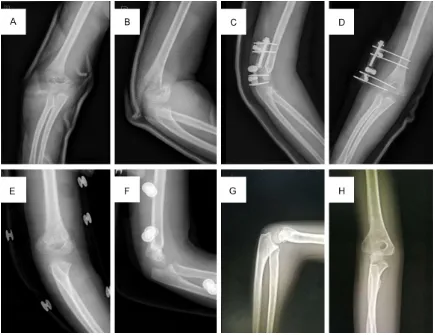
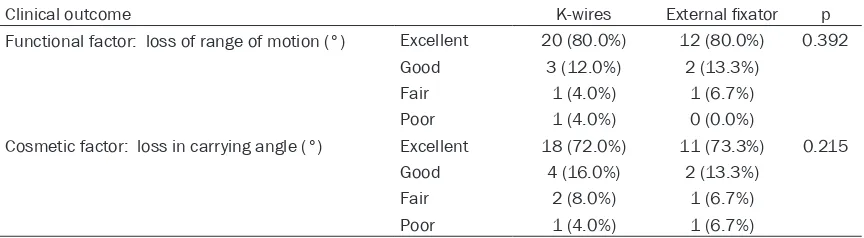
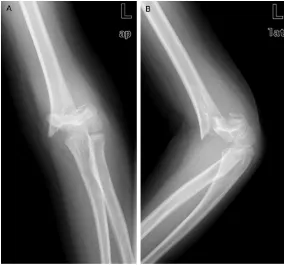
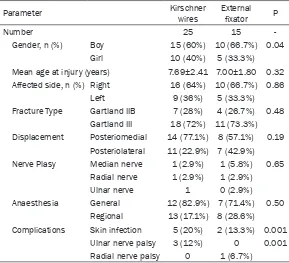
Original Article Comparison of Kirschner wires and Orthofix external fixator for displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Full text
Figure
Related documents
a) 58% of respondents rated Frooti as having Good Packaging. c) 17% of respondents rated Frooti as having Average Packaging. d) 3% of respondents rated Frooti as having Very
In cases where ulnar nerve injury occurs when the medial K-wire is fixated by decreasing the elbow flexion after placing two lateral K-wires, removal of the medial
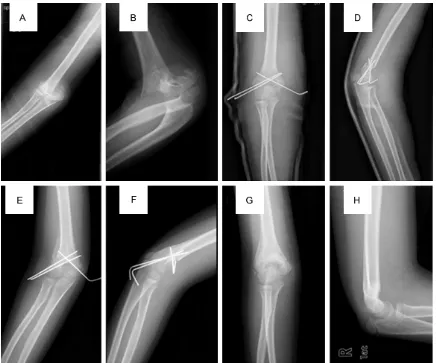
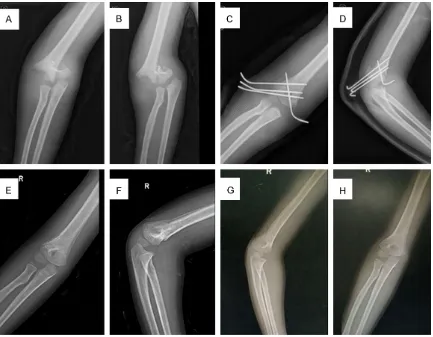
In our present study we evaluated the effectiveness of closed reduction and lateral percutaneous K wire fixation in the management of displaced supracondylar fractures
The purpose of this study is to determine the efficacy of management of displaced supracondylar fractures using closed reduction with percutaneous K-wire pinning and
Our series consists of 20 cases of displaced (Gartland’s Type III) supracondylar fractures of humerus in children treated by either closed reduction and percutaneous K
In this prospective study thirty cases of displaced extension type of supracondylar fractures (Gartland’s type III) of the humerus in children were treated by closed
After closed reduction and percutaneous pinning of a displaced, uncomplicated, supracondylar humerus fracture, 94% of the child’s normal elbow ROM should be expected by 6 months
Supracondylar humeral fractures in children aged seven years or older are more likely to be comminuted and associated with neurological injury.. Changes in