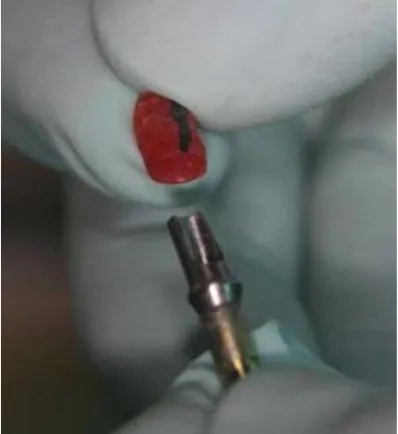
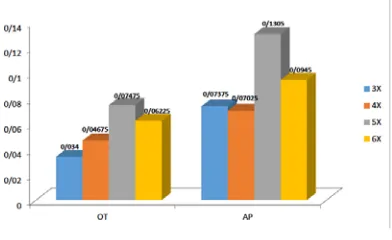
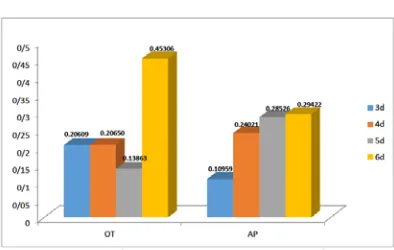
A Comparison between the New Method of Impression and Connected (Contiguous) Open-Tray Method in Implants
Full text
Figure

Related documents
The paper is discussed for various techniques for sensor localization and various interpolation methods for variety of prediction methods used by various applications
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
Fusarium infection in chili seeds tends to reduce leaf area, chlorophyll content, carbohydrate content, and increase plant dry weight, but the decrease is not
Methods: A follow-up study 5.5 years after the explosion, 330 persons aged 18 – 67 years, compared lung function, lung function decline and airway symptoms among exposed
It was decided that with the presence of such significant red flag signs that she should undergo advanced imaging, in this case an MRI, that revealed an underlying malignancy, which
Also, both diabetic groups there were a positive immunoreactivity of the photoreceptor inner segment, and this was also seen among control ani- mals treated with a
19% serve a county. Fourteen per cent of the centers provide service for adjoining states in addition to the states in which they are located; usually these adjoining states have
Anti-inflammatory effects of the preparation were studied according to the below methods: S.Salamon– burn induced inflammation of the skin, caused by hot water (80 0 C) in white