Mobile Enterprise
Vendor Benchmark 2014
A Comparison of Software Vendors and Service Providers
Germany
An Analysis by Experton Group AG
Munich, Germany
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Copyright
This analysis has been prepared by Experton Group AG. The information and data contained herein were gathered conscientiously and with the utmost care. Nevertheless, we cannot guarantee their exhaustiveness and accuracy. Nobody should take action, based on this information, without expert advice and an in-depth analysis of the individual situation.
All rights to the content of this analysis are reserved by Experton Group. The data and information remain the property of Experton Group. Reproduction – even of parts thereof – may only be made with the written permission of Experton Group AG.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Table of Content
1.
Management Summary
9
1.1. Mobile Enterprise Consulting ... 9
1.2. Mobile Device Management Software ... 9
1.3. Mobile Application Management Software ... 9
1.4. Mobile Information Management Software ... 10
1.5. Mobile Security Suites (Software) ... 10
1.6. Mobile Device Management Services ... 10
1.7. Workplace Management Managed Services ... 11
1.8. Client Virtualization Software ... 11
1.9. Mobile Application Development Platform Vendors ... 11
2.
Mobile Enterprise – An IT Hype Is Evolving Into a Business Topic
12
2.1. Demand Development ... 122.2. Mobile Device Management Software – Consolidation Is On Its Way ... 13
2.3. The Desktop in the Post-PC Era ... 14
2.4. ByoD Is Dead, Long Live CyoD ... 15
2.5. Do You Need Mobile Middleware for Mobile Apps? ... 16
2.6. Mobile Enterprise and Industrie 4.0 ... 16
2.7. Mobile Security: Mobile Risks and Security Functionality ... 18
2.7.1. Mobile Risks ... 18
2.7.2. Mobile Security Functionality ... 19
2.7.3. Mobile Security Suites as a Response to Mobile Risks... 20
2.8. Vendor selection was, is, and remains a challenge ... 22
3.
Methodology
23
3.1. Definitions ... 233.2. Methodology and Analysis Design ... 24
3.3. Selection of Analyzed Vendors ... 25
3.4. Analysis Design ... 26
3.5. Project Schedule: ... 27
4.
Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers
29
4.1. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Evaluation Criteria ... 294.2. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers for the Midmarket ... 29
4.2.1. Evaluated service providers for mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket ... 29
4.2.2. Benchmark of mobile enterprise consulting providers for the midmarket ... 30
4.2.3. Selected individual criteria – mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket segment ... 31
4.3. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers for the Upper Midmarket ... 33
4.3.1. Evaluated service providers for mobile enterprise consulting for the upper midmarket ... 33
4.3.2. Benchmarked mobile enterprise consulting providers for the upper midmarket ... 33
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
4.3.3. Selected individual criteria – mobile enterprise consulting for the upper
midmarket segment ... 35 4.4. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers for Large Accounts ... 37
4.4.1. Evaluated service providers for mobile enterprise consulting for large
accounts ... 37 4.4.2. Benchmark of mobile enterprise consulting services providers for large
accounts ... 37 4.4.3. Selected individual criteria for mobile enterprise consulting providers for
large accounts ... 39
5.
Mobile Device Management Software Vendors
42
5.1. Mobile Device Management Evaluation Criteria ... 42 5.2. Mobile Device Management Software for Smartphones and Tablets ... 42
5.2.1. Benchmarked vendors of mobile device management software for
smartphones and tablets ... 42 5.2.2. Benchmark of vendors with an offering of mobile device management
software for smartphones and tablets ... 43 5.2.3. Selected individual criteria for vendors of mobile device management
software for smartphones and tablets ... 45 5.3. Device Management Software for All Devices ... 48
5.3.1. Benchmarked vendors of mobile device management software for all
devices ... 48 5.3.2. Benchmark of vendors of mobile device management software for all
devices ... 48 5.3.3. Selected individual criteria for vendors of mobile device management
software for all devices ... 50
6.
Mobile Application Management Software Vendors
52
6.1. Mobile Application Management Evaluation Criteria ... 52 6.2. Benchmarked Mobile Application Management Software Vendors ... 52 6.3. Benchmark of Mobile Application Management Software Vendors ... 53 6.4. Selected Individual Criteria for Mobile Application Management Software
Vendors ... 54
7.
Mobile Information Management Software Vendors
58
7.1. Mobile Information Management Software Based on File Sharing ... 58 7.1.1. Evaluation criteria for mobile information management software based on
the file sharing approach ... 58 7.1.2. Benchmarked vendors of mobile information management software based
on the file sharing approach ... 58 7.1.3. Benchmark of vendors of mobile information management software based
on the file sharing approach ... 59 7.1.4. Selected individual criteria for vendors of mobile information management
software based on the file sharing approach ... 61 7.2. Mobile Information Management Software Based on Enterprise Content
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
7.2.2. Benchmarked vendors of ECM-based mobile information management
software ... 63
7.2.3. Benchmark of vendors of ECM-based mobile information management software ... 63
7.2.4. Selected individual evaluation criteria for ECM-based mobile information management software ... 64
8.
Mobile Security Suites Vendors
67
8.1. Mobile Security Suites Evaluation Criteria ... 678.2. Benchmarked Mobile Security Suites Vendors ... 68
8.3. Benchmark of Mobile Security Suites Vendors ... 69
8.4. Selected Individual Criteria for Mobile Security Suites ... 70
9.
Client Virtualization Software Vendors
73
9.1. Benchmarked Client Virtualization Software Vendors ... 739.2. Evaluation Criteria for Client Virtualization Software ... 73
9.3. Benchmark of Vendors of Client Virtualization Software ... 73
9.4. Selected Individual Criteria for Client Virtualization Software ... 75
10.
Mobile Device Management Service Providers
77
10.1. Evaluation Criteria for Mobile Device Management Services ... 7710.2. Mobile Device Management Service Providers for the Midmarket ... 77
10.2.1.Evaluated mobile device management service providers for the midmarket ... 77
10.2.2.Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for the midmarket ... 78
10.2.3.Selected individual criteria for mobile device management services for the midmarket ... 79
10.3. Mobile Device Management Service Providers for the Upper Midmarket ... 81
10.3.1.Evaluated mobile device management service providers for the upper midmarket ... 81
10.3.2.Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for the upper midmarket ... 82
10.3.3.Selected individual criteria for mobile device management services for the upper midmarket ... 83
10.4. Mobile Device Management Service Providers for Large Accounts ... 86
10.4.1.Benchmarked mobile device management service providers for large accounts ... 86
10.4.2.Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for large accounts ... 86
10.4.3.Selected individual criteria for mobile device management services for large accounts ... 87
11.
Managed Workplace Services Providers
90
11.1. Evaluation Criteria for Managed Workplace Services ... 9011.2. Managed Workplace Services Providers for the Midmarket ... 90
11.2.1.Benchmarked managed workplace services providers for the midmarket ... 91
11.2.2.Benchmarked providers of managed workplace services for the midmarket segment ... 91
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
11.2.3.Selected individual criteria for managed workplace services for the
midmarket ... 92
11.3. Managed Workplace Services Providers for the Upper Midmarket ... 95
11.3.1.Benchmarked providers of managed workplace services for the upper midmarket ... 95
11.3.2.Benchmarked providers of managed workplace services for the upper midmarket segment ... 95
11.3.3.Selected individual criteria for managed workplace services for the upper midmarket ... 97
11.4. Benchmarked service providers for managed workplace services for large accounts ... 99
11.4.1.Benchmarked service providers for managed workplace services for large accounts ... 99
11.4.2.Benchmarked providers of managed workplace services for large accounts ... 99
11.4.3.Selected individual criteria for managed workplace services for large accounts ... 100
12.
Mobile Application Development Platform Vendors
103
12.1. Benchmarked Vendors of Mobile Application Development Platforms ... 10312.2. Evaluation Criteria for Mobile Application Development Platforms ... 104
12.3. Benchmark of Mobile Application Development Platform Vendors ... 104
12.4. Selected individual criteria for mobile application development platforms ... 106
13.
Outlook
108
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Table of Figures
Figure 1: The four stages of mobile enterprise development ... 12
Figure 2: Apps classification by target groups ... 16
Figure 3: Experton Market Insight overview ... 24
Figure 4: Analyzed market segments ... 26
Figure 5: Research Plan ... 27
Figure 6: Methodology – from research to benchmark ... 28
Figure 7: Service provider benchmark – mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket segment ... 30
Figure 8: Mobility consulting services, midmarket– strategy & vision ... 31
Figure 9: Mobility consulting management services, midmarket – momentum ... 32
Figure 10: Mobility consulting management services, midmarket – awareness ... 32
Figure 11: Benchmarked mobile enterprise consulting providers for the upper midmarket .. 34
Figure 12: Mobility consulting services, upper midmarket– strategy & vision ... 35
Figure 13: Mobility consulting management services, upper midmarket – momentum ... 36
Figure 14: Mobility consulting management services, upper midmarket – awareness ... 36
Figure 15: Service provider benchmark – mobile enterprise consulting for large accounts . 38 Figure 16: Mobility consulting management services, large accounts – strategy & vision ... 40
Figure 17: Mobility consulting management services, large accounts – momentum ... 40
Figure 18: Mobility consulting management services, large accounts – awareness ... 41
Figure 19: Benchmark of mobile device management software vendors for smartphones and tablets ... 44
Figure 20: Mobile device management, smartphones and tablets – strategy & vision ... 46
Figure 21: Mobile device management, smartphones and tablets – momentum ... 47
Figure 22: Mobile device management, smartphones and tablets – awareness... 47
Figure 23: Vendor benchmark mobile device management software for all devices ... 49
Figure 24: Mobile device management, all end-user devices – strategy & vision ... 50
Figure 25: Mobile device management, all end-user devices– momentum ... 51
Figure 26: Mobile device management, all end-user devices – awareness ... 51
Figure 27: Benchmark of mobile application management software vendors ... 54
Figure 28: Mobile application management – strategy & vision ... 55
Figure 29: Mobile application management – momentum ... 56
Figure 30: Mobile application management – awareness ... 57
Figure 31: Benchmark of mobile information management software vendors based on the file sharing approach ... 60
Figure 32: Mobile information management, based on the file sharing approach – strategy & vision ... 61
Figure 33: Mobile information management, based on the file sharing approach – momentum ... 62
Figure 34: Mobile information management, based on the file sharing approach – awareness ... 62
Figure 35: Benchmark of vendors of ECM-based mobile information management software ... 64
Figure 36: ECM-based mobile information management software – strategy & vision ... 65
Figure 37: ECM-based mobile information management software – momentum ... 66
Figure 38: ECM-based mobile information management software – awareness ... 66
Figure 39: Benchmark of mobile security suites vendors ... 69
Figure 40: Mobile security vendors – functionality ... 70
Figure 41: Mobile security vendors – portfolio ... 71
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Figure 43: Mobile security vendors – hardware support ... 72
Figure 44: Mobile security vendors – marketing ... 72
Figure 45: Benchmark of client virtualization software vendors ... 74
Figure 46: Client virtualization software – strategy & vision... 75
Figure 47: Client virtualization software – momentum ... 76
Figure 48: Client virtualization software – awareness ... 76
Figure 49: Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for the midmarket 79 Figure 50: Mobile device management services, midmarket – strategy & vision ... 80
Figure 51: Mobile device management services, midmarket – momentum ... 80
Figure 52: Mobile device management services, midmarket – awareness ... 81
Figure 53: Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for the upper midmarket ... 83
Figure 54: Mobile device management services, upper midmarket – strategy & vision ... 84
Figure 55: Mobile device management services, upper midmarket – momentum ... 85
Figure 56: Mobile device management services, upper midmarket – awareness ... 85
Figure 57: Benchmark of mobile device management service providers for large accounts 87 Figure 58: Mobile device management services, large accounts – strategy & vision ... 88
Figure 59: Mobile device management services, large accounts – momentum ... 89
Figure 60: Mobile device management services, large accounts – awareness ... 89
Figure 61: Benchmarked managed workplace service providers for the midmarket segment ... 92
Figure 62: Managed workplace services, midmarket – strategy & vision ... 93
Figure 63: Managed Workplace Services, midmarket – momentum ... 94
Figure 64: Managed Workplace Services, midmarket – awareness ... 94
Figure 65: Benchmarked providers of managed workplace services for the upper midmarket segment ... 96
Figure 66: Managed workplace services, upper midmarket – strategy & vision... 97
Figure 67: Managed workplace services, upper midmarket – momentum ... 98
Figure 68: Managed workplace services, upper midmarket – awareness ... 98
Figure 69: Benchmarked service providers for managed workplace services for the large accounts segment ... 100
Figure 70: Managed workplace services, large accounts – strategy & vision ... 101
Figure 71: Managed workplace services, large accounts – momentum ... 102
Figure 72: Managed workplace services, large accounts – awareness ... 102
Figure 73: Benchmark of mobile application development platform vendors ... 105
Figure 74: Mobile application development platforms – strategy & vision ... 106
Figure 75: Mobile application development platforms – momentum ... 107
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
1. Management Summary
Altogether, both product and service offerings have improved significantly during the last 12 months and are addressing users' requirements, while these requirements have increased, due to higher numbers of users and an increased business value.
Products and services still show significant differences, which must be accounted for before respective investment decisions are made.
1.1. Mobile Enterprise Consulting
For both users and service providers, mobile enterprise consulting is key. Using mobile devices is not necessarily providing benefits, unless business processes are optimized and mobilized and respective applications are developed and the whole infrastructure is adjusted accordingly. User organizations have meanwhile acknowledged this necessity, which has increased the demand for respective services. While in the past, mobile device management services have been used by providers as door openers to enter respective customer accounts, mobile enterprise consulting is today's entry-level service to be offered to customers.
For the midmarket segment, the following service providers have been positioned in the leader quadrant: Bechtle, Cancom, Computacenter and Freudenberg IT.
Within the upper midmarket, Cancom, Computacenter and HP, as well as Bechtle, Atos, Fujitsu, Freudenberg IT and Realtech Consulting were positioned in the leader quadrant. Seven Principles was positioned as "Rising Star".
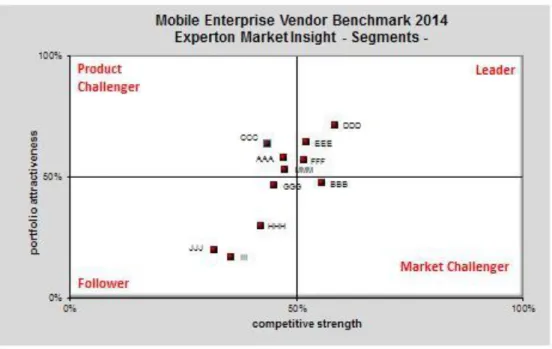
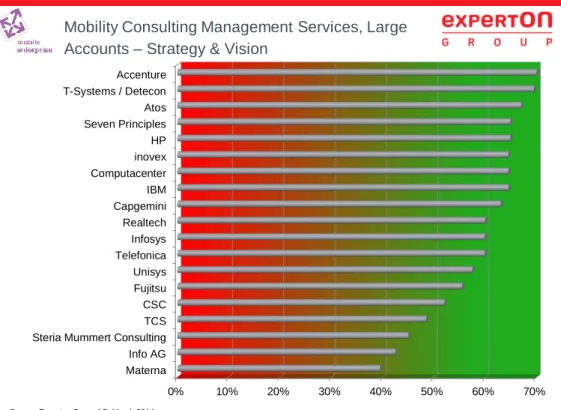
Within the large accounts segment, the list of service providers positioned in the leader quadrant is even longer: Accenture and T-Systems, followed by Atos, IBM, Computacenter, Capgemini, HP, Fujitsu, Unisys, Realtech Consulting, Seven Principles, CSC and QSC. inovex has been positioned as "Rising Star" in this segment.
1.2. Mobile Device Management Software
Mobile device management software is a key technical component for mobile enterprise implementations. Most IT managers have recognized that the professional usage of mobile devices also requires a certain degree of management and use such solutions accordingly.
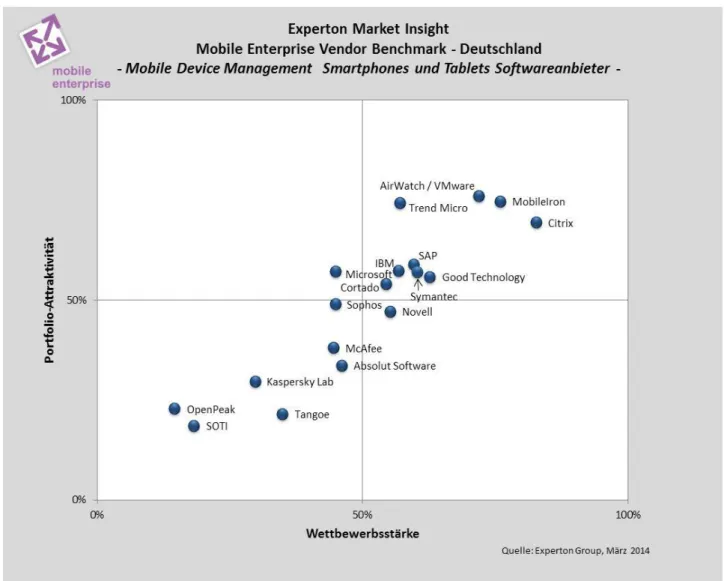
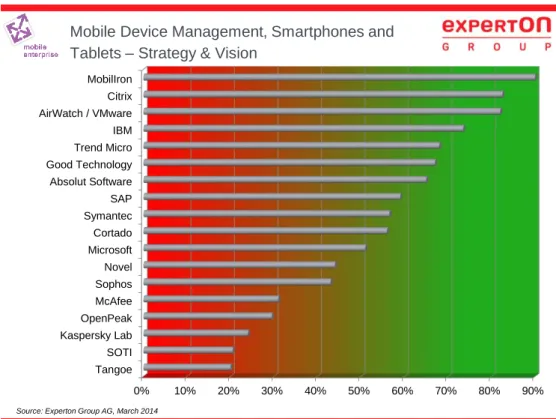
Within the mobile device management software solutions segment for smartphones and tablets, MobileIron, Citrix, TrendMicro, AirWatch/VMware and also SAP, IBM, Symantec, Good Technology and Cortado were positioned in the leader quadrant.
Within the mobile device management software solutions segment for all end-user devices, Matrix42, Microsoft, Novell, Cortado and IBM were positioned as leaders. FrontRange was positioned as "Rising Star".
1.3. Mobile Application Management Software
Mobile application management software is a relatively new market segment, where especially mobile device management software vendors are trying to differentiate their mobile device management solutions by adding application management features. For many companies this
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
additional functionality is quite interesting and might constitute quite an important decision-making parameter for mobile device management selection.
Within this segment, the following companies were positioned within the leader quadrant: MobileIron, TrendMicro, Citrix, AirWatch/VMware, Microsoft SAP, IBM, Cortado, Good Technology, LANDesk and Symantec. FrontRange was positioned as Rising Star.
1.4. Mobile Information Management Software
In 2013, issues concerning how documents and other information can be provisioned safely to and stored securely on mobile devices, including rights management, were hype issues. Many security officers have prohibited free, easy-to-use cloud solutions, due to security concerns, but have not approved of respective alternative solutions, much to the disliking of their users. Meanwhile, there is a multitude of solutions available, based on the file-sharing approach or traditional enterprise content management systems.
Within the segment of file-sharing-based mobile information management software, IBM, Microsoft, AirWatch/VMware, Citrix, Cortado, TrendMicro, Acronis, Alfresco, Box, EMC, NetApp and Good Technology were positioned in the leader quadrant.
When it comes to mobile information management software, based on enterprise content management, the leaders are IBM, Microsoft, OpenText, Hyland Software, EMC and Alfresco.
1.5. Mobile Security Suites (Software)
Mobile security suites for enterprise environments secure tablets and smartphones, which exceeds traditional notebook security. Functionality is depending on the respective vendor, but may include scanners that do not only search for malicious apps or files, but also for privacy risks. Various solutions do not only provide remote deletion capabilities in case a device gets lost or stolen, but also offer mobile encryption functionality. In response to spam mails which are introduced to mobile devices not only through e-mails, SMS filters are displayed accordingly. Some mobile security suites have a special focus on BYOD scenarios through the separation of business and personal apps and data. Trend Micro, Mc Afee and Symantec were identified as the top leaders in the mobile security suites category, followed by Sophos, Kaspersky, F-Secure, G Data and Lookout, which were also positioned in the leader quadrant. Bitdefender has been positioned as Rising Star.
1.6. Mobile Device Management Services
In early 2013, mobile device management services were an ideal door opener to win new customers and to then take over the whole workplace as managed service or within a complete outsourcing scenario. While today mobility consulting is better suited to win new customers, respective high-quality mobile device management services are still available.
Therefore, most vendors in this segment have been positioned in the leader quadrant. In the midmarket segment, leaders include the following vendors: Deutsche Telekom, Cancom, Bechtle, Computacenter, Freudenberg IT and Seven Principles.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
In the upper midmarket, the following vendors were positioned in the leader quadrant: Deutsche Telekom, Computacenter, Cancom, Bechtle, HP, IBM, Atos, Unisys, Freudenberg IT, Fujitsu, QSC and Materna.
In the large accounts segment, Deutsche Telekom / T-Systems, HP, Atos, IBM, Colt, Capgemini, Computacenter, Unisys, CSC, Fujitsu and QSC were positioned as leaders.
1.7. Workplace Management Managed Services
Today's workplace management managed services mostly comprise client management and also collaboration, telephony, mobile solutions and e-mail capabilities.
Most service providers are transforming this category of services into an "as a service" approach to also offer optional cloud-based desktops (private or public cloud). Demand for such services depends on the company size. Larger enterprises are more interested in such offerings than smaller businesses.
The following vendors were positioned as leaders for the midmarket segment: Deutsche Telekom, Cancom, Bechtle, and Computacenter.
The leader quadrant for the larger midmarket includes the following companies: Deutsche Telekom, Computacenter, Bechtle, Cancom, Atos, HP, Unisys, QSC and IBM.
T-Systems, Atos, IBM, HP, Computacenter, Capgemini, Unisys, Colt, Fujitsu, CSC and QSC were positioned in the leader quadrant for the large accounts segment.
1.8. Client Virtualization Software
When it comes to client virtualization software, server-based computing still plays a dominant role. While VDI is gaining relevance, it is of minor importance. As a rule, client virtualization, i.e. a centralized data repository, is directly opposed to higher mobility, and as such, virtual clients can only be used as smaller or larger isolated solutions within user organizations. However, virtual clients in all kinds of variations are still a key component of corporate client strategies.
The following vendors were positioned in the leader quadrant: Citrix, VMware, Microsoft and AppSense.
1.9. Mobile Application Development Platform Vendors
The great success of mobile devices is accompanied by a high demand for respective apps. Companies develop suitable apps either internally or through external service providers for all kinds of use cases: B2C, i.e., apps for consumers, including games, information platforms or other entertainment offerings; B2B, i.e., apps for corporate customers, mostly combined with respective products or solutions offerings, such as machine control or diagnostic systems; and B2E, i.e., apps that enable employees to access enterprise applications or data.
All these use cases require development environments that ensure the efficient application development, efficient and safe access to data or applications and app life cycle management. The following vendors were positioned in the leader quadrant: IBM, SAP, jQuery Mobile, Kony, Adobe, Antenna, Microsoft, Salesforce.com and Appcelerator.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
2. Mobile Enterprise – An IT Hype Is Evolving Into a Business
Topic
Hardly any other IT topic has evolved into a business topic as quickly as the mobility issue. Devices, which were formerly belittled by the IT experts, became suitable for the senior management level very quickly and must be managed accordingly. In 2013, there was the great breakthrough – away from the device-centric hype towards real business process support and optimization. In 2014 and 2015, this trend will continue to reach the broad mass of companies, driving further growth in the market for respective solutions and services as well as the need for respective IT skills and talents.
2.1. Demand Development
According to Experton Group, the development from the mobile enterprise hype into a business topic will occur in four stages. Most users have already mastered the first two stages; stage 3 is pending, and stage 4 will not happen short-term (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: The four stages of mobile enterprise development
We have left behind the times when mobile enterprise was only about the hardware in use. While the device continues to play a key role for many users, these devices are now subject to management and at least the most rudimentary security measures have been taken. A lot of midmarket businesses are still in this phase. The next step – which has already been initiated by larger enterprises – Is to mobilize business processes, to not only equip employees with the desired devices, but to also achieve tangible business value, which makes the mobile enterprise a real business endeavor.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Experton Group expects that the final stage will not be reached before 2015, which is highly optimistic. In this stage, both business users and the IT side will be more relaxed about device questions, and the focus will again be on devices that are optimal for the respective workplace description. At present, we do not expect the "post-PC age" in the foreseeable future, as has been conjured up by some vendors. Rather, Experton Group expects smartphones, tablets, notebooks, desktops and thin clients to co-exist in the foreseeable future, ideally managed with one single tool (see section 2.3).
2.2. Mobile Device Management Software – Consolidation Is On Its Way
The market for mobile device management software is still characterized by a multitude of small and very small vendors with a very strong focus on mobile device management.
While large IT vendors and service providers, on the other hand, have recognized that they need to address the mobile device management issue, developing such solutions themselves is a very costly business, and so, they would like to engage in close partnerships with suitable solution vendors or acquire such vendors.
For quite some time, both financial and IT analysts have been waiting for the first major acquisition wave within the mobile device management software market. 2014 seems to be the year of such consolidation. Late 2013, IBM announced its acquisition of Fiberlink; in January 2014, AirWatch agreed to be acquired by VMware.
Mobile device management vendors that do not want to become acquisition candidates, are enhancing their portfolio to include mobile application management and mobile information management solutions, which makes them a more interesting choice for customers and results in faster growth rates, but does not reduce their attractiveness for interested parties with acquisition aspirations, although a higher purchase price might be possible, at best.
For users, selecting the right mobile device management solutions becomes even more difficult. They must consider the following:
Coverage of the internal catalog of criteria: While such catalogs are, of course, specific and individual, they should cover the following general key aspects:
o Packaging (SaaS, appliance, availability for Windows, Mac, Linux) o Licensing o Maintenance o Support o Scalability o Fault tolerance o Enrollment o Enrollment authentication o Mobile configuration features o Support of iOS 7 features o On-demand features o Profile features
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
o App management o Administration console o Data export o Integration o Certificate features o LDAP featureso Support of non-iOS devices
Costs: While software costs are not of key importance for a TCO analysis, they must not be ignored either.
Implementation: When it comes to implementation, the availability of integration service providers and partners is of key importance. While many companies implement their mobile device management solutions themselves, more and more businesses want to commission these tasks to external parties, also due to a lack of internal resources; this makes partners an essential prerequisite.
The vendor's viability: While in many companies, mobile solutions are hardly mission-critical, switching to another mobile device management solution costs additional efforts, is annoying, and should be avoided. Therefore most companies make a careful evaluation of individual solutions. Evaluating the vendor's viability is especially difficult, since the IT department is hardly able to understand the strategic options of the various players in the market. A small vendor with leading-edge technology may be an acquisition candidate, but that may also apply for a larger vendor. While vendors that are not leading-edge might be interesting for individual user organizations, they are hardly that attractive for the majority of users, which has a negative impact on the respective vendor's financial viability. Also, the question is whether a potential acquisition would have negative consequences for the user. If the acquiring party uses the acquired vendor to enhance and round off its portfolio, this might pose no problems, as opposed to a purchaser who only wants to integrate parts of the product with his own technology. The newly developed product would have to be reevaluated and, at worst, be replaced by another solution.
For many companies, respective managed service solutions for mobile device management become even more attractive, since it is the service provider who has to bear the risks related to vendor selection and also related migration risks.
2.3. The Desktop in the Post-PC Era
The press and vendor publications speak of the post-pc era, when PCs and notebooks have become obsolete. Quite a few of these articles see signs of this era already dawning in our present times.
Experton Group thinks that this era cannot be expected soon, mainly because of the following reasons:
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
While travelling employees should be able to work efficiently and be supplied respective hardware and software solutions, these mobile solutions are mostly additional equipment, in addition to conventional desktop or notebook computers.
Also, many or even the majority of employees still have a permanent workplace, and for them, a thin client, desktop or – in case of a certain degree of mobility within the premises is required, for instance, due to frequent meetings – a notebook is the optimal equipment.
In most companies, the workplace of the future is still an illusion. While many CEOs are talking about work-life balance, the search for talent, new work(place) models etc., such ideas become reality in surprisingly few companies, except for some flagship projects. But without such changes, changing employees' IT equipment makes only sense in selective cases.
Therefore, IT departments must be prepared to support a mix of co-existing traditional PCs, thin clients and today's mobile solutions for quite some time.
Thus, it is important to work with highly integrated management solutions, if possible, since these solutions ensure the efficient management of PC landscapes as well as thin clients and, of course, mobile solutions. Alternatively, companies can pursue a best-of-breed approach, which is still the preferred option for many user organizations, although this means that the IT staff must work with various tools, which often results in higher costs (training, licensing, number of staff…).
Companies that have no plans to introduce the workplace of the future short-term, must be especially careful when evaluating which approach is most useful and whether a managed service or complete outsourcing of workplaces may be an option and even more useful and appropriate
2.4. ByoD Is Dead, Long Live CyoD
In Europe and specifically in Germany, only few hypes coming from the US have failed to such extent as has the bring-your-own device hype. Interestingly, both US and European vendors try to position this topic as a competitive differentiator, although corporate executives have rejected it from the beginning and still tolerate ByoD implementations to a very limited degree only.
As we know, there are more questions on the bring-your-own-device issue than answers and solutions.
As new studies show, companies are dissatisfied with their "high potentials" – the primary target group for bring-your-own-device initiatives, because young academics could not be expected to work with standard hardware, because it is old-fashioned to not allow them to use Facebook and Twitter during working hours, because it is practically impossible to tell young employees how to do their work and what tools to use etc. Now, companies are realizing with surprise that their employees are actually making use of the freedom they were granted.
To avoid at least the most urgent ByoD challenges (chargeback/tax, support, exclusion of liability etc.) Experton Group recommends the slightly modified "Choose your own Device" approach. While this model provides the employee the same freedom of choice as ByoD, the company purchases the device itself and owns the device. Whether such device can also be used for private purposes, can easily be regulated through tax-neutral policies or company agreements.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
2.5. Do You Need Mobile Middleware for Mobile Apps?
Again and again, the question arises whether mobile middleware is a necessity or not. Which companies of which company size do really need and how relevant is such middleware? Or can they do without?
To find answers, it is necessary to classify the apps accordingly (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Apps classification by target groups
Apps that have been designed for the business-to-consumer category, are mostly not connected to enterprise IT and their back-office systems, but are stand-alone apps, maybe with read access to few data, and do not require mobile middleware.
Ideally, business-to-business apps are connected to the publisher's back-office systems and also to the customer's systems, requiring standardized middleware, if possible, to allow multiple companies with multiple back-office solutions to use the app without continued customizations. Business-to-employee apps mostly have one or several interfaces with back-office systems; related maintenance may be quite time-consuming and costly, if the number of apps increases, which makes it necessary to consider the usage of respective middleware when a certain number of apps and connected back-office systems is reached. While these boundaries are blurred in real-world implementations, we can say that it makes sense to initiate a mobile middleware project when about 5 apps and 4 back-office systems are involved and further growth is expected.
2.6. Mobile Enterprise and Industrie 4.0
According to Experton Group's definition, the "Industrie 4.0" trend describes the convergence of cybernetics and informatics, pervading all areas of manufacturing and creating intelligent, self-configuring and self-controlled products and production systems.
From a technical perspective, Industrie 4.0 is the convergence of the Internet of things with the
5 Experton Group AG
Expertonale 2013
Mobile Enterprise Strategy
Various Perspectives
• Business-to-Consumer
- Entertainment / Games with product or company relation
• Business-to-Business
- Solutions with a clear product or solution relation (machine control through tablet, etc.)
- Industrie 4.0 relation
• Business-to-Employee
- Solutions that enable employees‘ mobile work styles
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
(cyber physical systems), ICS (industry control systems), embedded systems, M2M, new sensors and standardized communications protocols, the Internet of data and services provides practically unlimited storage and network capacities, high-availability and high-performance networks, new applications, mobility, big data and cloud computing.
For the Industrie 4.0 approach, mobility is of great relevance, even before it comes to real manufacturing. The basic idea is to supply knowledge about how to manufacture a product, together with the first product component for further usage within the manufacturing chain, rather than manufacturing products, based on a central blueprint, as has been done in the past. While there are various ways to do this, it always involves a change of paradigms, compared to current production control concepts, facilitating the easier customization of small-volume products significantly. A new challenge are the communications between production equipment and streets and the respective components, based on appropriate technologies – a challenge that will keep both the IT industry and the equipment manufacturers quite busy during the next few years.
As a matter of course, mobility is also key in the logistics process, after the product has been manufactured; in this process, bar codes, RFID and other technologies have played a key role since years. Industrie 4.0 will replace stationary terminals and expensive – often rather unhandy – special scanners through state-of-the-art smartphones or tablets.
Mobile enterprise or mobility interfaces are also of interest for products that are subject to maintenance during their life cycle and should be able to communicate respective required maintenance work.
For stationary devices such as multifunctional printers predictive maintenance approaches have been in use for quite some time. The underlying idea is simple and appealing. The respective device reports any impending breakdown due to wear to the manufacturer or service partner before such failure occurs, reducing downtimes practical to zero.
Meanwhile first mobile examples show how to develop new business models and increase customer satisfaction rates through appropriate data about machines in use. For instance, a premium car manufacturer offers a paid service, allowing the vehicle to collect data about the style of driving, environmental parameters and data from sensors within the vehicle, such as the engine, the gear unit, the chassis etc. and transmit these data via a GSM module to the manufacturer, where they are analyzed automatically to inform the holder of the car, for instance, about any required maintenance (this information is often provided by the car computer) or provide an alert that one unit may break down within the next few weeks or kilometers, together with a suggested data and time in the customer's (authorized) repair shop.
Such examples can be used to derive analogous solutions for a great variety of engineering and electro-technical products and also for solutions such as smart home solutions, where the owner of the apartment or house, rather than the manufacturer, are informed accordingly.
Prior to technical implementation, some basic challenges must be taken into consideration:
Machines that shall supply data via mobile connections may not be online around the clock. For instance, a tunnel boring machine will not be online during extended usage, which means that data must be stored over a longer period of time. Also, it must be possible to apply traditional service or maintenance models in such cases.
Machines that must be monitored this way mostly have a long life, and communications standards in use must work and be available beyond the planned life cycle.
While the transferred data per machine can be handled easily, the great number of monitored machines may result in giant data streams, which puts a heavy strain on the manufacturer's and his service partners' data connections as well as on the internal
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
networks and the servers and storage units used to process these data. Appropriate sizing is of key importance, which may require big data and also cloud computing technologies to deal with peak loads.
Security, too, is extremely important. It is one thing to let data flow from the machine to the manufacturer, and quite another thing to allow the manufacturer to adjust the machine settings. Very safe interfaces are required for this purpose.
Besides these technical aspects, business aspects should also be taken into consideration:
Which business model does really provide a competitive advantage over competitors?
How can you expand or at least maintain such advantage?
Are the customers willing to spend money on such services or is it sufficient to increase the reliability of one's products and the customers' satisfaction, as a result of Industrie 4.0 considerations?
2.7. Mobile Security: Mobile Risks and Security Functionality
2.7.1. Mobile Risks
While mobile devices and applications are the technical foundation to ensure successful mobile enterprise scenarios, they also bear a high risk for enterprise data. Mobile security risks result from the specifics related to mobile IT, for instance, the risk of losing a mobile device, including stored business data. Also, the proliferation of smartphones, tablets and apps attracts cyber criminals and data thieves. Meanwhile, mobile devices and apps are among the main targets of attacks, as has, for instance, been revealed in the study "ENISA Threat Landscape Mid-Year 2013" of the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA), which counts risks related to mobile devices among the largest cyber risks..
Key mobile security risks include the following, also based on an ENISA risk analysis:
Loss of devices: The flip side of the great mobility and flexibility of smartphones and tablets is the high risk of losing such mobile device or of respective device thefts. Resulting damages are not limited to the loss of hardware, but also include the potential abuse of confidential data stored on the devices, unless mobile data encryption technology is used as a protection.
Return of devices: New models are launched all the time, with employees retiring and returning their smartphones and tablets, due to the highly dynamic development of mobile devices. The same is true with respect to job market dynamics: When employees leave the company, they return the company-owned device, which will be given to a new user. Without target data deletion and wipe-out – after a centralized backup – the stored data can be accessed by unauthorized persons.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): If personal smartphones or tablets are used for business purposes, data may be mixed up on the user level, the application level and the data level. Business applications can access the user's personal data, and private apps can access business data. Also, various security measures, such as the remote deletion of data if a device gets lost, is more difficult, as is the company's control of how the device is used; the latter may even be impossible due to legal regulations, since employers are not entitled to simply delete or access personal data.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Phishing: While phishing attacks bear high risks for all kinds of devices, additional threat factors apply for mobile devices: On the one hand, mobile browsers and mail apps do not always provide a phishing filter to alert the user accordingly. On the other hand, mobile web sites often have a different look than the familiar web sites, and so, users may not easily detect any fakes. The small displays of smartphones may make it even more difficult to detect forged log-in pages.
Spyware: Smartphones and tablets may be infiltrated with spy files and malicious files not only through e-mail attachments or infected web sites, but also through apps from an app store, which may contain spyware. For Android-based devices, the spyware apps risk is especially high, since many app stores do not provide sufficient security. However, even the large, well-known app stores have been known to offer malware-infected apps.
Network spoofing (rogue hotspot): For cost reasons, many mobile Internet users prefer WLAN hotspots. When travelling, they often use external hotspots with insufficient protection, i.e., they do not provide sufficient encryption or are not encrypted at all. Also, data thieves could work with a rogue hotspot to access, view and manipulate all data that pass through this supposed hotel or restaurant hotspot.
Monitoring/motion profiles: Spyware apps may secretly collect personal data that can be used to monitor the user, for instance, through prohibited analyses of his Internet activities. Illicit scans of the user's GPS position data can be used to create motion profiles, which allows third parties to follow the user permanently undetected.
Dialerware: Dialerware is a special kind of mobile malware used to illicitly and secretly use paid telephone and mobile services, which may cause enormous financial damage for individual users or companies, if, for instance, large volumes of premium SMS are sent through such account.
Financial malware (mobile banking): Mobile malware is also used to abuse the popular mobile online banking or mobile banking trend. Specialized malware may, for instance, try to catch mobile TANS which are received as SMS on a smartphone, which cancels the additional protection through the second password when logging into the online banking account.
Network resource overload: Mobile devices are online practically all the time and might be abused for attacks to send mass network queries into the enterprise network and web server to bring it down. This way, mobile devices are used by cyber criminals as a tool without the user's knowledge.
Professional mobile security suites should be used to address most of these risks. Add-ons can be used to provide any missing security functionality to defend the company against such risks. It is important to inform the users about the risks addressed and not addressed by the respective solutions to make them aware of any additional security needs. Mobile device and mobile apps users should not be left in the dark in case only partial data protection is supplied.
2.7.2. Mobile Security Functionality
To address the mobile risks described above, mobile security suite should combine multiple security functionality. For Experton Group, a mobile security suite is not a solution that only provides individual functionality such as mobile data deletion or mobile malware scans.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Privacy scanner: App rights verification, alerts on critical authorizations
Mobile encryption: Encryption of stored data on the internal device storage unit and on any potential storage cards
Remote wipe: Remote deletion in case the device gets lost or stolen
Data wipe: secure deletion of data, based on an acknowledged methodology
Backup: Mobile data backups
Device localization: Localization of lost or stolen devices, no permanent localization of the user (to avoid motion profiles)
Virus protection: Scans of new and existing apps, stored data and transferred data (such as mobile downloads) for the purpose of malware detection
E-mail protection: Scans of incoming and outgoing e-mails to detect any malware or spam
SMS filter: SMS spam handling
App control: Basic functionality to block apps in case no mobile device management (MDM) is available
Firewall: Control of mobile network traffic
VPN functionality: Set-up of encrypted connections into the enterprise network, which is of key importance for WLAN usage "on the road"
Differentiation between personal and business usage: specific function to divide the device into personal and business users, applications and data
Our evaluation of the functional performance of analyzed mobile security suites was based on these security functions.
2.7.3. Mobile Security Suites as a Response to Mobile Risks
Various test institutes, journals and associations are offering anti-malware tests to evaluate the quality of a solution's mobile malware detection, including an analysis to determine how often the respective solution fails to detect mobile malware and also the frequency of false positives. These tests are useful, and this analysis should not be used as a replacement of such tests. Rather, this analysis wants to point out that mobile security suites should provide more functionality than anti-malware solutions.
An evaluation of mobile security suites and their risk prevention capability should also include additional aspects, which are discussed within this Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014 and are analyzed to determine the performance of various mobile security suites. Required functionality includes support services, innovative new products and product versions, customer satisfaction rates, the solution's integratability and the scope of functionality, which must go far beyond simply detecting mobile malware.
Experton Group's analysis of mobile security suites is a valuable addition and extension of known anti-malware tests for smartphones and tablets, as offered by various test institutes.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
The European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA), the German Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik (BSI; Federal Office for Information Security) and regulatory privacy authorities have published the following guidelines on mobile security:
o Smartphones: Information security risks, opportunities and recommendations for users (Dec 10, 2010), http://www.enisa.europa.eu/activities/identity-and-trust/risks- and-data-breaches/smartphones-information-security-risks-opportunities-and-recommendations-for-users
o Resolution of the Düsseldorfer Kreis of May 04/05, 2011: May 2011: Datenschutzgerechte Smartphone-Nutzung ermöglichen!,
http://www.bfdi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Publikationen/Entschliessungssammlung/Dues seldorferKreis/0050052011SmartphoneNutzung.pdf
o App store security: 5 lines of defence against malware (Sep. 12, 2011),
http://www.enisa.europa.eu/activities/Resilience-and-CIIP/critical- applications/smartphone-security-1/appstore-security-5-lines-of-defence-against-malware/at_download/fullReport
o Smartphone Secure Development Guidelines (Nov 25, 2011), http://www.enisa.europa.eu/activities/Resilience-and-CIIP/critical- applications/smartphone-security-1/smartphone-secure-development-guidelines/at_download/fullReport
o Consumerization of IT: Risk Mitigation Strategies and Good Practices (Jan 07, 2013), http://www.enisa.europa.eu/media/news-items/security-is-key-for-byod o Overview smartphones,
https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/BSI/Grundschutz/Download/U eberblickspapier_Smartphone_pdf.pdf
o Overview consumerisation and BYOD,
https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/BSI/Grundschutz/Download/U eberblickspapier_BYOD_pdf.pdf
o Mobile devices and mobile applications: Sicherheitsgefährdungen und Schutzmaßnahmen,
https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/BSI/Publikationen/Broschuere n/MobilEndgeraete/mobile_endgeraete_pdf.pdf
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
2.8. Vendor selection was, is, and remains a challenge
Selecting a suitable service provider or software solution is always a difficult and complex endeavor. Ideally, the following approach should be pursued:
IT-internal requirements and target analysis
Requirements and target analysis on the user side
Requirements and target analysis of other stakeholders (works committee, HR department, security officers, legal department)
Deduction of a comprehensive mobile enterprise strategy
Deduction of a comprehensive client strategy
Make or buy decision for all business units
Requirements definition and prioritization (for service provider or software)
Selection, based on the concrete individual requirements
As such, this benchmark is a first good overview, but does not replace any concrete evaluation for the purpose of individual investment decisions.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
3. Methodology
3.1. Definitions
The following definitions are important to properly classify the results of the individual benchmarks:
Mobile Enterprise Consulting; Consulting around the whole mobile enterprise topic, including
processes, management solutions and services, if required.
Mobile Device Management Software
Software that enables user organizations to manage their mobile devices. Within this analysis, we differentiate between software offerings for smartphones and tablets and offerings for all end-user devices.
Mobile Application Management Software
Software that enables user organizations to provision apps to mobile devices (tablets and smartphones) internally. Often, such software is provided by mobile device management providers. Mobile Information Management
Software
Software that allows and manages users' access to and use of documents and files on mobile devices (tablets and smartphones). This category includes vendors from the mobile device
management and document management segments.
Mobile Security Suites (Software) Software that supports mobile devices (tablets and smartphones) through functionality such as anti-virus, anti-malware, a firewall for mobile devices, anti-spam.
Client Virtualization Software Software for client virtualization. Mobile Device Management
Services
Managed services for mobile device operations and maintenance.
Managed Workplace Services Managed services covering the complete workplace (operations and maintenance), i.e., thin clients, desktops, notebooks, smartphones, tablets and also fixed-line telephony, mobile telephony and, depending on the vendor, e-mail and collaboration solutions.
Mobile Application Development Platform
Application development environments that enable users to create apps for various use cases.
Midmarket Companies with about 100 and more employees, with central headquarters in Germany, ideally managed by the owner(s). Upper midmarket Companies with about 1,000 and more employees, with central
headquarters in Germany, ideally managed by the owner(s); international subsidiaries may exist, but usually they have no decision-making powers.
Large Accounts Multinational corporations with about 5,000 and more employees, global activities and internationally distributed decision-making structures.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
3.2. Methodology and Analysis Design
This „Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014“ is based on the “Experton Market Insight” methodology developed by Experton Group AG. This validated and internationally acknowledged methodology serves as basis for the evaluation and positioning of the individual vendors.
For each vendor, a detailed scoring based on 7-10 key and additional 3-5 secondary criteria is provided for each product category. These criteria are weighted, based on the respective product category, resulting in an assessment of the individual mobile enterprise offering’s attractiveness (“portfolio attractiveness”) and the strength of the individual vendor (“competitive strength”).
The “Experton Market Insight” Quadrant contains four segments where the vendors are positioned accordingly:
Leaders:
The „leaders“ among the vendors have a highly attractive product and service offering and a very strong market and competitive position; they fulfill all requirements for successful market cultivation. They can be regarded as opinion leaders, providing strategic impulses to the market.
Market challengers:
„Market challengers“ are also very competitive, but there is still significant portfolio potential and they clearly lack behind the „leaders“.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Product challengers:
The “product challengers” offer a product and service portfolio that provides above-average coverage of corporate requirements, but are not able to provide the same resources and strengths as the leaders regarding the individual market cultivation categories.
Followers:
„Followers“ are still lacking mature products and services or sufficient depth and breadth of their offering, while also showing weaknesses and improvement potentials in their market cultivation efforts.
Rising Star:
For all “rising stars” there are indicators of a positive future development, since their solution or portfolio comprises many interesting aspects, while being backed up by a balanced and strategically sound management approach. However, they mostly lack competitive strength and/or a highly attractive portfolio required for a better positioning.
3.3. Selection of Analyzed Vendors
This benchmark has a focus on software vendors and IT service providers that are active in the German market and in the following segments:
Mobile enterprise consulting
Mobile device management software
Mobile application management software
Mobile information management software
Mobile security suites (software)
Mobile device management managed services
Client virtualization software
Workplace management managed services
Mobile application development platforms
Selection criteria for vendors to be benchmarked included the following:
Dedicated offering within at least one of the defined segments
Availability of the vendor’s offering in the local market;
Relevant project implementations, revenues and references in the local market;
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Due to the multitude of offerings Experton Group does not guarantee the exhaustiveness of the listed vendors and services. Only services and offerings that were available by February 1, 2014 were analyzed.
Figure 4: Analyzed market segments
3.4. Analysis Design
The analysis for this „Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014” was conducted based on four phases:
Research:
Extensive secondary research was performed to ensure sound data for those evaluations that are not based on the vendors' own information; it included a review of the individual vendors' offerings and also an analysis of their Internet presences, product specifications and marketing materials. Many interviews with product managers, technology experts and vendors' customers also contributed greatly to this benchmark. Based on numerous consulting engagements on the user side, Experton Group also has comprehensive experience when it comes to assess the actual performance of the individual vendors.
Vendor survey: Mobile Device Management Software Mobile Information Management Software Workplace Management Managed Service Mobile Security Suites (Software) Mobile Application Management Software Mobile Device Management Managed Service Mobile Enterprise Consulting Client Virtualization Software Mobile Application Development Platform
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
A vendor survey, which was conducted, based on a questionnaire and interviews between our analysts and executives on the vendor side formed another key part of this study.
Depending on the segment, the questionnaire comprised 30 to 44 questions that covered the complete scope, from strategy and technology to product and service offerings and support.
Testing/demo:
Various product tests with varying degrees of depths were performed to get a clear picture of the practical relevance and usability of individual platforms and services. For instance, products were tested in customers' live environments to determine their functional scope and ease of use; also, services were evaluated, based on customers' service statistics. These insights have also been included in our analysis.
Benchmark:
The three previous steps are the basis for the final evaluation and vendor positioning within this „Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014“. Information and insights gained in the individual steps were consolidated and analyzed, based on the predefined criteria.
Figure 5: Research Plan
3.5. Project Schedule:
From November 2013 to March 2014 Experton Group has analyzed the mobile enterprise offerings of relevant providers in Germany, based on a standardized and proven methodology. The analysis was based on a catalog comprising more than 100 criteria and will be conducted by experienced advisors to provide the following:
Product and segment evaluation in quadrants
Theme-based scoring / ranking;
Strengths / weaknesses – analysis of products / services / technologies. • Internet • Blogs / Media 2.0 • Product Specs • Technical Papers • Marketing Collateral • Experton Interviews • Customer Interviews • Vendor Survey • Duration: November 2013 to March 2014 • Analyst Interviews With Responsible Managers • Product Tests • Usability Tests • Demos • Analysis of Buying Process • Analysis & Evaluation • Vendor Positioning (Quadrants) • Strengths/ Weaknesses • Report / Study
Research
Vendor
Survey
Testing /
Demo
Benchmark
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
Related decisions will be based on product tests, vendor specifications and expert interviews as well as results from Experton Group’s multi-client studies.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
A Comparison of Software Vendors and Service Providers
An Analysis by Experton Group AG Author: Wolfgang Schwab Munich, Germany Bechtle Colt Computacenter CSC Dell Deutsche Telekom Fujitsu Technolgy Solutions HP IBM Atos Tata Consultancy Services T-Systems Unisys Comparex 0% 50% 100% 0% 50% 100% Po rtf olio A ttrac tiv en es s Competitive Strength
Experton Market Insight, Managed Client and Client Hosting Services Providers, Germany, August 2012 Subcategory Weighting Subcategory Rating Subcategory Result Subcategory Vision/Strategy 20% 35% 0,07
Strategy Alignment with Corporate
Strategy 20% 45% 0,09
Innovator / Market Thought
Leadership 10% 15% 0,03
Competitive Strength 30% 28% 0,056 Market Thought Leader 20% 15% 0,03
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
4. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers
In the initial phase of the smartphone and tablet hype, there were no business value considerations regarding these new devices, in addition to constituting an image symbol for the respective user (and often, the company).
Since mid-2013, there has been a clear shift towards a more integrated view, i.e., the focus is more on enterprise mobilization or a mobile enterprise strategy. Within this change process, it is not the latest smartphones or tablets that play the key role, but rather a mobile enterprise strategy, related processes and business value considerations being transformed into an infrastructure strategy and, in a final step, purchase decisions for suitable infrastructures consisting of devices, apps, application interfaces, security solutions and management software. User organizations are increasingly looking for consultants to support this strategy approach with a business and process-oriented perspective, but also with their technical competence to suggest suitable solutions and, ideally, also help with their implementation. As such, successful mobile enterprise consulting may serve as door opener for respective managed services.
4.1. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Evaluation Criteria
Consulting evaluation criteria do not differ for the various target segments, i.e., midmarket, upper midmarket and large accounts.
Ideally and most importantly, the consulting providers should be able support users with their mobile enterprise transformation, from business process optimization and mobilization to final technical implementation or managed service/outsourcing.
While a provider's competitive strength is of only secondary relevance for users, they do have a look at the consulting portfolio and the provider's mobile enterprise consulting momentum.
4.2. Mobile Enterprise Consulting Providers for the Midmarket
This section analyses mobile enterprise consulting providers with a specific offering for the German midmarket segment.
4.2.1. Evaluated service providers for mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket
While the market for mobile enterprise consulting with a special focus on midmarket businesses is still relatively young, some providers have already established themselves in this market.
The following service providers with German market presence have been evaluated:
Bechtle Cancom Computacenter Freudenberg IT Realtech Consulting Seven Principles Telefonica
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
4.2.2. Benchmark of mobile enterprise consulting providers for the midmarket
A clear majority of five out of seven relevant providers for the midmarket segment have been positioned in the leader quadrant – a result that speaks in favor of these providers' performance and users' appreciation.
Figure 7: Service provider benchmark – mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket segment
The portfolio attractiveness of the benchmarked providers is similarly high. The top leaders are Cancom and Bechtle with very similar ratings, followed by Computacenter and Freudenberg IT with a slightly lower competitive strength.
SAP specialist Realtech lags slightly behind, both with respect to the competitive strength and the portfolio attractiveness.
Mobile Enterprise Vendor Benchmark 2014
4.2.3. Selected individual criteria – mobile enterprise consulting for the midmarket segment
Only slight differences can be observed with respect to the benchmarked providers' strategy and vision. While Freudenberg IT received slightly better ratings, Bechtle, Computacenter and Cancom, too, provide clear and comprehensible plans and ideas.
Source: Experton Group AG, March 2014
Mobility Consulting Services, Midmarket– Strategy
& Vision 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% Realtech Seven Principles Telefonica Cancom Computacenter Bechtle Freudenberg IT
Figure 8: Mobility consulting services, midmarket– strategy & vision
A provider's momentum reflects this company's popularity in the market. Computacenter and Freudenberg IT are the leaders, closely followed by Bechtle and Cancom, and the other providers lagging behind.
The awareness rating reveals a very similar picture: Again, the four leading companies are well ahead of their competitors.