The timescale and extent of thermal expansion of the global ocean due to climate change
Full text
Figure
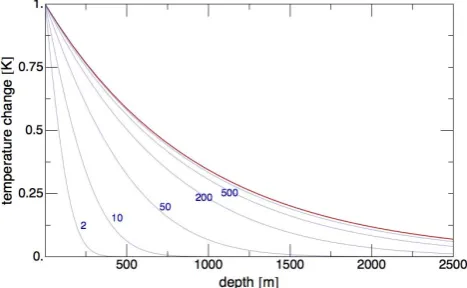
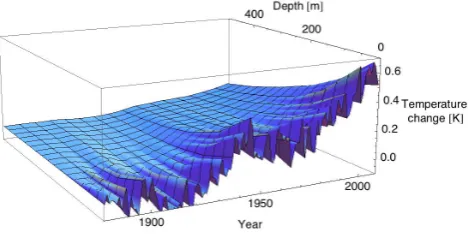
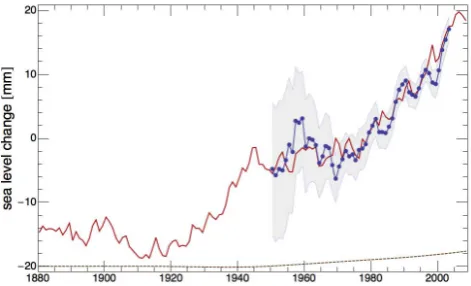
Related documents
It would therefore appear that in their concept of industrial policy formulated in the late 1950s Lemass and Whitaker not only anticipated the shakeout of traditional import
Effective demand building requires effort throughout the supply chain – from the farm, mill, brand, retailer to consumer. PRESENTATION TITLE | PAGE PRESENTATION TITLE |
She is currently Instructor of structural geology and tectonics at the earth sciences department of the Islamic Azad University, Fars science and research
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
Because of the importance and sensitivity of CA1 area of hippocampus and the pathophysiological mechanisms of cerebral ischemia, this study provided the novel thera- peutic window
Rather than focusing exclusively on incentives and expectations about the base rate of errors, the field interview study examines payoffs of error detection more broadly by
In theory, FRET is a radiationless energy transfer process, so ideally, a single emission spectrum of the output fluorophore should be observed, as illustrated in Fig.2.7
19% serve a county. Fourteen per cent of the centers provide service for adjoining states in addition to the states in which they are located; usually these adjoining states have