Understanding the Effect of Textual Adversaries in Multimodal Machine Translation
Full text
Figure
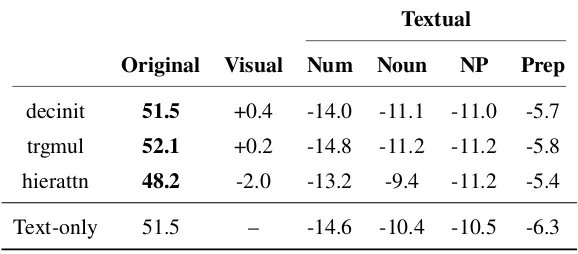
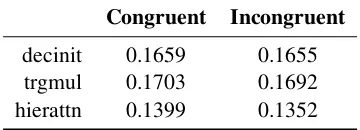

Related documents
Furthermore, while symbolic execution systems often avoid reasoning precisely about symbolic memory accesses (e.g., access- ing a symbolic offset in an array), C OMMUTER ’s test
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
Antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive patients imme- diately post stroke may be effective and cost-effective compared with placebo from the acute hospital perspec- tive at
This study aimed to assess the prevalence of anxiety and depression and to identify their associated factors including metabolic components among people with type 2 diabetes..
Using a stepped- wedge trial design to randomly assign HIV care clinics to scaled initiation of PrEP integrated into HIV care for cou- ples, the RE-AIM (Reach, Effectiveness,
In summary, we have presented an infant with jaundice complicating plorie stenosis. The jaundice reflected a marked increase in indirect- reacting bilirubin in the serum. However,
diallylacetic acid rather than bismuth since in one case in which analysis was performed only minute amounts of bismuth were recovered, and there was, in his opinion, ‘ ‘no
How Many Breeding Females are Needed to Produce 40 Male Homozygotes per Week Using a Heterozygous Female x Heterozygous Male Breeding Scheme With 15% Non-Productive Breeders.