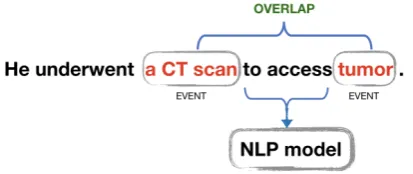
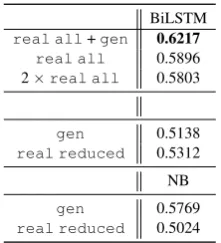
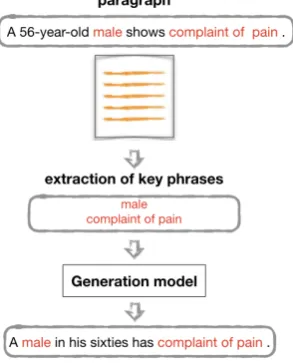
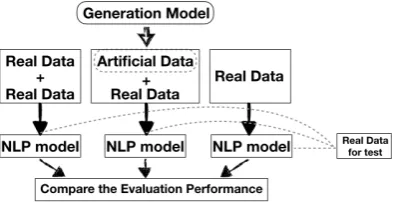
Is artificial data useful for biomedical Natural Language Processing algorithms?
Full text
Figure

Related documents
Figure 5 shows the cavitation generated cloud consisting of millions of bubbles, notice the phenomenon is taking place in the expansion side of the venturie tube; as the
138 del 2011, che stabiliscono le incompatibilità per i gestori: gli amministratori, i dirigenti e i responsabili degli uffici o dei servizi dell’ente locale, nonché degli
The statistical accident data was collected from Balai Polis Trafik Batu Pahat, JKR Daerah Batu Pahat, Road Safety Research Center (UPM), Road Transport Department of Malaysia,
In the first model, which is named the MLCV model, local constant estimators were used to carry out the localised estimation step using a pair of bandwidths: both horizontal
Lung cancer susceptibility genetic variants modulate HOXB2 expression in the lung ALISSON CLEMENCEAU#,1, OLIVIER BOUCHERAT#,2, KIM LANDRY TRUCHON#,2, MAXIME LAMONTAGNE1, SABRINA
We have outlined our work in applying dialectical theories developed within the field of informal logic to dialogue involving people and computers, Le. the development
following the G20 mandate, there has been a move from incurred loss approaches for the recognition of credit losses to expected credit loss approaches. since 1 January 2018,
Intensified PA counseling supported with an option for monthly thematic meetings with group exercise proved feasible among pregnant women at risk for gestational diabetes and was