Assessment of cloud supersaturation by size-resolved aerosol particle and cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) measurements
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Estimating cloud condensation nuclei number concentrations using aerosol optical properties: role of particle number size.. distribution
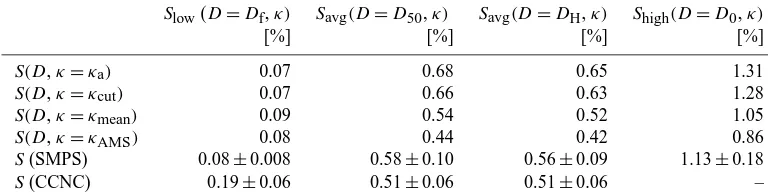
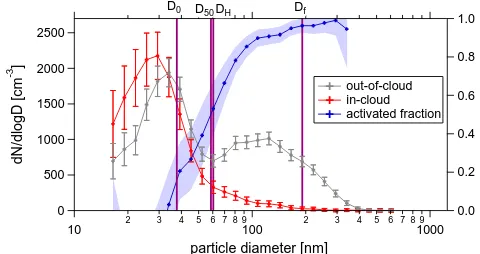
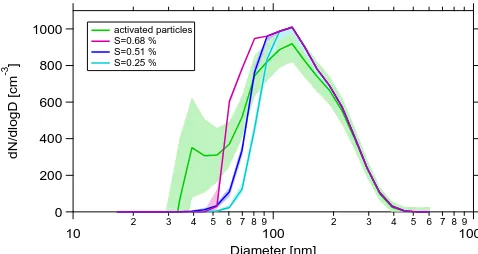
The observed values are significantly lower than those observed in the megacity region of Beijing (Gunthe et al., 2011). Figure 2b shows the activated fraction, i.e. the ratio of
We measured the mobility equivalent critical dry diameter for cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) activation ( d c me ) and the particle mass of size-selected (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 and
It has been widely accepted that the key criterion for discern- ing an NPF event is to identify an acute burst of nucleation- mode particles, known as newly formed particles up to a
The aims of this work are to (i) assess the accuracy of state-of-the-art global aerosol models in simulating the chemical composition and number concentration of aerosol particles,
The observed positive cor- relation between CCN concentration and temperature is con- trary to the global net effect of aerosol particles, which is to cool the surface (Solomon et
C., Riemer, N., and West, M.: Particle-resolved simulation of aerosol size, composition, mixing state, and the associated optical and cloud condensation nuclei activation properties
3.1 Analysis of the diameter growth rates (GR) and the condensational mass fluxes to nucleation mode particles from particle size distribution data For the EUCAARI campaign