The Modulatory Actions of FMRFamide and Related Peptides on Locust Skeletal Muscle
Full text
Figure
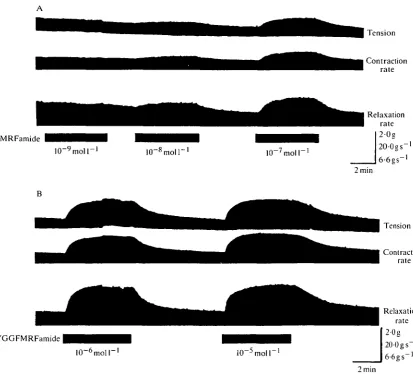
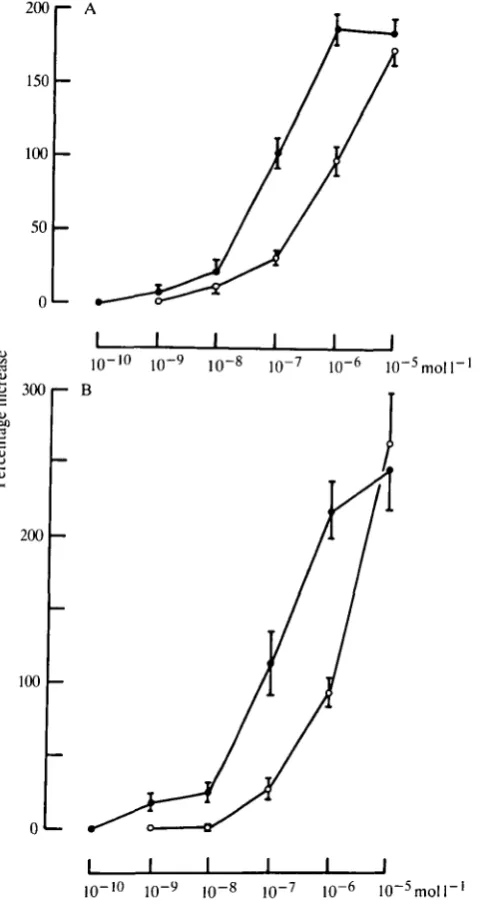
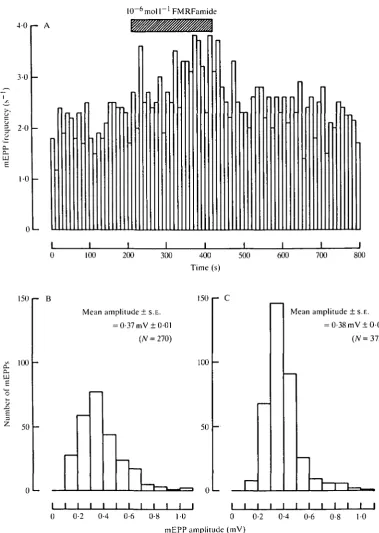
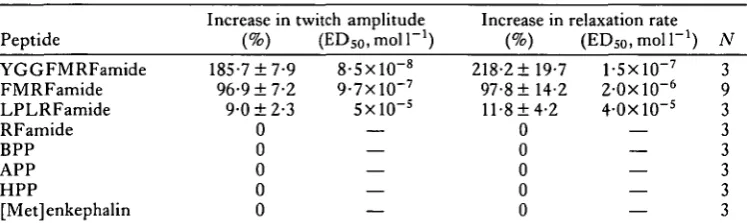
Related documents
The paper deals with Badaranj Boya- Nepeta hindostana herb a nutrimental potent ethnomedicinal plant and all the above ground parts are used in management of
While expression of SOCS1 both at mRNA and protein levels were significantly increased after miR-19a inhibitor treatment, compared to the NC group ( Figure 2D ).. ses were
The expression of NF-кB p65 and OPN protein and mRNA decreased significantly ( P < 0.05) after intervention with OPN siRNA in eutopic primary EECs.... liferative phase
In current study, we use MRC-5 cells, a fibroblast-like cell line in morphology, to document for the first time that cell proliferation and differentiation which pre-
12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid, represses human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by regulating cell death pathways via the mTOR
Abstract: Purpose: This study aimed to explore the effects of arsenic trioxide (As 2 O 3 ) on the growth and apoptosis of MBT-2 bladder cancer (BC) cells, and on T cell subgroup
However, the overex- pression of miR-212 significantly decreased ZEB2 protein levels in A549 cells, while inhibi- tion of miR-212 significantly increased ZEB2 protein
Conclusions: Significant differentiation in lipid profile and biochemical markers between all three groups shows that North Indian patients having T2DM and obesity are at higher