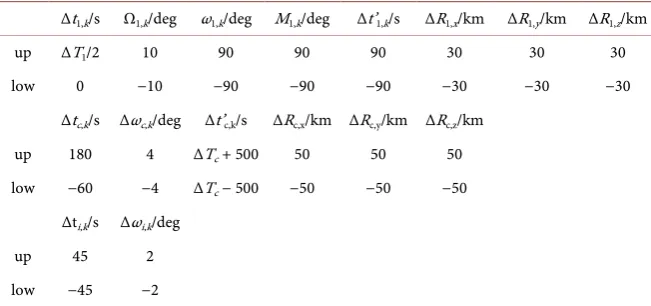
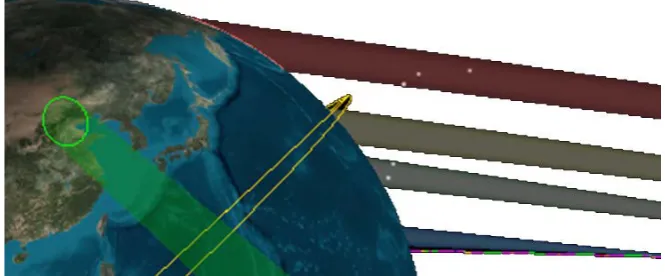
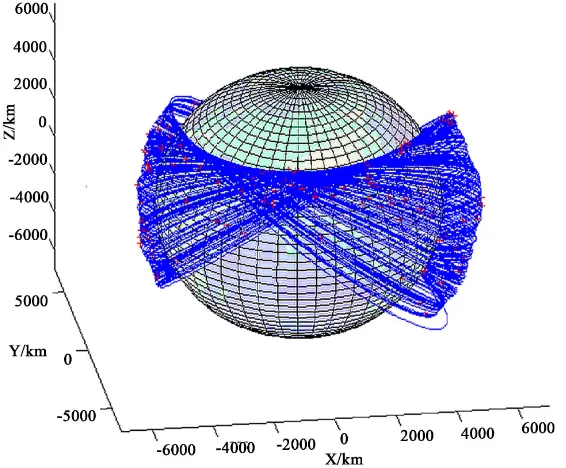
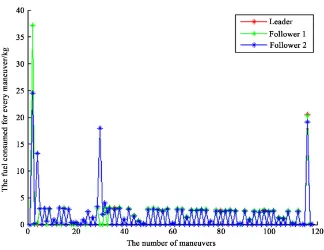
Trajectory Design and Optimization for LEO Satellites in Formation to Observe GEO Satellites’ Beams
Full text
Figure




Related documents
Your first step is to collect some preliminary information such as optimum growth temperature and colony morphology and perform a Gram stain to place the species in a broad
That is, if we would like to assume a different Total Shares amount, we would simply need to make a corresponding adjustment to the New Share Price (or vice versa). For example,
• Microscale material and structural alterations: A reduced average mineral content and increased heterogeneity of mineralization were accompanied by signi ficant increases in
In other word, you want to define a global variable to be local to a particular module (file) - make sense in cases where no functions other than those contained inside a
The proposed growth methods provide improved confidence intervals for the mean of Negative Binomial random variables with unknown dispersion.. Re- moving a small number of zeros
This ―word-spreading‖ is one of AR‘s goals (Interview with AR‘s Process Leader, 2009) and as the analysis of the website show, the interest is there (see 6.1
The proposed method is dedicated for new product develop- ment in an enterprise that uses an ERP system. New product development is often connected with the superficial changes
We study the resulting bankruptcy probability for the compound Poisson risk model with exponential claim sizes for different bankruptcy rate functions, deriving analytical