Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Subcortical Auditory Tract in Subjects with Congenital Cochlear Nerve Deficiency
Full text
Figure
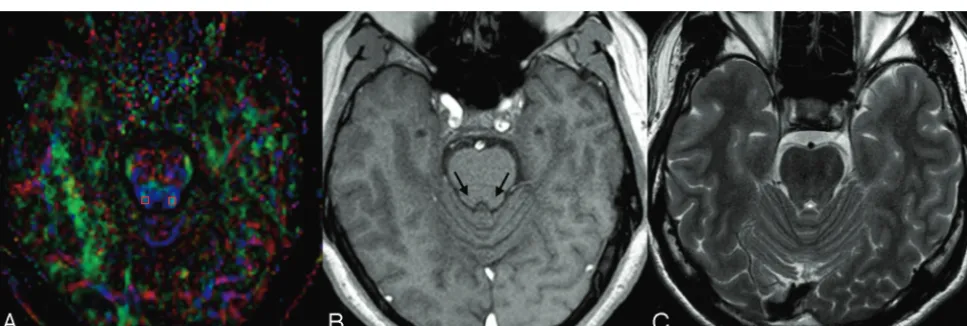
Related documents
ABBREVIATIONS: CI ⫽ confidence interval; DTI ⫽ diffusion tensor imaging; EDSS ⫽ Expanded Disability Status Scale; EPI ⫽ echo-planar imaging; FA ⫽ fractional anisotropy; HV
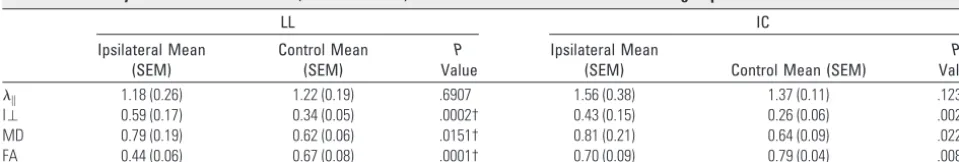
RESULTS: The mean ADC and orthogonal eigenvalue ⬜ in affected nerves increased, and the mean FA was reduced compared with clinically unaffected contralateral nerves ( P ⬍ .001)
Fibers of this type typically identified on DTI color maps include cingulum, su- perior and inferior occipitofrontal fasciculi, uncinate fasciculus, superior longitudinal
Resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) acquisitions quantify global network organization and neural integrity, respectively,
DTI metrics ( p : q tensor decomposition) and DSC perfusion demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the mean values of ADC, the isotropic component of the
Methodology/Principal Findings: Using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to measure the differences of whole-brain white matter integrity between 44 chronic smoking subjects