metal-organic papers
Acta Cryst.(2005). E61, m1199–m1200 doi:10.1107/S160053680501617X Tianet al. [Sn(C
6H11)3(C14H11O2)]
m1199
Acta Crystallographica Section E
Structure Reports
Online
ISSN 1600-5368
(4-Biphenylacetato)tricyclohexyltin(IV)
Lai-Jin Tian,a* Yu-Xi Sun,a Yi-Zhen Gaoaand Guo-Ming Yangb
aDepartment of Chemistry, Qufu Normal
University, Qufu 273165, Shandong, People’s Republic of China, andbDepartment of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence e-mail: laijintian@163.com
Key indicators
Single-crystal X-ray study
T= 295 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.005 A˚
Rfactor = 0.030
wRfactor = 0.081
Data-to-parameter ratio = 16.3
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
#2005 International Union of Crystallography Printed in Great Britain – all rights reserved
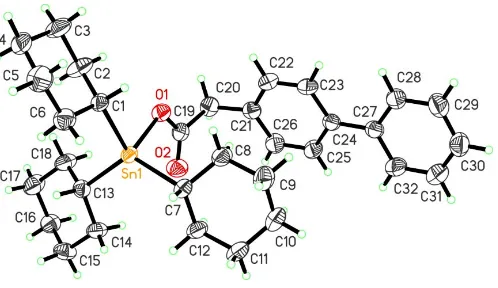
The Sn atom of the title compound, [Sn(C6H11)3(C14H11O2)], is four-coordinate and possesses a distorted tetrahedral geometry.
Comment
Tricyclohexyltin carboxylates, [(C6H11)3Sn(O2CR)], generally have a tetrahedral structure and do not auto-associate into chain structuresviacarboxylate bridging, due to the crowding of the three bulky cyclohexyl groups at the Sn atom (Chan-drasekharet al., 2002; Tiekink, 1991, 1994).
4-Biphenylacetic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Bundgaard & Nielsen, 1988) and in its tricyclohexyltin ester, (I), the Sn atom is four-coordinate and possesses a distorted tetrahedral geometry (Fig. 1). The Sn O2 separa-tion of 2.900 (2) A˚ is not indicative of a significant interaction between these atoms. The major stereochemical role of atom O2 is to distort the tetrahedral geometry by opening up the C7—Sn1—C13 angle to 121.90 (11) and reducing the O1—
Sn1—C1 angle to 93.81 (9). The monodentate mode of
coordination of 4-biphenylacetate is reflected in the disparate O1—C19 and O2—C19 bond lengths of 1.292 (4) and 1.206 (4) A˚ , respectively. The four bond lengths to Sn (Table 1)
[image:1.610.211.460.576.720.2]Received 4 May 2005 Accepted 20 May 2005 Online 28 May 2005
Figure 1
are similar to those found in other reported tricyclohexyltin carboxylates, such as tricyclohexyltin indole-3-acetate (Molloy
et al., 1986), trifluoroacetate (Calogero et al., 1980),
N-phthaloylglycinate (Ng & Kumar Das, 1997a), (N,N -diethylthiocarbamoylthio)acetate (Ng & Kumar Das, 1997b) and 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyrate (Songet al., 2003).
Experimental
Tricyclohexyltin hydroxide (0.577 g, 1.5 mmol) and 4-biphenylacetic acid (0.318 g, 1.5 mmol) in benzene (60 ml) were refluxed for 6 h with azeotropic removal of water viaa Dean–Stark trap. The resulting clear solution was evaporated under vacuum. The white solid obtained, the title compound, was recrystallized from ethanol and crystals of (I) were obtained from a methanol solution of the compound (yield 81.7%, m.p. 351–352 K). Analysis, found: C 66.34, H 7.49%; calculated for C32H44O2Sn: C 66.33, H 7.65%.
Crystal data
[Sn(C6H11)3(C14H11O2)]
Mr= 579.36 Triclinic,P1 a= 9.3181 (12) A˚ b= 11.6211 (15) A˚ c= 13.9327 (18) A˚
= 87.052 (2)
= 76.227 (2)
= 77.460 (2)
V= 1430.4 (3) A˚3
Z= 2
Dx= 1.345 Mg m
3 MoKradiation Cell parameters from 885
reflections
= 3.0–22.9
= 0.92 mm1
T= 295 (2) K Block, colourless 0.320.220.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX area-detector diffractometer
’and!scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) Tmin= 0.758,Tmax= 0.875 7734 measured reflections
5165 independent reflections 4834 reflections withI> 2(I) Rint= 0.018
max= 25.5
h=11!11 k=14!9 l=16!16
Refinement
Refinement onF2
R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.030
wR(F2) = 0.081
S= 1.05 5165 reflections 316 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
w= 1/[2(F
o2) + (0.0418P)2 + 0.6525P]
whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3 (/)max= 0.002
max= 0.93 e A˚
3 min=0.65 e A˚
[image:2.610.314.566.94.153.2]3
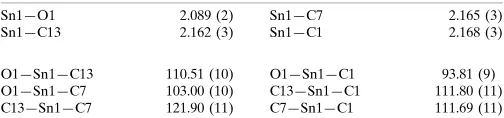
Table 1
Selected geometric parameters (A˚ ,).
Sn1—O1 2.089 (2)
Sn1—C13 2.162 (3)
Sn1—C7 2.165 (3)
Sn1—C1 2.168 (3)
O1—Sn1—C13 110.51 (10) O1—Sn1—C7 103.00 (10) C13—Sn1—C7 121.90 (11)
O1—Sn1—C1 93.81 (9) C13—Sn1—C1 111.80 (11) C7—Sn1—C1 111.69 (11)
H atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined in the riding-model approximation, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier C).
Constrained C—H distances were 0.93 for aromatic CH, 0.97 for methylene CH2and 0.98 A˚ for methine CH.
Data collection:SMART(Bruker, 2002); cell refinement:SAINT
(Bruker, 2002); data reduction:SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure:SHELXS97(Sheldrick, 1997); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997); molecular graphics: XP
(Bruker, 2002); software used to prepare material for publication:
SHELXL97.
The authors thank the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province and Qufu Normal University for supporting this work.
References
Bundgaard, H. & Nielsen, N. M. (1988).Int. J. Pharm.43, 101–110. Bruker (2002). SADABS, SAINT, SMART and XP. Bruker AXS Inc.,
Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Calogero, S., Ganis, P., Peruzzo, V. & Tagliavini, G. (1980).J. Organomet. Chem.191, 381–390.
Chandrasekhar, V., Nagendran, S. & Baskar, V. (2002).Coord. Chem. Rev.235, 1–52.
Molloy, K. C., Purcell, T. G., Hahn, E., Schumann H. & Zuckerman, J. J. (1986). Organometallics,5, 85–89.
Ng, S. W. & Kumar Das, V. G. (1997a).Acta Cryst.C53, 546–548. Ng, S. W. & Kumar Das, V. G. (1997b).Acta Cryst.C53, 548–549.
Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of Go¨ttingen, Germany.
Song, X., Cahill, C. & Eng, G. (2003).Appl. Organomet. Chem.17, 743–744. Tiekink, E. R. T. (1991).Appl. Organomet. Chem.5, 1–23.
supporting information
sup-1 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m1199–m1200
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m1199–m1200 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S160053680501617X]
(4-Biphenylacetato)tricyclohexyltin(IV)
Lai-Jin Tian, Yu-Xi Sun, Yi-Zhen Gao and Guo-Ming Yang
(4-Biphenylacetato)tricyclohexyltin(IV)
Crystal data
[Sn(C6H11)3(C14H11O2)] Mr = 579.36
Triclinic, P1 Hall symbol: -P 1 a = 9.3181 (12) Å b = 11.6211 (15) Å c = 13.9327 (18) Å α = 87.052 (2)° β = 76.227 (2)° γ = 77.460 (2)° V = 1430.4 (3) Å3
Z = 2 F(000) = 604 Dx = 1.345 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å Cell parameters from 885 reflections θ = 3.0–22.9°
µ = 0.92 mm−1 T = 295 K Block, colourless 0.32 × 0.22 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX area-detector diffractometer
Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube Graphite monochromator
φ and ω scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) Tmin = 0.758, Tmax = 0.875
7734 measured reflections 5165 independent reflections 4834 reflections with I > 2σ(I) Rint = 0.018
θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.5° h = −11→11
k = −14→9 l = −16→16
Refinement Refinement on F2 Least-squares matrix: full R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 wR(F2) = 0.081 S = 1.05 5165 reflections 316 parameters 0 restraints
Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods
Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map
Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites
H-atom parameters constrained w = 1/[σ2(F
o2) + (0.0418P)2 + 0.6525P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3
(Δ/σ)max = 0.002 Δρmax = 0.93 e Å−3 Δρmin = −0.65 e Å−3
Special details
Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq
Sn1 1.07467 (2) 0.213603 (15) 0.740839 (12) 0.04818 (8)
O1 0.8739 (2) 0.22157 (18) 0.69628 (15) 0.0595 (5)
O2 0.8168 (3) 0.4063 (2) 0.7445 (2) 0.0767 (6)
C1 1.1726 (3) 0.0357 (2) 0.6862 (2) 0.0528 (6)
H1 1.1146 −0.0164 0.7286 0.063*
C2 1.1583 (5) 0.0205 (3) 0.5821 (3) 0.0821 (11)
H2A 1.2097 0.0743 0.5386 0.099*
H2B 1.0523 0.0409 0.5804 0.099*
C3 1.2247 (5) −0.1051 (3) 0.5440 (3) 0.0905 (12)
H3A 1.1672 −0.1585 0.5832 0.109*
H3B 1.2174 −0.1096 0.4760 0.109*
C4 1.3862 (4) −0.1416 (3) 0.5495 (3) 0.0847 (11)
H4A 1.4454 −0.0936 0.5045 0.102*
H4B 1.4244 −0.2231 0.5287 0.102*
C5 1.4041 (4) −0.1287 (4) 0.6517 (4) 0.0953 (13)
H5A 1.5108 −0.1474 0.6512 0.114*
H5B 1.3565 −0.1851 0.6945 0.114*
C6 1.3349 (4) −0.0047 (3) 0.6940 (3) 0.0724 (9)
H6A 1.3392 −0.0042 0.7628 0.087*
H6B 1.3938 0.0500 0.6585 0.087*
C7 1.0016 (3) 0.2180 (3) 0.9005 (2) 0.0546 (6)
H7 1.0850 0.1712 0.9264 0.066*
C8 0.8689 (4) 0.1576 (3) 0.9324 (2) 0.0715 (9)
H8A 0.9001 0.0767 0.9090 0.086*
H8B 0.7881 0.1972 0.9019 0.086*
C9 0.8089 (5) 0.1578 (4) 1.0444 (3) 0.0925 (12)
H9A 0.7190 0.1247 1.0604 0.111*
H9B 0.8844 0.1086 1.0746 0.111*
C10 0.7714 (5) 0.2797 (4) 1.0855 (3) 0.0888 (11)
H10A 0.7400 0.2763 1.1569 0.107*
H10B 0.6874 0.3262 1.0613 0.107*
C11 0.9036 (5) 0.3385 (4) 1.0571 (2) 0.0837 (11)
H11A 0.9835 0.2970 1.0876 0.100*
H11B 0.8732 0.4188 1.0817 0.100*
C12 0.9636 (5) 0.3400 (3) 0.9458 (2) 0.0741 (9)
H12A 0.8885 0.3907 0.9163 0.089*
H12B 1.0537 0.3728 0.9308 0.089*
C13 1.1971 (3) 0.3398 (2) 0.6595 (2) 0.0547 (6)
H13 1.3048 0.3046 0.6515 0.066*
supporting information
sup-3 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m1199–m1200
H14A 1.1991 0.4403 0.7751 0.079*
H14B 1.0605 0.4890 0.7284 0.079*
C15 1.2522 (5) 0.5443 (3) 0.6533 (3) 0.0760 (9)
H15A 1.2208 0.6192 0.6880 0.091*
H15B 1.3598 0.5169 0.6478 0.091*
C16 1.2227 (4) 0.5620 (3) 0.5525 (2) 0.0710 (8)
H16A 1.2845 0.6139 0.5152 0.085*
H16B 1.1175 0.5998 0.5578 0.085*
C17 1.2572 (5) 0.4475 (3) 0.4981 (3) 0.0872 (12)
H17A 1.3647 0.4140 0.4862 0.105*
H17B 1.2311 0.4620 0.4345 0.105*
C18 1.1697 (5) 0.3598 (3) 0.5563 (2) 0.0751 (10)
H18A 1.0625 0.3891 0.5610 0.090*
H18B 1.1998 0.2853 0.5212 0.090*
C19 0.7821 (3) 0.3226 (3) 0.7155 (2) 0.0552 (7)
C20 0.6218 (4) 0.3270 (3) 0.7066 (2) 0.0677 (8)
H20A 0.5795 0.4040 0.6832 0.081*
H20B 0.6220 0.2683 0.6595 0.081*
C21 0.5278 (3) 0.3029 (3) 0.8068 (2) 0.0585 (7)
C22 0.5041 (4) 0.1919 (3) 0.8336 (3) 0.0740 (9)
H22 0.5390 0.1318 0.7868 0.089*
C23 0.4305 (4) 0.1672 (3) 0.9273 (3) 0.0711 (9)
H23 0.4160 0.0910 0.9421 0.085*
C24 0.3767 (3) 0.2530 (3) 1.0011 (2) 0.0560 (7)
C25 0.3969 (4) 0.3652 (3) 0.9718 (3) 0.0740 (9)
H25 0.3596 0.4263 1.0174 0.089*
C26 0.4706 (4) 0.3894 (3) 0.8772 (3) 0.0730 (9)
H26 0.4817 0.4661 0.8608 0.088*
C27 0.3040 (3) 0.2252 (3) 1.1040 (2) 0.0591 (7)
C28 0.2720 (4) 0.1160 (3) 1.1307 (3) 0.0847 (11)
H28 0.2968 0.0578 1.0826 0.102*
C29 0.2047 (5) 0.0900 (4) 1.2259 (3) 0.0961 (13)
H29 0.1834 0.0157 1.2410 0.115*
C30 0.1690 (4) 0.1732 (4) 1.2986 (3) 0.0834 (10)
H30 0.1259 0.1556 1.3635 0.100*
C31 0.1975 (5) 0.2818 (4) 1.2743 (3) 0.0886 (11)
H31 0.1712 0.3396 1.3228 0.106*
C32 0.2648 (4) 0.3082 (3) 1.1789 (3) 0.0777 (9)
H32 0.2842 0.3831 1.1645 0.093*
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
Sn1 0.05575 (13) 0.04147 (12) 0.04393 (12) −0.00882 (8) −0.00526 (8) −0.00516 (8)
O1 0.0615 (12) 0.0550 (12) 0.0609 (12) −0.0073 (9) −0.0156 (9) −0.0059 (9)
O2 0.0793 (15) 0.0548 (13) 0.0953 (18) −0.0095 (11) −0.0208 (13) −0.0126 (12)
C1 0.0590 (16) 0.0391 (14) 0.0549 (15) −0.0094 (12) −0.0026 (12) −0.0048 (11)
C3 0.100 (3) 0.066 (2) 0.100 (3) 0.004 (2) −0.023 (2) −0.040 (2)
C4 0.080 (2) 0.060 (2) 0.099 (3) −0.0118 (18) 0.011 (2) −0.0245 (19)
C5 0.068 (2) 0.070 (2) 0.138 (4) 0.0154 (18) −0.029 (2) −0.016 (2)
C6 0.0658 (19) 0.069 (2) 0.080 (2) −0.0043 (16) −0.0200 (17) −0.0105 (17)
C7 0.0584 (16) 0.0579 (17) 0.0439 (14) −0.0053 (13) −0.0106 (12) −0.0036 (12)
C8 0.100 (3) 0.065 (2) 0.0511 (17) −0.0326 (18) −0.0049 (16) −0.0037 (14)
C9 0.121 (3) 0.101 (3) 0.0545 (19) −0.046 (3) 0.000 (2) 0.0094 (19)
C10 0.099 (3) 0.107 (3) 0.0517 (19) −0.021 (2) 0.0015 (18) −0.0144 (19)
C11 0.104 (3) 0.092 (3) 0.0544 (18) −0.022 (2) −0.0098 (18) −0.0245 (18)
C12 0.102 (3) 0.067 (2) 0.0555 (18) −0.0325 (19) −0.0057 (17) −0.0152 (15)
C13 0.0543 (15) 0.0488 (15) 0.0591 (16) −0.0119 (12) −0.0092 (12) 0.0021 (12)
C14 0.092 (2) 0.0595 (18) 0.0541 (16) −0.0308 (17) −0.0199 (16) −0.0023 (14)
C15 0.099 (3) 0.063 (2) 0.080 (2) −0.0369 (19) −0.031 (2) 0.0059 (17)
C16 0.090 (2) 0.0560 (18) 0.068 (2) −0.0233 (17) −0.0146 (17) 0.0065 (15)
C17 0.132 (3) 0.066 (2) 0.0579 (19) −0.037 (2) 0.004 (2) 0.0005 (16)
C18 0.121 (3) 0.0594 (19) 0.0491 (16) −0.0375 (19) −0.0101 (17) −0.0036 (14)
C19 0.0582 (16) 0.0573 (17) 0.0483 (15) −0.0094 (14) −0.0123 (12) 0.0049 (13)
C20 0.0618 (18) 0.079 (2) 0.0620 (18) −0.0070 (16) −0.0209 (15) 0.0008 (16)
C21 0.0485 (15) 0.0611 (18) 0.0675 (18) −0.0051 (13) −0.0216 (13) −0.0041 (14)
C22 0.083 (2) 0.070 (2) 0.068 (2) −0.0183 (18) −0.0097 (17) −0.0231 (17)
C23 0.086 (2) 0.0513 (17) 0.078 (2) −0.0216 (16) −0.0128 (18) −0.0138 (15)
C24 0.0429 (14) 0.0510 (16) 0.0718 (18) −0.0067 (12) −0.0092 (13) −0.0128 (14)
C25 0.077 (2) 0.0473 (17) 0.084 (2) −0.0071 (15) 0.0067 (18) −0.0203 (16)
C26 0.074 (2) 0.0484 (17) 0.086 (2) −0.0070 (15) −0.0034 (18) −0.0034 (16)
C27 0.0455 (14) 0.0539 (17) 0.0756 (19) −0.0076 (12) −0.0098 (13) −0.0130 (14)
C28 0.090 (3) 0.062 (2) 0.091 (3) −0.0249 (19) 0.014 (2) −0.0208 (19)
C29 0.101 (3) 0.081 (3) 0.098 (3) −0.037 (2) 0.010 (2) −0.001 (2)
C30 0.068 (2) 0.101 (3) 0.075 (2) −0.019 (2) −0.0031 (17) −0.002 (2)
C31 0.101 (3) 0.089 (3) 0.073 (2) −0.018 (2) −0.010 (2) −0.020 (2)
C32 0.093 (3) 0.064 (2) 0.076 (2) −0.0189 (18) −0.0138 (19) −0.0140 (17)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
Sn1—O1 2.089 (2) C13—H13 0.9800
Sn1—C13 2.162 (3) C14—C15 1.526 (4)
Sn1—C7 2.165 (3) C14—H14A 0.9700
Sn1—C1 2.168 (3) C14—H14B 0.9700
O1—C19 1.292 (4) C15—C16 1.491 (5)
O2—C19 1.206 (4) C15—H15A 0.9700
C1—C6 1.511 (4) C15—H15B 0.9700
C1—C2 1.511 (4) C16—C17 1.500 (5)
C1—H1 0.9800 C16—H16A 0.9700
C2—C3 1.525 (5) C16—H16B 0.9700
C2—H2A 0.9700 C17—C18 1.524 (5)
C2—H2B 0.9700 C17—H17A 0.9700
C3—C4 1.491 (6) C17—H17B 0.9700
C3—H3A 0.9700 C18—H18A 0.9700
supporting information
sup-5 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m1199–m1200
C4—C5 1.491 (6) C19—C20 1.517 (4)
C4—H4A 0.9700 C20—C21 1.510 (5)
C4—H4B 0.9700 C20—H20A 0.9700
C5—C6 1.531 (5) C20—H20B 0.9700
C5—H5A 0.9700 C21—C26 1.370 (5)
C5—H5B 0.9700 C21—C22 1.374 (5)
C6—H6A 0.9700 C22—C23 1.371 (5)
C6—H6B 0.9700 C22—H22 0.9300
C7—C12 1.517 (4) C23—C24 1.394 (4)
C7—C8 1.518 (4) C23—H23 0.9300
C7—H7 0.9800 C24—C25 1.385 (4)
C8—C9 1.526 (5) C24—C27 1.485 (4)
C8—H8A 0.9700 C25—C26 1.379 (5)
C8—H8B 0.9700 C25—H25 0.9300
C9—C10 1.493 (6) C26—H26 0.9300
C9—H9A 0.9700 C27—C28 1.379 (5)
C9—H9B 0.9700 C27—C32 1.386 (5)
C10—C11 1.500 (5) C28—C29 1.374 (6)
C10—H10A 0.9700 C28—H28 0.9300
C10—H10B 0.9700 C29—C30 1.369 (6)
C11—C12 1.518 (5) C29—H29 0.9300
C11—H11A 0.9700 C30—C31 1.355 (6)
C11—H11B 0.9700 C30—H30 0.9300
C12—H12A 0.9700 C31—C32 1.377 (5)
C12—H12B 0.9700 C31—H31 0.9300
C13—C14 1.511 (4) C32—H32 0.9300
C13—C18 1.516 (4)
O1—Sn1—C13 110.51 (10) C14—C13—Sn1 113.7 (2)
O1—Sn1—C7 103.00 (10) C18—C13—Sn1 111.7 (2)
C13—Sn1—C7 121.90 (11) C14—C13—H13 106.6
O1—Sn1—C1 93.81 (9) C18—C13—H13 106.6
C13—Sn1—C1 111.80 (11) Sn1—C13—H13 106.6
C7—Sn1—C1 111.69 (11) C13—C14—C15 112.9 (3)
C19—O1—Sn1 112.23 (18) C13—C14—H14A 109.0
C6—C1—C2 110.8 (3) C15—C14—H14A 109.0
C6—C1—Sn1 112.5 (2) C13—C14—H14B 109.0
C2—C1—Sn1 112.3 (2) C15—C14—H14B 109.0
C6—C1—H1 107.0 H14A—C14—H14B 107.8
C2—C1—H1 107.0 C16—C15—C14 112.0 (3)
Sn1—C1—H1 107.0 C16—C15—H15A 109.2
C1—C2—C3 112.5 (3) C14—C15—H15A 109.2
C1—C2—H2A 109.1 C16—C15—H15B 109.2
C3—C2—H2A 109.1 C14—C15—H15B 109.2
C1—C2—H2B 109.1 H15A—C15—H15B 107.9
C3—C2—H2B 109.1 C15—C16—C17 111.7 (3)
H2A—C2—H2B 107.8 C15—C16—H16A 109.3
C4—C3—H3A 109.5 C15—C16—H16B 109.3
C2—C3—H3A 109.5 C17—C16—H16B 109.3
C4—C3—H3B 109.5 H16A—C16—H16B 107.9
C2—C3—H3B 109.5 C16—C17—C18 111.5 (3)
H3A—C3—H3B 108.1 C16—C17—H17A 109.3
C3—C4—C5 111.4 (3) C18—C17—H17A 109.3
C3—C4—H4A 109.3 C16—C17—H17B 109.3
C5—C4—H4A 109.3 C18—C17—H17B 109.3
C3—C4—H4B 109.3 H17A—C17—H17B 108.0
C5—C4—H4B 109.3 C13—C18—C17 112.0 (3)
H4A—C4—H4B 108.0 C13—C18—H18A 109.2
C4—C5—C6 113.1 (3) C17—C18—H18A 109.2
C4—C5—H5A 109.0 C13—C18—H18B 109.2
C6—C5—H5A 109.0 C17—C18—H18B 109.2
C4—C5—H5B 109.0 H18A—C18—H18B 107.9
C6—C5—H5B 109.0 O2—C19—O1 123.1 (3)
H5A—C5—H5B 107.8 O2—C19—C20 121.4 (3)
C1—C6—C5 111.8 (3) O1—C19—C20 115.3 (3)
C1—C6—H6A 109.3 C21—C20—C19 108.8 (2)
C5—C6—H6A 109.3 C21—C20—H20A 109.9
C1—C6—H6B 109.3 C19—C20—H20A 109.9
C5—C6—H6B 109.3 C21—C20—H20B 109.9
H6A—C6—H6B 107.9 C19—C20—H20B 109.9
C12—C7—C8 110.8 (3) H20A—C20—H20B 108.3
C12—C7—Sn1 114.8 (2) C26—C21—C22 117.1 (3)
C8—C7—Sn1 109.20 (19) C26—C21—C20 121.2 (3)
C12—C7—H7 107.2 C22—C21—C20 121.6 (3)
C8—C7—H7 107.2 C23—C22—C21 121.8 (3)
Sn1—C7—H7 107.2 C23—C22—H22 119.1
C7—C8—C9 112.7 (3) C21—C22—H22 119.1
C7—C8—H8A 109.0 C22—C23—C24 122.0 (3)
C9—C8—H8A 109.0 C22—C23—H23 119.0
C7—C8—H8B 109.0 C24—C23—H23 119.0
C9—C8—H8B 109.0 C25—C24—C23 115.3 (3)
H8A—C8—H8B 107.8 C25—C24—C27 122.5 (3)
C10—C9—C8 111.3 (3) C23—C24—C27 122.1 (3)
C10—C9—H9A 109.4 C26—C25—C24 122.3 (3)
C8—C9—H9A 109.4 C26—C25—H25 118.8
C10—C9—H9B 109.4 C24—C25—H25 118.8
C8—C9—H9B 109.4 C21—C26—C25 121.4 (3)
H9A—C9—H9B 108.0 C21—C26—H26 119.3
C9—C10—C11 111.8 (3) C25—C26—H26 119.3
C9—C10—H10A 109.3 C28—C27—C32 116.2 (3)
C11—C10—H10A 109.3 C28—C27—C24 122.2 (3)
C9—C10—H10B 109.3 C32—C27—C24 121.6 (3)
C11—C10—H10B 109.3 C29—C28—C27 122.3 (4)
H10A—C10—H10B 107.9 C29—C28—H28 118.8
supporting information
sup-7 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, m1199–m1200
C10—C11—H11A 109.3 C30—C29—C28 120.1 (4)
C12—C11—H11A 109.3 C30—C29—H29 119.9
C10—C11—H11B 109.3 C28—C29—H29 119.9
C12—C11—H11B 109.3 C31—C30—C29 118.8 (4)
H11A—C11—H11B 108.0 C31—C30—H30 120.6
C7—C12—C11 112.5 (3) C29—C30—H30 120.6
C7—C12—H12A 109.1 C30—C31—C32 121.2 (4)
C11—C12—H12A 109.1 C30—C31—H31 119.4
C7—C12—H12B 109.1 C32—C31—H31 119.4
C11—C12—H12B 109.1 C31—C32—C27 121.3 (4)
H12A—C12—H12B 107.8 C31—C32—H32 119.3
C14—C13—C18 111.1 (2) C27—C32—H32 119.3
C13—Sn1—O1—C19 −63.4 (2) C18—C13—C14—C15 −51.4 (4)
C7—Sn1—O1—C19 68.3 (2) Sn1—C13—C14—C15 −178.4 (2)
C1—Sn1—O1—C19 −178.4 (2) C13—C14—C15—C16 52.6 (4)
O1—Sn1—C1—C6 173.9 (2) C14—C15—C16—C17 −54.2 (5)
C13—Sn1—C1—C6 60.0 (2) C15—C16—C17—C18 55.7 (5)
C7—Sn1—C1—C6 −80.5 (2) C14—C13—C18—C17 52.6 (4)
O1—Sn1—C1—C2 48.1 (3) Sn1—C13—C18—C17 −179.3 (3)
C13—Sn1—C1—C2 −65.8 (3) C16—C17—C18—C13 −55.0 (5)
C7—Sn1—C1—C2 153.7 (2) Sn1—O1—C19—O2 8.5 (4)
C6—C1—C2—C3 54.2 (4) Sn1—O1—C19—C20 −167.07 (19)
Sn1—C1—C2—C3 −179.1 (3) O2—C19—C20—C21 −82.3 (4)
C1—C2—C3—C4 −56.4 (5) O1—C19—C20—C21 93.3 (3)
C2—C3—C4—C5 55.6 (5) C19—C20—C21—C26 80.1 (4)
C3—C4—C5—C6 −54.3 (5) C19—C20—C21—C22 −95.6 (4)
C2—C1—C6—C5 −51.3 (4) C26—C21—C22—C23 −1.9 (5)
Sn1—C1—C6—C5 −177.9 (3) C20—C21—C22—C23 174.0 (3)
C4—C5—C6—C1 52.2 (5) C21—C22—C23—C24 −0.6 (6)
O1—Sn1—C7—C12 −93.2 (2) C22—C23—C24—C25 2.7 (5)
C13—Sn1—C7—C12 31.4 (3) C22—C23—C24—C27 −176.8 (3)
C1—Sn1—C7—C12 167.3 (2) C23—C24—C25—C26 −2.5 (5)
O1—Sn1—C7—C8 32.0 (2) C27—C24—C25—C26 177.0 (3)
C13—Sn1—C7—C8 156.5 (2) C22—C21—C26—C25 2.1 (5)
C1—Sn1—C7—C8 −67.6 (2) C20—C21—C26—C25 −173.8 (3)
C12—C7—C8—C9 −52.0 (4) C24—C25—C26—C21 0.1 (6)
Sn1—C7—C8—C9 −179.4 (3) C25—C24—C27—C28 174.1 (4)
C7—C8—C9—C10 53.9 (5) C23—C24—C27—C28 −6.5 (5)
C8—C9—C10—C11 −55.2 (5) C25—C24—C27—C32 −6.1 (5)
C9—C10—C11—C12 55.6 (5) C23—C24—C27—C32 173.4 (3)
C8—C7—C12—C11 52.0 (4) C32—C27—C28—C29 0.2 (6)
Sn1—C7—C12—C11 176.3 (3) C24—C27—C28—C29 −180.0 (4)
C10—C11—C12—C7 −54.2 (5) C27—C28—C29—C30 −1.0 (7)
O1—Sn1—C13—C14 95.8 (2) C28—C29—C30—C31 1.7 (7)
C7—Sn1—C13—C14 −25.2 (3) C29—C30—C31—C32 −1.7 (7)
C1—Sn1—C13—C14 −161.1 (2) C30—C31—C32—C27 0.9 (7)
C7—Sn1—C13—C18 −152.0 (2) C24—C27—C32—C31 −179.9 (3)