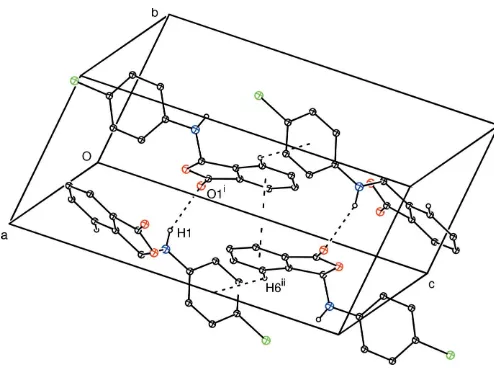
The occurrence of N—H O hydrogen bonds results in the formation ofC(6) chains (Etter, 1990) developing parallel to the a axis (Table 1, Fig. 2). TheseC(6) chains are linked to each other by C—H and–interactions, resulting in the formation of a sheet parallel to thebcplane (Table 1, Fig. 2). The–interaction occurs between the C2–C7 six-membered ring and its symmetry-related counterpart at (x,y+ 1,z), with a centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.618 A˚ and a plane-to-plane separation of 3.596 A˚ .
Experimental
The title compound was prepared according to the method described by Odabas¸og˘lu & Bu¨yu¨kgu¨ngo¨r (2006), using phthalaldehydic acid and 4-chloroaniline as starting materials (yield 90%; m.p. 454–455 K). Crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol (95%) solution at room temperature.
Crystal data
C14H10ClNO2
Mr= 259.68 Monoclinic,P21=c a= 12.9256 (14) A˚ b= 7.2383 (10) A˚ c= 15.6115 (16) A˚
= 122.196 (7) V= 1236.0 (3) A˚3
Z= 4
Dx= 1.395 Mg m3 MoKradiation
= 0.30 mm1 T= 296 K
Prismatic plate, pale yellow 0.600.420.16 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer
’scans
Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) Tmin= 0.848,Tmax= 0.955
16688 measured reflections 2422 independent reflections 1385 reflections withI> 2(I) Rint= 0.090
max= 26.0
Refinement
Refinement onF2 R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.055
wR(F2) = 0.139 S= 1.05 2422 reflections 167 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w= 1/[2
(Fo2) + (0.0645P)2 + 0.036P]
whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3 (/)max< 0.001
max= 0.15 e A˚
3
min=0.22 e A˚
3
Table 1
Selected geometric parameters (A˚ ,).
C1—O1 1.213 (3)
C1—O2 1.347 (3)
C2—C7 1.375 (4)
C7—C8 1.492 (4)
C8—N1 1.404 (4)
C8—O2 1.505 (3)
C9—N1 1.400 (4)
O1—C1—O2 121.5 (3)
O1—C1—C2 130.0 (3)
N1—C8—C7 114.2 (2)
N1—C8—O2 111.6 (2)
Table 2
Hydrogen-bond geometry (A˚ ,).
Cg1 is the centroid of ring C9–C14.
D—H A D—H H A D A D—H A
N1—H1 O1i
0.82 (2) 2.29 (3) 3.046 (4) 155 (2) C6—H6 Cg1ii
0.93 3.29 3.987 (4) 134
Symmetry codes: (i)x;yþ1 2;zþ
1
2; (ii)x;yþ 3 2;z
1 2.
All H atoms attached to C atoms were treated as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 A˚ for aromatic H and 0.98 A˚ for methine H, and withUiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The H atom of the amino group was located in a Fourier difference map and freely refined.
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2002); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction:X-RED32(Stoe & Cie, 2002); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97(Sheldrick, 1997); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997); molecular graphics:ORTEP-3 for Windows(Farrugia, 1997); software used to prepare material for publication:WinGX(Farrugia, 1999).
The authors wish to acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the Stoe IPDS-II diffractometer (purchased under grant F.279 of the University Research Fund).
References
Aoki, K., Furusho, T., Kimura, T., Satake, K. & Funayama, S. (1973). Jpn. Patent 7 324 724;Chem. Abstr.(1974),80, 129246.
Etter, M. C. (1990).Acc. Chem. Res.23, 120–126. Farrugia, L. J. (1997).J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565. Farrugia, L. J. (1999).J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
Kubota, Y. & Tatsuno, T. (1971).Chem. Pharm. Bull.19, 1226–1233. Odabas¸og˘lu, M. & Bu¨yu¨kgu¨ngo¨r, O. (2006).Acta Cryst.E62, o1879–o1881. Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of
Go¨ttingen, Germany.
Stoe & Cie (2002).X-AREA(Version 1.18) andX-RED32(Version 1.04). Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
[image:2.610.45.292.68.252.2]Tsi, D. & Tan, B. K. H. (1997).Phytother. Res.11, 576–582.
Figure 2
A packing diagram for (I), showing the N—H O, C—H and– interactions represented as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been omitted for clarity. [Symmetry codes: (i)x, y+1
2,z+ 1
2; (ii)x,y+ 3 2,z+
supporting information
sup-1 Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o2003–o2004
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o2003–o2004 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S160053680601436X]
3-(4-Chloroanilino)isobenzofuran-1(3
H
)-one
Orhan B
ü
y
ü
kg
ü
ng
ö
r and Mustafa Odaba
ş
o
ğ
lu
3-(4-chloroanilino)isobenzofuran-1(3H)-one
Crystal data
C14H10ClNO2
Mr = 259.68 Monoclinic, P21/c
Hall symbol: -P 2ybc a = 12.9256 (14) Å b = 7.2383 (10) Å c = 15.6115 (16) Å β = 122.196 (7)° V = 1236.0 (3) Å3
Z = 4
F(000) = 536 Dx = 1.395 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å Cell parameters from 16688 reflections θ = 1.9–27.9°
µ = 0.30 mm−1
T = 296 K
Prismatic plate, pale yellow 0.60 × 0.42 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer
Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus
Plane graphite monochromator Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1
φ–scan rotation method
Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002)
Tmin = 0.848, Tmax = 0.955
16688 measured reflections 2422 independent reflections 1385 reflections with I > 2σ(I) Rint = 0.090
θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 1.9°
h = −15→15 k = −8→8 l = −18→19
Refinement
Refinement on F2
Least-squares matrix: full R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055
wR(F2) = 0.139
S = 1.05 2422 reflections 167 parameters 0 restraints
Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods
Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map
Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w = 1/[σ2(F
o2) + (0.0645P)2 + 0.036P]
where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3
(Δ/σ)max < 0.001
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Special details
Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2,
conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used
only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2
are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq
C1 −0.0602 (3) 0.6539 (4) 0.1814 (2) 0.0696 (7) C2 −0.0331 (3) 0.6997 (3) 0.10313 (19) 0.0661 (7) C3 −0.1129 (3) 0.7428 (4) 0.0023 (2) 0.0800 (8)
H3 −0.1968 0.7490 −0.0256 0.096*
C4 −0.0624 (4) 0.7762 (4) −0.0555 (2) 0.0857 (9)
H4 −0.1133 0.8033 −0.1240 0.103*
C5 0.0629 (4) 0.7697 (4) −0.0123 (2) 0.0888 (9)
H5 0.0945 0.7941 −0.0525 0.107*
C6 0.1419 (3) 0.7282 (4) 0.0882 (2) 0.0802 (8)
H6 0.2260 0.7257 0.1167 0.096*
C7 0.0913 (3) 0.6900 (4) 0.1459 (2) 0.0685 (7) C8 0.1515 (3) 0.6305 (4) 0.2536 (2) 0.0708 (7)
H8 0.1902 0.5098 0.2621 0.085*
C9 0.3168 (2) 0.7160 (4) 0.4265 (2) 0.0678 (7) C10 0.3829 (3) 0.8603 (5) 0.4909 (2) 0.0831 (9)
H10 0.3694 0.9802 0.4657 0.100*
C11 0.4683 (3) 0.8290 (5) 0.5917 (2) 0.0880 (9)
H11 0.5129 0.9267 0.6342 0.106*
C12 0.4871 (3) 0.6528 (5) 0.6289 (2) 0.0832 (9) C13 0.4212 (3) 0.5084 (5) 0.5677 (2) 0.0874 (9)
H13 0.4341 0.3894 0.5940 0.105*
C14 0.3352 (3) 0.5395 (5) 0.4661 (2) 0.0805 (8)
H14 0.2897 0.4415 0.4245 0.097*
N1 0.2387 (2) 0.7557 (4) 0.32346 (18) 0.0752 (7) O1 −0.15716 (19) 0.6504 (3) 0.17627 (15) 0.0834 (6) O2 0.04538 (17) 0.6100 (3) 0.26746 (13) 0.0756 (5) Cl1 0.59850 (9) 0.61279 (18) 0.75589 (6) 0.1182 (4) H1 0.220 (2) 0.864 (4) 0.3083 (19) 0.059 (8)*
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
supporting information
sup-3 Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o2003–o2004
C9 0.0631 (16) 0.0783 (19) 0.0626 (16) −0.0025 (14) 0.0339 (13) 0.0000 (14) C10 0.082 (2) 0.082 (2) 0.0757 (19) −0.0026 (16) 0.0354 (16) 0.0016 (16) C11 0.082 (2) 0.099 (2) 0.074 (2) −0.0102 (17) 0.0359 (17) −0.0114 (18) C12 0.0688 (18) 0.111 (3) 0.0668 (17) 0.0052 (18) 0.0342 (15) 0.0053 (17) C13 0.080 (2) 0.096 (2) 0.084 (2) 0.0082 (18) 0.0421 (17) 0.0204 (18) C14 0.0782 (19) 0.082 (2) 0.0729 (18) −0.0036 (16) 0.0344 (15) 0.0064 (15) N1 0.0787 (16) 0.0680 (17) 0.0694 (15) 0.0004 (14) 0.0331 (13) 0.0035 (13) O1 0.0792 (14) 0.0857 (14) 0.0887 (14) −0.0069 (11) 0.0471 (11) 0.0005 (10) O2 0.0781 (12) 0.0872 (13) 0.0618 (11) 0.0012 (10) 0.0376 (10) 0.0073 (9) Cl1 0.0970 (7) 0.1644 (10) 0.0694 (5) 0.0160 (6) 0.0284 (4) 0.0124 (5)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
C1—O1 1.213 (3) C8—O2 1.505 (3)
C1—O2 1.347 (3) C8—H8 0.9800
C1—C2 1.477 (4) C9—C14 1.384 (4)
C2—C7 1.375 (4) C9—C10 1.384 (4)
C2—C3 1.382 (4) C9—N1 1.400 (4)
C3—C4 1.388 (4) C10—C11 1.377 (4)
C3—H3 0.9300 C10—H10 0.9300
C4—C5 1.384 (4) C11—C12 1.368 (4)
C4—H4 0.9300 C11—H11 0.9300
C5—C6 1.374 (4) C12—C13 1.366 (5)
C5—H5 0.9300 C12—Cl1 1.745 (3)
C6—C7 1.393 (4) C13—C14 1.386 (4)
C6—H6 0.9300 C13—H13 0.9300
C7—C8 1.492 (4) C14—H14 0.9300
C8—N1 1.404 (4) N1—H1 0.82 (2)
O1—C1—O2 121.5 (3) C7—C8—H8 109.3
O1—C1—C2 130.0 (3) O2—C8—H8 109.3
O2—C1—C2 108.5 (3) C14—C9—C10 118.6 (3)
C7—C2—C3 122.3 (3) C14—C9—N1 123.4 (3)
C7—C2—C1 108.6 (2) C10—C9—N1 117.9 (3)
C3—C2—C1 129.1 (3) C11—C10—C9 121.0 (3)
C2—C3—C4 117.1 (3) C11—C10—H10 119.5
C2—C3—H3 121.5 C9—C10—H10 119.5
C4—C3—H3 121.5 C12—C11—C10 119.5 (3)
C5—C4—C3 120.7 (3) C12—C11—H11 120.3
C5—C4—H4 119.7 C10—C11—H11 120.3
C3—C4—H4 119.7 C13—C12—C11 120.9 (3)
C6—C5—C4 121.9 (3) C13—C12—Cl1 119.8 (3)
C6—C5—H5 119.0 C11—C12—Cl1 119.3 (3)
C4—C5—H5 119.0 C12—C13—C14 119.8 (3)
C5—C6—C7 117.5 (3) C12—C13—H13 120.1
C5—C6—H6 121.3 C14—C13—H13 120.1
C7—C6—H6 121.3 C9—C14—C13 120.2 (3)
C2—C7—C8 109.5 (2) C13—C14—H14 119.9
C6—C7—C8 130.0 (3) C9—N1—C8 123.3 (3)
N1—C8—C7 114.2 (2) C9—N1—H1 116.8 (18)
N1—C8—O2 111.6 (2) C8—N1—H1 113.9 (18)
C7—C8—O2 102.8 (2) C1—O2—C8 110.5 (2)
N1—C8—H8 109.3
O1—C1—C2—C7 178.1 (3) C14—C9—C10—C11 2.2 (4) O2—C1—C2—C7 −2.6 (3) N1—C9—C10—C11 −175.0 (3) O1—C1—C2—C3 −3.2 (5) C9—C10—C11—C12 −0.8 (5) O2—C1—C2—C3 176.1 (3) C10—C11—C12—C13 −0.8 (5) C7—C2—C3—C4 0.1 (4) C10—C11—C12—Cl1 178.1 (2) C1—C2—C3—C4 −178.5 (3) C11—C12—C13—C14 0.8 (5) C2—C3—C4—C5 −1.2 (4) Cl1—C12—C13—C14 −178.1 (2) C3—C4—C5—C6 0.8 (5) C10—C9—C14—C13 −2.1 (4) C4—C5—C6—C7 0.8 (5) N1—C9—C14—C13 174.9 (3) C3—C2—C7—C6 1.5 (4) C12—C13—C14—C9 0.7 (5) C1—C2—C7—C6 −179.7 (2) C14—C9—N1—C8 14.5 (4) C3—C2—C7—C8 −176.8 (2) C10—C9—N1—C8 −168.4 (3)
C1—C2—C7—C8 2.0 (3) C7—C8—N1—C9 −171.3 (3)
C5—C6—C7—C2 −1.9 (4) O2—C8—N1—C9 72.6 (3) C5—C6—C7—C8 176.0 (3) O1—C1—O2—C8 −178.5 (2) C2—C7—C8—N1 −121.8 (3) C2—C1—O2—C8 2.1 (3) C6—C7—C8—N1 60.0 (4) N1—C8—O2—C1 121.9 (2) C2—C7—C8—O2 −0.8 (3) C7—C8—O2—C1 −0.9 (3) C6—C7—C8—O2 −178.9 (3)
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
D—H···A D—H H···A D···A D—H···A
N1—H1···O1i 0.82 (2) 2.29 (3) 3.046 (4) 155 (2)
C6—H6···Cg1ii 0.93 3.29 3.987 (4) 134