EMT and tumor metastasis
Full text
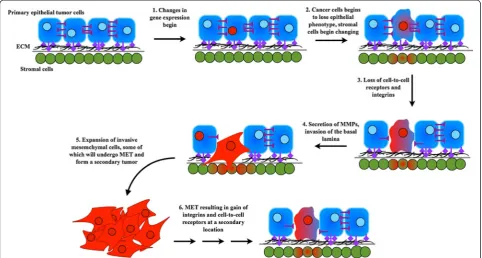
Figure

Related documents
BC: Breast cancer; BM-DTC: bone marrow disseminated tumor cells; CTC: circulating tumor cells; Cx43: Connexin 43; EDTA: ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; EMT:
ACTA2 = alpha-smooth muscle actin; BCSC = breast cancer stem cell; CTC = circulating tumor cell; EMT = epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ERBB2 = human epidermal growth
We investigated CTCs, including epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) status, from metastatic breast cancer patients who had received eribulin-based treatment, which reportedly
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are frequently associated with epithelial- mesenchymal transition (EMT).The objective of this study was to detect EMT phenotype through Vimentin
BC: breast cancer; BCSCs: breast cancer stem cells; CAFs: cancer-associated fibroblasts; CSCs: cancer stem cells; DFS: disease-free survival; EMT: epithelial- to-mesenchymal
Chen et al., “Molecular de- tection of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in circulating tumor cells from pancreatic cancer patients: potential role in clinical practice,”
CTC, Circulating Tumor Cells; GC, Gastric Cancer; AGC, Advanced Gastric Cancer; EMT, Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transition; CTM, Circulating Tumour Microemboli; OS, Overall
Background: Assuming that tumor cell dissemination requires a shift to a mesenchymal phenotype, we analyzed the incidence of epithelial-to-mesenchymal- transition