Cell-autonomous heparanase modulates self-renewal and migration in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Full text
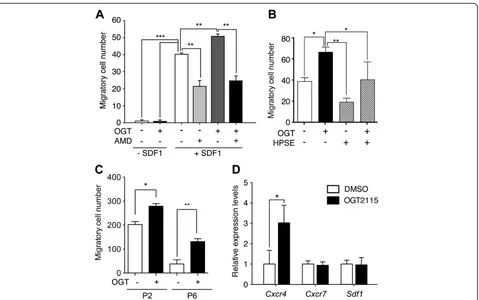
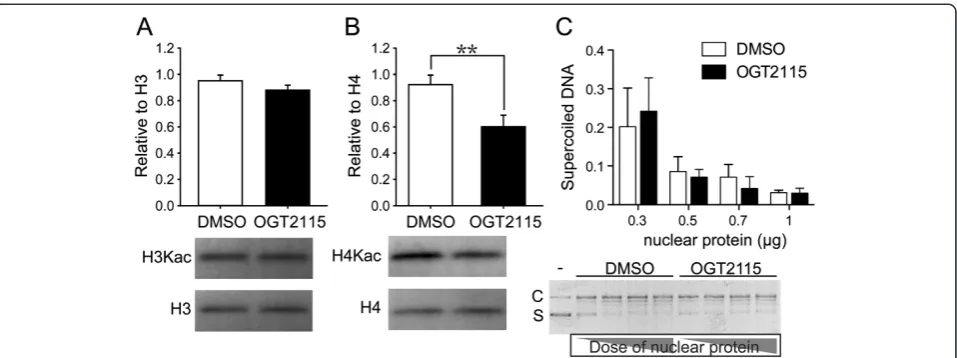
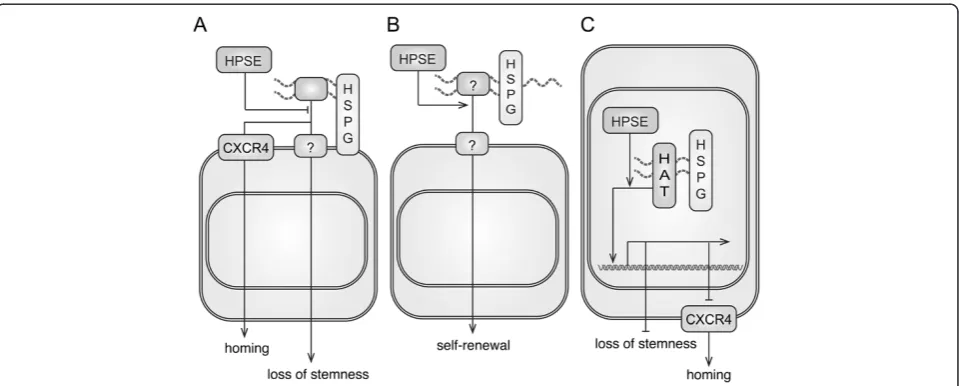
Figure
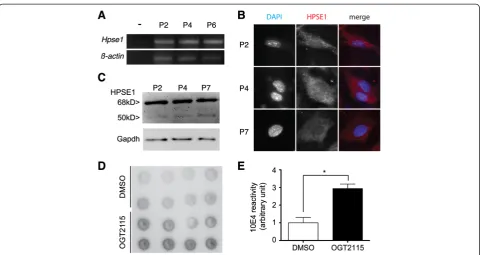
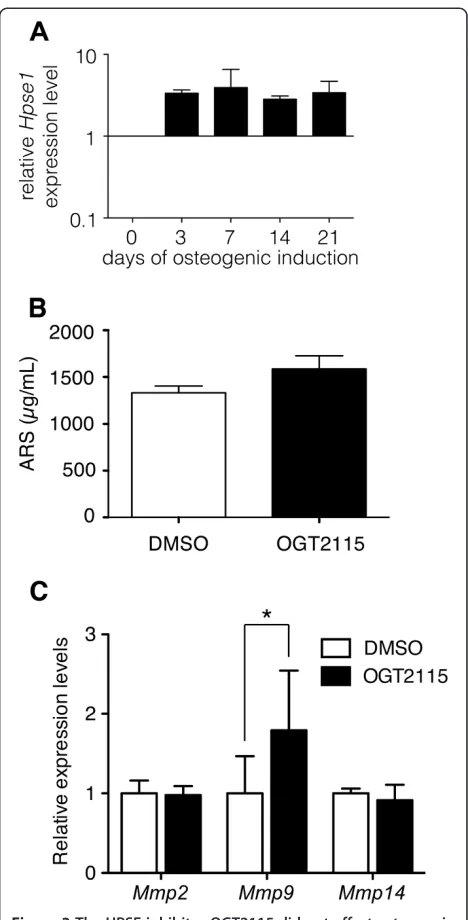
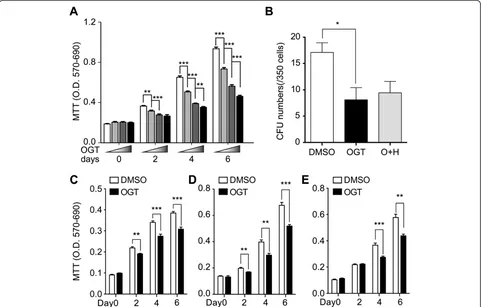
Related documents
Within the limitations of this study, panoramic radiographs were used to assess the asymmetry ratio between the two rami based on the fact that the percentages of right and
Taking the knowledge-intensive service enterprises as the example, we have made empirical study on how the different dimensions of dynamic capabilities, namely, sensing
Ideally, as a partnership progresses different practices and attitudes are required at both partnership and organizational level if the partnership is to continue to sustain
Protective effect of single or combined treatment of Moringa oleifera and Citrullus colocynthis on carbon tetrachloride induced hematological and cardiac toxicity
To evaluate whether ultrastructural safeguard- ing of thymocytes by 4-OH-TEMPO protection against ButOOH induced apoptosis, we checked the effect of this antioxidant on
This significant influx of terrestrial debris together with the associated palynomorph assemblages indicate deposition in a shallow marine environment in close proximity to
The JASAL (Japanese Association of Self-Access Learning) 10 th Anniversary Conference was held on December 12 th , 2015 at Kanda Institute of Foreign Languages (KIFL) in Tokyo..
Hence the aim of our study was to investigate the expression of both immunogenic potential- representing markers (CD80, CD86, HLA-DR) and tolerogenic properties-representing markers