Heart rate regulation in diving sea lions: the vagus nerve rules
Full text
Figure
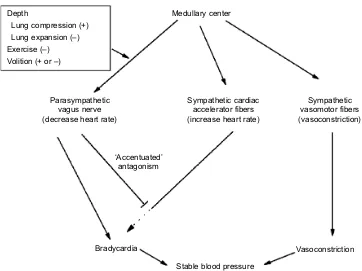
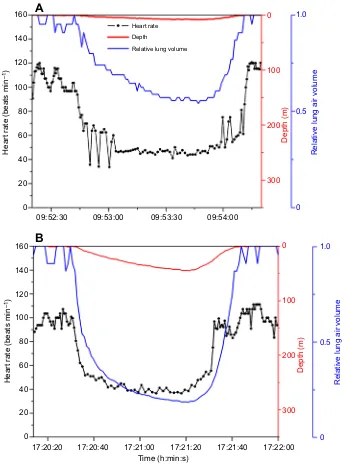
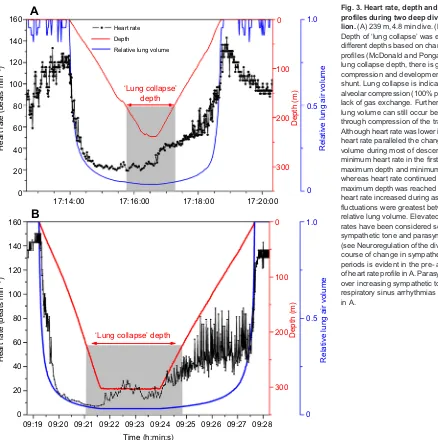
Related documents
The purpose of this quasi-experimental project was the modification of an existing HF education book, which aimed to improve the quality of HF patient education and increase
Client-lender relationships are established through several practices and mechanisms, which include but are not limited to: The location of branch offices near the target group to
OData can only be used to interact with Advantage data dictionaries that have been configured for access through the Advantage Web Platform, and only through the Advantage
Banks handle between twenty- five and fifty million items each day.' A comment to the Code states: "There is needed a uniform statement of the principal
The Chief Justice, Justice White, and now Justices Scalia and Kennedy (in this respect different from Justice Powell, who overall came closer to his Virginia
7 Rule 23(b)(3) requires the party seeking certification to prove that “questions of law or fact common to class members predominate over any questions affecting only individual
Cloud computing is a computing model for enabling convenient and on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable and often virtualised computing resources (e.g.,
The effect of transmission range on throughput of random waypoint model across different mobility models and concluded that as the transmission range is increased, the