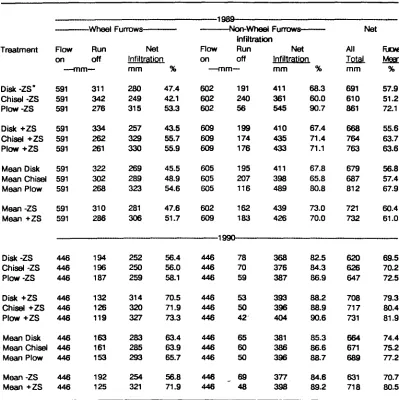
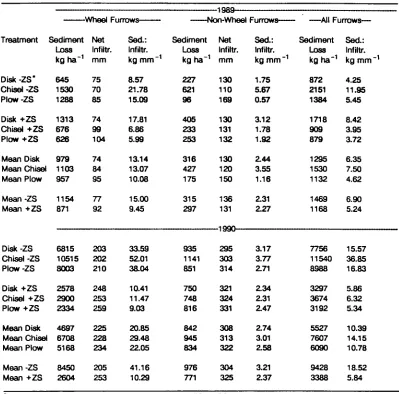
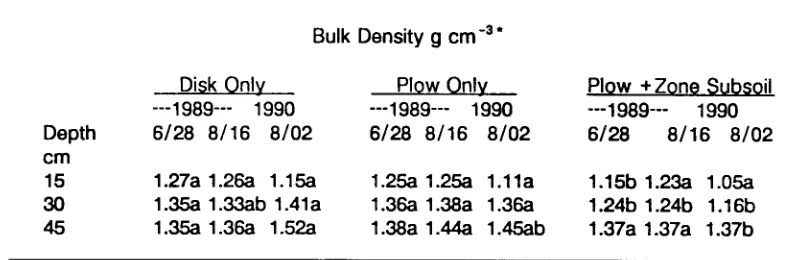
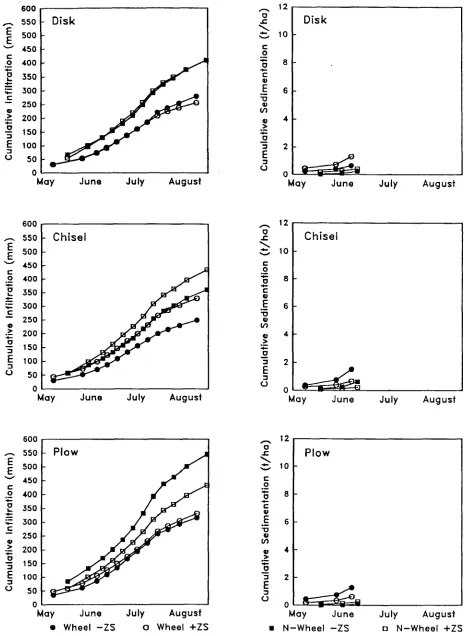
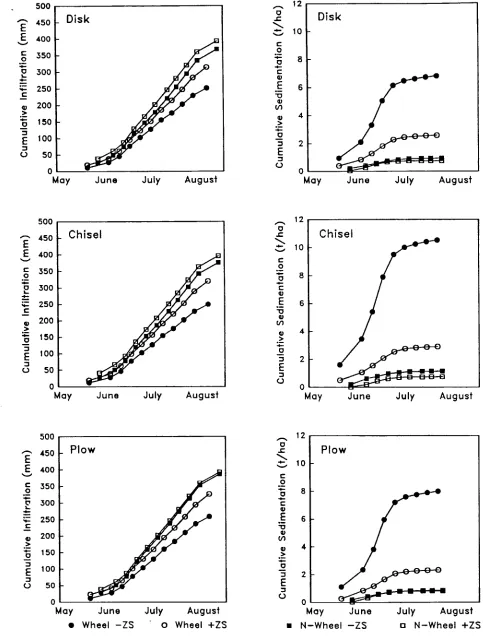
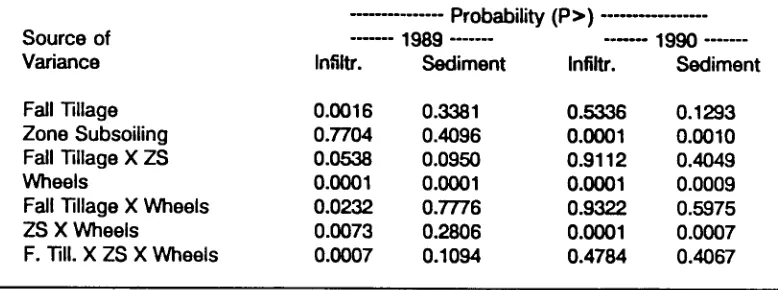
Erosion and infiltration of furrow irrigated potato fields as affected by zone subsoiling
Full text
Figure
Related documents
We aimed to investigate whether season of birth influences the risk of rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and systemic lupus erythematosus in addition to
We have identified a likely com- plete set of genes, putative primary targets of Klf5 in ESCs, by comparing the early changes of the gene expression profile induced by Klf5 KD and
Background: The evolving epidemiology of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is characterized by the emergence of infections caused by non multiresistant MRSA
Cells were induced with osteogenic cocktail and osteogenesis was measured by quantitative alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) and ( b ) Alizarin red staining. ALP and Alizarin
Methods: Streptomyces strains (n = 18) isolated from cases of actinomycetoma were tested in vitro against 15 commonly prescribed antibacterial agents using MIC agar dilution method
Furthermore, lipases that can function as biocatalysts in nearly anhydrous organic solvents offer new possibilities such as shifting of the thermo- dynamic equilibrium in favor
Digital content files are critical to transfer for online journals and this clause balances the desire of the Transferring Publisher to have as much time as possible to get the
A meta-analysis of these nine studies showed a significant benefit of single- patient bedrooms in reducing the healthcare-associated colonization and infection rate compared