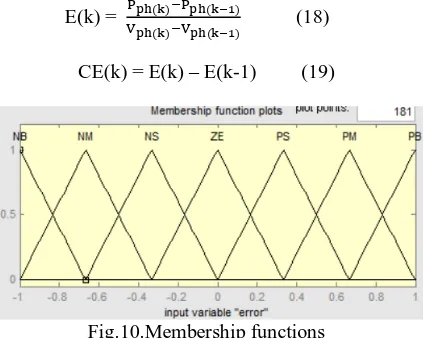
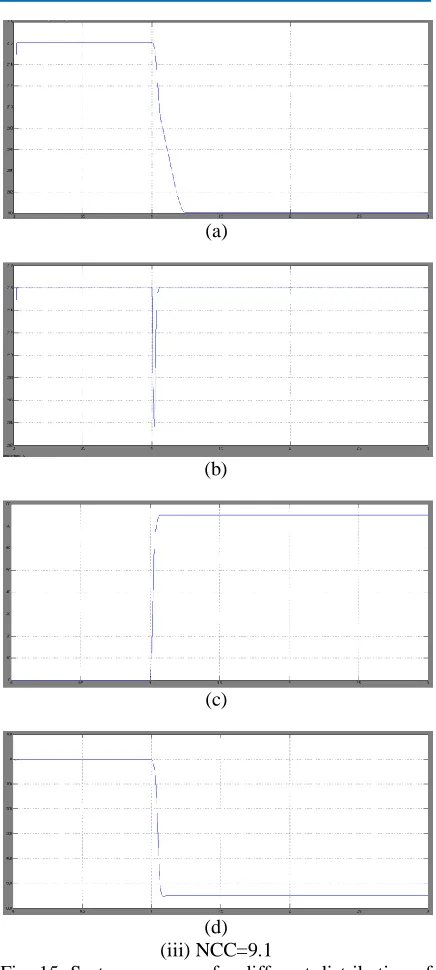
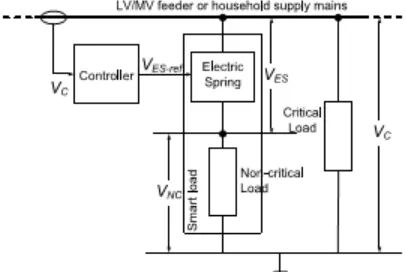
Distributed Voltage Using Fuzzy Logic Control Comparison Of Electric Springs With Statcom
Full text
Figure



Related documents
Throughout this text there are chapter titles including “Western Origins of Art Education” (p. v) and headings including “European Origins of Common School Pedagogy” (p. Though
Problematic Internet use, health anxiety aroused by online searches for health information and escalation of health concerns as an indicator of cyberchondria, are all associated
resting with active muscle is by using the Central Activation Ratio (CAR) which only 89.. depends on the superimposed force or joint moment during MVC and not the stimulation at
Figure 2 The four dimensions of embeddedness... building blocks [64] also warrant further investigation. For an organization to be embedded into the flow of informa- tion in
aureus in 30 μ l DEB was inoculated onto outer shell swatches, dried for 30 min at 37 °C, and washed by high-speed vortexing (10 s or 10 min) in 50 ml test tubes containing 10 ml
In addition, the molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) graph clears that the nitrogen atoms of the said compound have more electron density. So, these atoms probably participate
Perforated duodenal ulcer due to acid peptic disease was the most common cause of perforation peritonitis noticed in 43.6%, followed by small bowel perforation due to tuberculosis
We compute three measures of intergenerational educational mobility: the beta-coefficient, which quantifies the rate of transmission of educational achieve- ments between one