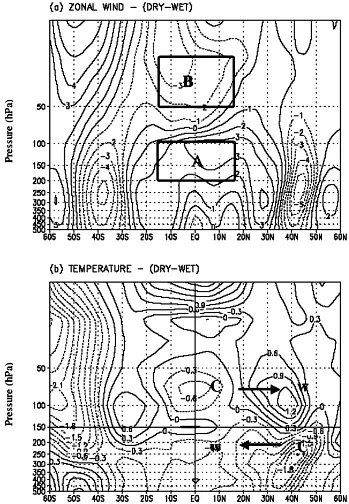
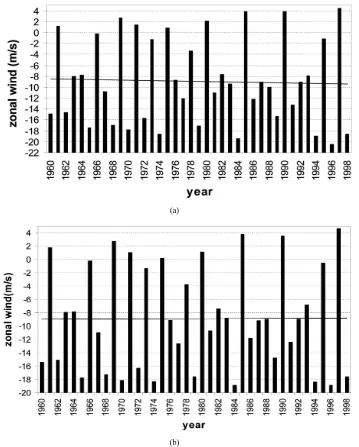
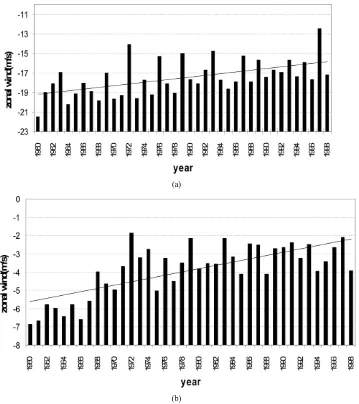
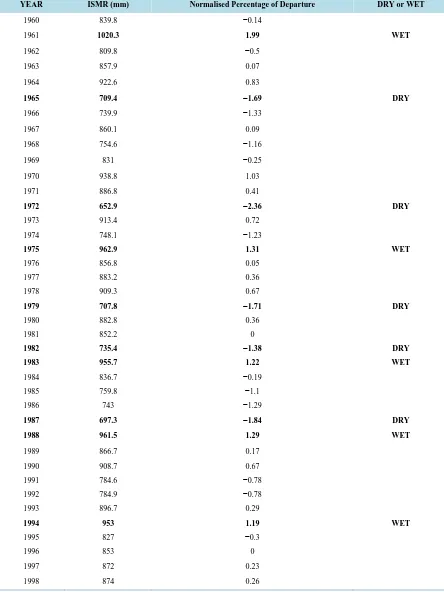
Variation of Zonal Winds in the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere in Association with Deficient and Excess Indian Summer Monsoon Scenario
Full text
Figure
Related documents
heart disease among subjects with increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, including those with plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein deficiency. Zhong
In Section 4 we take up the problem o f discrimination when the parameters are unknown and find conditions on the hyper-parameters o f the conjugate prior under
The widespread need for the micronutrients observed in recent years can be accounted for in three ways viz. i) Naturally deficient in some soil types ii) their deficiency has
New uses of the Migraine Screen Questionnaire (MS-Q): validation in the Primary Care setting and ability to detect hidden migraine.. MS-Q in Primary
Cite this article as: Zivadinov et al.: Decreased brain venous vasculature visibility on susceptibility-weighted imaging venography in patients with multiple sclerosis is related
We have used micro data covering the 1993-2004 period on food, and non-durable household spending, and evaluated the causal effect of retirement on consumption by exploiting
AMI: Acute myocardial infarction; AUC: Area under the curve; BMI: Body mass index; CI: Confidence interval; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; CK-MB: Creatine kinase-MB fraction;
In conclusion, low physical activity level and unhealthy eating behavior among medical study encourages imple- mentation of health education programs about obesity and risk