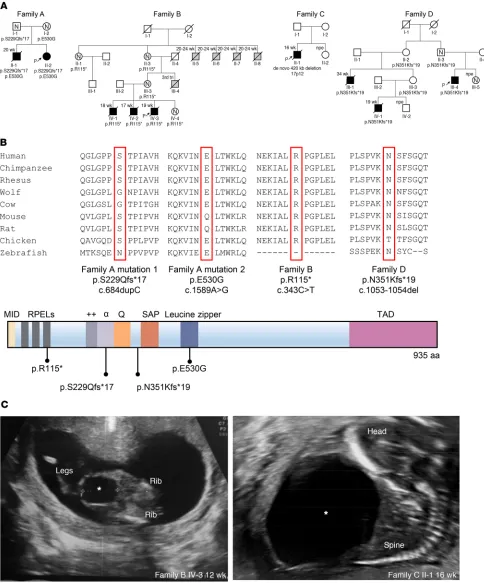
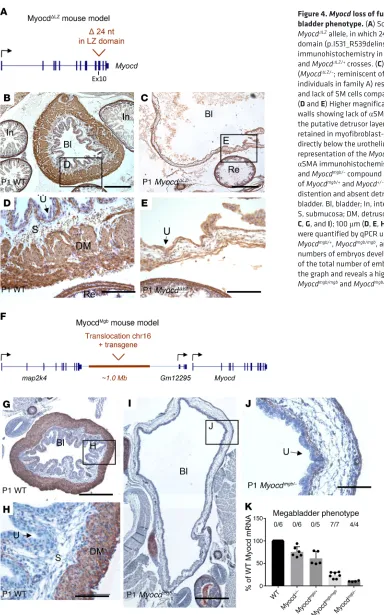
Loss of function variants in myocardin cause congenital megabladder in humans and mice
Full text
Figure

Related documents
This study develops an inventory model to find the minimum relevant inventory cost per unit time for non-instantaneous deteriorating goods over a finite time horizon
Terdapat empat objektif yang perlu dicapai dalam kajian ini iaitu: (i) mengenalpasti tahap keupayaan jurulatih dalam menyampaikan program latihan daripada perspektif pelatih,
Using an prospectively collected internal database, a retrospective review on all patients with a diagnosis of IPN between Jan, 2012 and Dec, 2012 at the Jinling Hospital,
Ultrasound imaging of hyperplastic mouse prostate The volume of the ventral prostate was monitored during development in a mouse model of benign pros- tatic hyperplasia using
Sexual compulsivity is an intriguing, though unpopular, topic in China as it is seldom discussed among the general public, in what is characteristically a sexually conservative
These included intended purposes of the mission statement, standards for faculty staff, requirements for clinical training by students, program budgetary autonomy and transparency,
Conclusion: This study shows a persistent number of patients requiring emergency laparotomy after (blunt) abdominal trauma over 10 years in a European trauma center.. When performed
The novelty of our work is the detection of dynamic communities in temporal software dependency networks, the use of tensor decompositions on software ecosystems, and the use