Electric Vehicle Regenerative Braking Control Strategy Based on Braking Time Identification
Full text
Figure
Related documents
This heuristic controller provides positive torque from the regenerative braking system when the instantaneous fuel usage of the vehicle is over a pre-set
Using ANFIS and PID control the regenerative braking system of electric vehicle driven by BLDC motor is achieved as shown in figure 6.. Figure 6 RBS of EV using ANFIS
A fuzzy control strategy for regenerative braking system in electric vehicle (EV) presented in [10], the controller shows significant improvement over initial
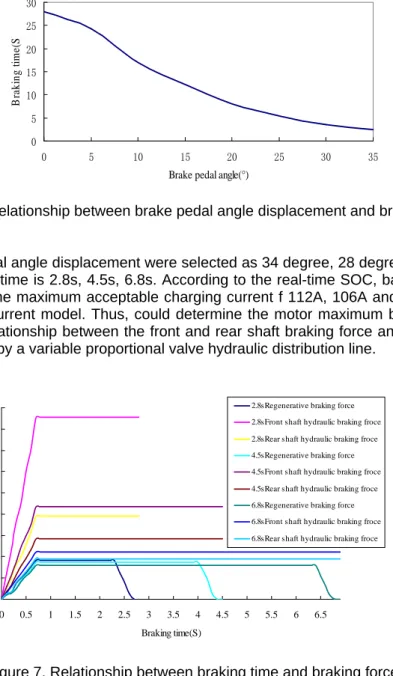
The model allows for the implementation of a regenerative brake controller that utilizes floating pedal regen, custom shift logic, and brake pedal blended regen.. The floating
In two-pedal cooperative braking, when the regenerative and friction brakes are simultaneously activated by the driver interacting with the (emergency) brake pedal, the
In other regions, where speed of the vehicle is such that the motor speed is more than 100 rpm and less than 330 rpm, then the regenerative braking is effective and feeds
electric parking brake Front ventilated and heated seats 10-way power driver seat with lumbar support. Paddle shifters (for regenerative braking) One pedal driving Utility mode
T orque Good Bad Fuel economy Engine speed Rpm control Generator rpm Engine rpm Motor rpm Acceleration pedal Vehicle speed Battery Air conditioning Shift lever position Brake