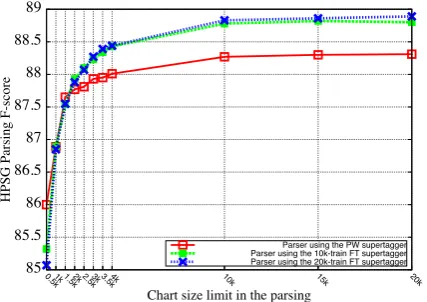
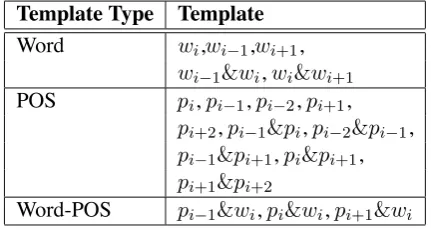
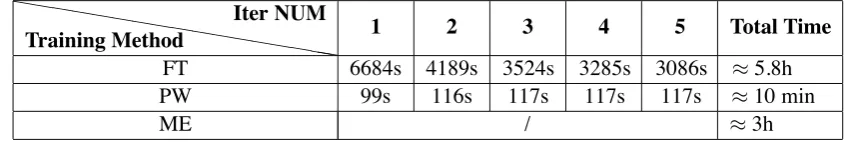
Forest guided Supertagger Training
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Effect of an education and activation programme on functional limitations and patient-perceived recovery in acute and sub-acute shoulder complaints – a randomised clinical
The frequency of self-reported knee complaints was lower among floor layers presently at work in the trade in year 2005 (26.3%) compared with baseline in 1995 (41.1%), while
Major findings in the present study on stress responses in healthy subjects can be summarized as: 1) A significant proportion of healthy subjects (64%) respond with a pain increase
Methods: We used a dynamic model to determine the changes in intraarticular forces and peak- pressure in the talonavicular joint and in the calcaneocuboid joint on 8 cadaver feet
It would appear that an essential aspect to effective man- agement of patients with spinal pain would include the identification and management of those factors that place the acute
For complicated gastrointestinal events we chose to use data only from meta-analyses of randomised trials for celecoxib [28], etoricoxib [29], and valdecoxib [30], for rofecoxib
Although pectoralis minor shortening is central to the the- ory that is used to underpin the muscle imbalance approach in relation to shoulder and upper quadrant pathology the
Methods/Design: This study was designed to test the feasibility of an assessor-blind randomised controlled trial which assess the effects on clinical outcomes and exercise adherence