Interaction of Helicobacter pylori Cell Membrane with Non Esterified Cholesterol and Other Steroids
Full text
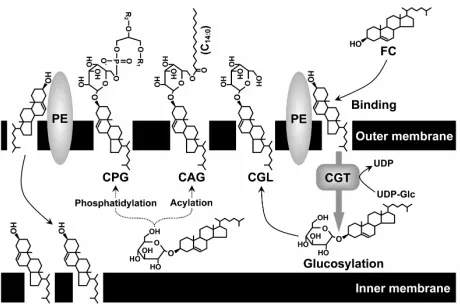
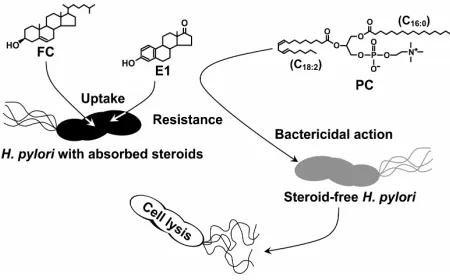
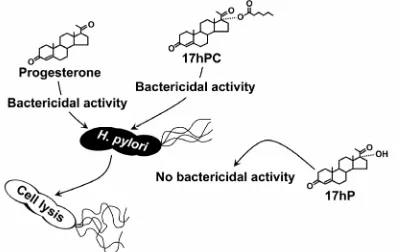
Figure

Related documents
Runoff: basal and surface melting of the ice sheet; iceberg FWF: melt flux related to iceberg calving; direct FWF: input of calving mass as freshwater flux into the first ocean
A comparative study of multiple clinical enterovirus 71 isolates and evaluation of cross protection of inactivated vaccine strain FY 23 K B in vitro RESEARCH Open Access A comparative
The objective of this research was to explore the challenges, the stakes, and the difficulties of clinical teachers who super- vised final year medical students in their primary
(I) the trademark or other intellectual property rights of the person, if any, in the domain name; (II) the extent to which the domain name consists of the legal name
The methanol extract possess significant anti-oxidant property at the concentration of 250 µg/ml than aqueous extract at a dose of 250 µg/ml when compared to standard drug
Social Networks and Supply chain Management in Rural Areas: A Case Study Focusing on Organic Olive OilU. Medicamento, Umberto and
To make safe, reliable, non-repudiation collaboration space and to identify partners in the domains, guarantee of access control to resources, recovery of
