The influence of conservation tillage methods on soil water regimes in semi-arid southern Zimbabwe
Full text
Figure
Related documents
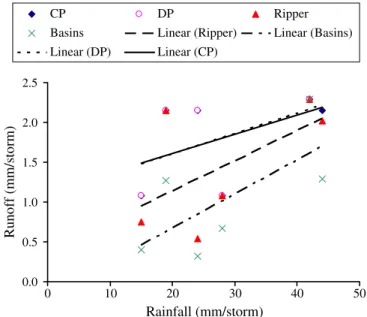
The significantly lower runoff volume in the grass planting treatments during the raining season indi- cated that adopting the best management practices such as grass planting
The yield of sweet corn and total weight of dry matter (TWDM) were increased at any given planting densities and tillage treatments. When plant population was lower or there was the
The effect of conventional tillage appears to correlate with the changes in soil structure that can disturb microbial diversity including impact on the community dynamics,
It shows the effects of cover cropping and reduced tillage on chemical characteristics of soil including soil mineral nitrogen, organic matter, phosphorus, calcium and magnesium.. In
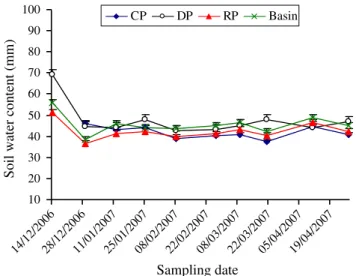
This study demonstrated that under semi-arid conditions of southern Zimbabwe the effect of CP, DP, ripper and basin tillage methods on soil water distribution in the profile depended
The soil surface roughness data from the different tillage treat- ments show that during the early part of rainy season the soil surface depression storage values are significantly
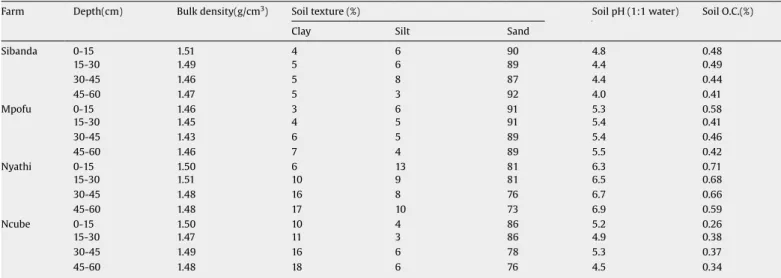
The presence of tree leaf biomass and crop residue in plots maintained under minimum tillage, zero tillage and ridges led to improved soil texture, low bulky density, a
With the aim of evaluating the effects of agroforestry based conservation tillage (AFCT) on water infiltration and selected soil properties, two tillage types: