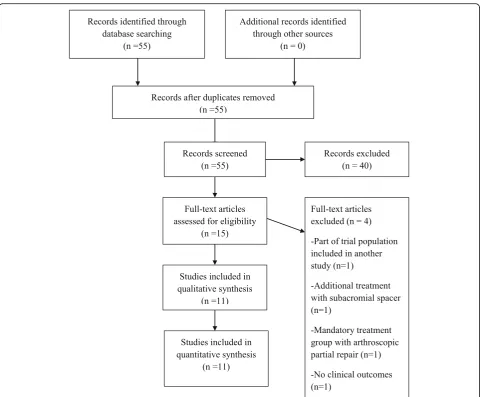
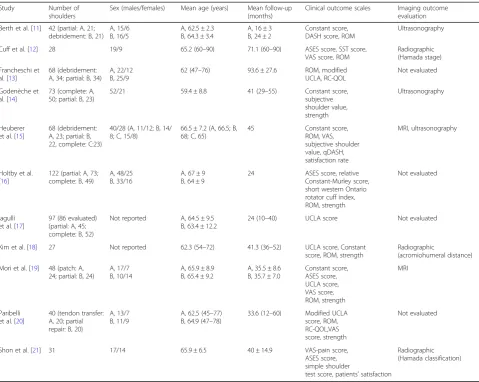
Arthroscopic partial repair for massive rotator cuff tears: does it work? A systematic review
Full text
Figure


Related documents
• Owners of properties served by septic tanks and other on-site waste water treatment systems would continue to operate without an appropriate inspection system and any directions
As a brief on the program in 2006 observed, “TCHC has provided continued support to the development of community gardens and food security initiatives in TCHC communities to
Both auto and life in- surance providers have more brand advo- cates in tier 3, tier 4, and tier 5 cities (which have smaller populations and less competitive insurance markets)
mation of the low‐level circulation by Hurricane Vince (October 8–11; Figure 9a) and the subsequent development of the anomalous low‐level cyclone over and
The result of experiments conducted on TPC-H data set and the real Twitter data set, demonstrates that (1) the join plan selected by AQUA outperforms the manually optimized
With regard to the remainder, your former employer has an obligation to withhold a level of tax from this payment but check too that if you have any additional tax liability on
Stephen is a member of the Association of Financial Advisers (AFA) and has completed the Advanced Diploma of Financial Services (Financial Planning)..
In a previous retrospective study including episodes of bacterial infection among patients with liver cirrhosis, a non-statistically significant trend toward a higher
