The role of folic acid in carcinogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer
Full text
Figure

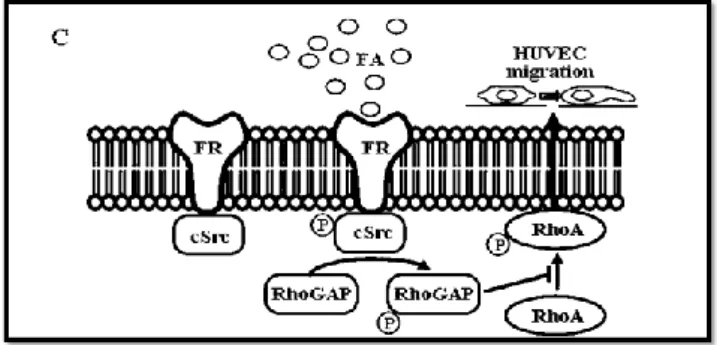
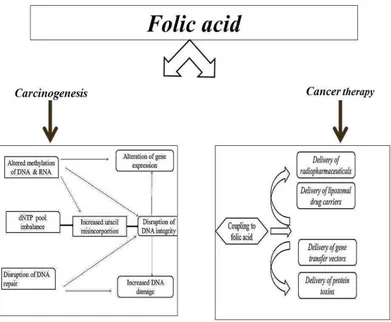
Related documents
Koluama and Nembe samples are having same calcium content after distillation process and do not exceed the WHO limits of calcium content required in water sample as
The objective of this study was to investigate the adsorption of electrocoagulated laundry waste- water via PAn/HS and PPy/HS composites in terms of the COD removal efficiencies
This accounting will also provide information for the comparison of book inventory to the actual physical count of inventory stocked.Inventory control may be defined as "a
In a representative sample of US adults, we found that serum perfluoroalkyl chemical levels were positively asso- ciated with elevated uric acid. The association was found
The theoretical literature we have reviewed support a major proposition that paintings are stimuli to the human brain, and can indeed immerse the viewers in moments of pleasure when
Methods: In a cross-sectional study, 112 women with the history of Pomeroy type of tubal ligation achieved by minilaparatomy as the case group and 288 women with no previous
The angle of internal friction (shearing resistance) ɸ increases with increase in dry density of fine sand and quantity of the sanitary ware waste. As the angle of
Similar results are observed with public sector claims which significantly increase banks’ exposure to cross border risk by 0.21%, while reducing derivative risk exposure by