Evaluation of the Functional Impression Technique with Various Impression Materials on the Surface Topography of Dental Stone Casts and Their Effect on Retention
Full text
Figure

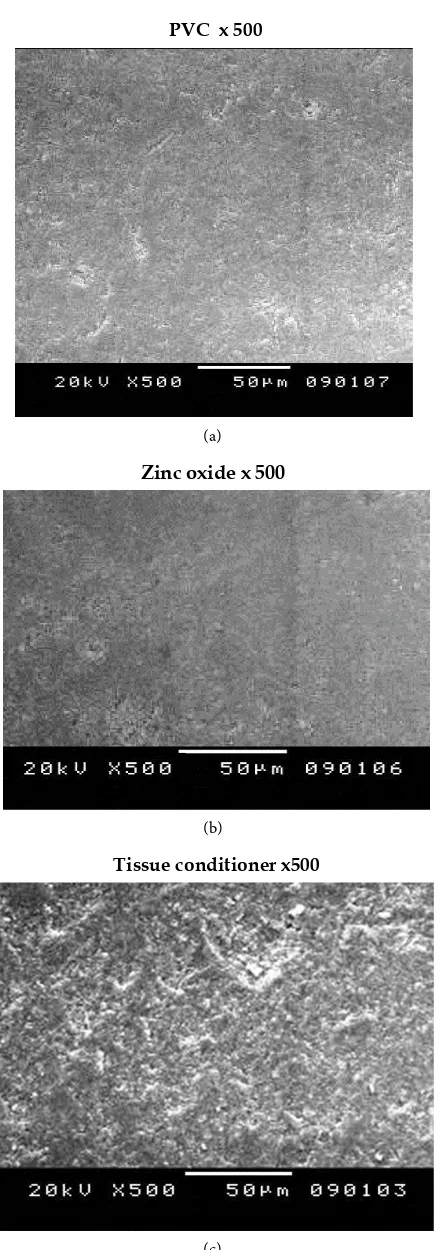
Related documents
Most representatives emphasized the importance of an open dialogue between health care professionals and pa- tients. They believed that patients should be provided with information
Biofilm production by selected strains of bacteria (a) and yeasts (b) in the presence of Textus bioactiv, Textus multi dressings, and culture broth without dressing.. The figures
Screening of cytotoxic activities using WiDr and Vero cell lines of ethyl acetate extracts of fungi-derived from the marine sponge
Abstract: This study examines the unique experience of participants who during their reintegration back into the community, following a conviction for sexual offending, re-
The results of this study showed that in 2010, in France, about 1 to 10 patients managed for primary lung cancer in the respiratory department of a general hospital died within 1
In conclusion, the finding of this cross-sectional study of pre and post menopausal women show no evidence of a significant difference in BMD between Ocs users and never user
Another study with diabetic patients and the West Nile virus had observed that these patients were at greater risk of developing encephalitis and other severe forms of the disease
Antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive patients imme- diately post stroke may be effective and cost-effective compared with placebo from the acute hospital perspec- tive at