47
Performance Analysis Of Soliton Transmission For
Dispersion Management In Dwdm Optical
Systems
Gebrekiros Gebreyesus Gebremariam
Abstract: A soliton is a special form of light pulses that can be transmitted over long distances through fiber which maintains its shape. This work investigates the performance analysis of soliton transmission in dispersion managed DWDM optical fiber with base line of 32.68 mW power, 15 Gbps and 27.46 Km fiber length. The results show an improvement in Q-factor value for the system with soliton parameters compared to the system without soliton parameters. Also, the eye diagram obtained is best for the system with soliton parameters.
Keywords: dispersion management; Soliton transmission; WDM optical systems; Shape ofsoliton signal; BER; Q-Factor
————————————————————
1. INTRODUCTION
Communications is one of the sectors, which suffers comparatively milder recession. This recession is observed for the last several years in nearly all industries. Demand for new telecom services rises uninterruptedly together with intensive and broad introduction of optical technologies. A communication network commits transformation of information from one place to another.
1.1 WDM Technology
WDM increases the carrying capacity of the physical medium (fiber) using a completely different method from TDM. WDM assigns incoming optical signals to specific frequencies of light (wavelengths, or lambdas) within a certain frequency band.
1.2 Solitons
The soliton is a pulse that has the property of being able to propagate without alteration over extremely long distances by using mutual compensation of linear and nonlinear effects. A semiconductor laser is used to generate pulses in soliton mode.
1.3 Fiber Dispersion
In telecommunication the term of dispersion is used to describe the processes which cause that the signal carried by the electromagnetic wave and propagating in an optical fiber is degraded as a result of the dispersion phenomena. WDM in soliton based communication systems.
Figure 1: Dispersion in Optical fiber
2. Design and Implementation
In this section and multiple channels are modelled and simulated with and without soliton parameters.
2.1. NRZ Modulation
The system consists of a transmitter section with 15 Gbs/Sec Pseudo Random Bit Sequence Generator, laser diode as a light source and a Mach Zehnder Modulator, followed by an optical fiber link and a receiver section.
Figure 3: Simulation model for the system without soliton parameters.
2.2 Soliton System
It contains the following elements: (ABS) is the arbitrary binary sequence, its bit rate is 15Gbits/s and percentage of sequence is 80, (NRZ) is the binary NRZ encoder, its duty cycle is 5, (SOLT) is the soliton pulse converter, (MZM) is the Mach Zehnder, (OF) is the optical fiber with 27.46 km of length, factors of attenuation and dispersion are 0.2dB/km, 1.17 ps/nm/km, and receiver.
Figure 2: Block diagram of a single-channel using the soliton as an information carrier.
The bit sequence to be transmitted in our case, "010101010", modulates the stream of solitons resulting signal represents the transmission of information. The presence of a soliton gives the binary "1" and its absence provides the binary "0".
_______________________________
Gebrekiros Gebreyesus Gebremariam (M.Tech)
Email: Kiros2004comp@gmail.com
Under the guidance of Dr. Manjit Singh, Professor
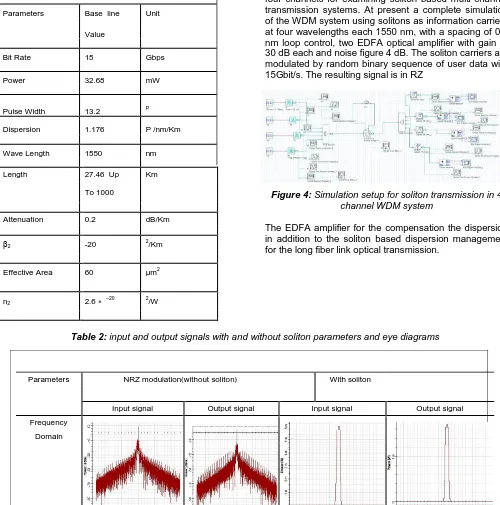
Table 1: Simulation parameters of soliton system.
Parameters Base line Unit
Value
Bit Rate 15 Gbps
Power 32.68 mW
Pulse Width 13.2 P
Dispersion 1.176 P /nm/Km
Wave Length 1550 nm
Length 27.46 Up Km
To 1000
Attenuation 0.2 dB/Km
β2 -20
2 /Km
Effective Area 60 µm2
n2 2.6 ∗ −20 2/W
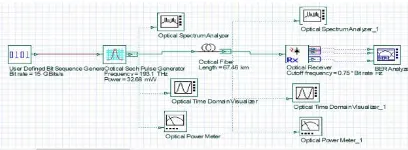
2.3 Soliton Transmission in Multichannel System format. The length of the optical fiber is 1000 Km using four channels for examining soliton based multi channel transmission systems. At present a complete simulation of the WDM system using solitons as information carriers at four wavelengths each 1550 nm, with a spacing of 0.4 nm loop control, two EDFA optical amplifier with gain of 30 dB each and noise figure 4 dB. The soliton carriers are modulated by random binary sequence of user data with 15Gbit/s. The resulting signal is in RZ
Figure 4: Simulation setup for soliton transmission in 4 channel WDM system
The EDFA amplifier for the compensation the dispersion in addition to the soliton based dispersion management for the long fiber link optical transmission.
Table 2: input and output signals with and without soliton parameters and eye diagrams
Parameters NRZ modulation(without soliton) With soliton
Input signal Output signal Input signal Output signal
49 Time
Domain
Eye Diagram
Q-factor
Graph With varying parameters
Result and Discussion
As shown from the above table the pulse without soliton parameter gets broadened and the power is reduced. The eye height of 0.000761205a.u is obtained for the system without soliton parameters. The system with soliton parameters an eye height of 0.0045068a.u is achieved. Thus, the eye opening is greater for the system with soliton parameters. Here, a Q-factor of 3.38225dB is achieved for the system without soliton parameters with a minimum BER of2.6*10-54. While, for the system with soliton parameters, a Q-factor of 806.05dBwith a minimum BER of 0 is obtained.
(a)
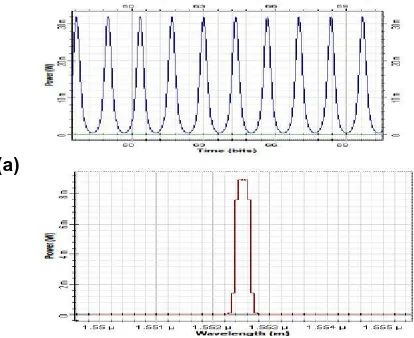
Figure 5:(a) input and (b) output signals channel1 of the multi soliton transmission for 1000km and GVD cancel out
each other.
This shows the presence of soliton which remains distortion less, because both SPM and GVD cancel out each other.
Figure 6:
eye diagram of channel one
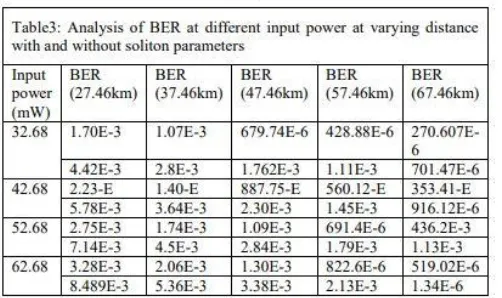
A spectrum analyzer at the receiver end gives the output power spectrum in the frequency domain and the time domain. The BER tester gives the BER for the input signals as well as a number of useful parameters such as the Q-factor and the properties of electrical eye. Table 4 shows the analysis of the BER of the single channel at varying input power and distance with and without soliton parameters. From the table it has been observed that the optimized value of BER is obtained as the distance increases with increase power. Similarly the table 5 consists of the Q-factor at different input power and
distance and it has been observed that the Q-factor value gets optimized as the distance increases with and without soliton parameters.
Conclusion
In this work, the performance analysis of solitons transmission in dispersion managed DWDM system is studied and it also compares the system with and without soliton parameters with varying these parameters. A soliton is a special form of light pulses that can be transmitted over long distances through fibre which maintains its shape. The Observation through Q factor, BER revealed that transmission has been bested performance for long distance optical communication system because of low Bit Error rate.
Acknowledgement
First of all, I would like to say thanks to GOD for blessing me with the spirit’s ability, courage and strength to prepare this work. I would like also to express my deepest gratitude thanks to my Supervisor,
Dr MANJIT SINGH, Professor,
department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, for his valuable continuous guidance. He is constant source of energy to me.
Reference
[1] H. Singh and M. Singh, ―Dispersion Management in Optical Soliton Transmission Systems: A Review,‖ Ijarcce, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 717–720, 2017.
[2] B. Pamukti, A. H. Ir, A. Dias, and P. St, ―SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS NONLINEAR EFFECTS ON DWDM LINK WITH MULTI SPACING AND MULTI LAMBDA USING SOLITON PULSE TRANSMISSION,‖ pp. 1–7.
[3] S. Subi and G. B. Lakshmi, ―Optical Solitons Simulation Using DSF and Optical Pulse Generator in Single Mode Optical Fiber,‖ vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 254–258, 2015.
[4] M. R. H. R. and R. B. Tamal Roy, Avijit Das, Sujan Howlader, ―Design and Performance Analysis of An,‖ vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 197–207, 2014.
[5] M. G. Patel and S. B. Khant, ―Soliton Transmission in Fiber Optics for Long Distance Communication,‖ Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electonics Instrum. Eng., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 7100–7107, 2014.
[6] B. Gupta, S. Kaur, and K. S. Bhatia, ―Simulative analysis of dispersion managed solitons for Long-haul optical communication system,‖ vol. 2, no. 10, pp. 3944–3949, 2013.
[7] R. Nagesh, R. Rajesh Mohan, and R. S. Asha, ―A Survey on Dispersion Management Using Optical Solitons in Optical Communication System,‖ Procedia Technol., vol. 25, no. Raerest, pp. 552–559, 2016.
51 Compensation with Dispersion Compensating Fibers
(DCF),‖ Ijarcce, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 354–356, 2015.
[9] X. Li, M. Wu, W. Zou, and S. Dai, ―Purified Dissipative Solitons with a Rectangle Spectrum from a Hybrid Mode- Locked Fiber Laser,‖ IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett., vol. 29, no. 19, pp. 1635– 1638, 2017.
[10] D. A. Dvoretskiy et al., ―Comb Peculiarities of Dispersion-Managed Solitons in a Hybrid Mode-Locked All-Fiber Ring Laser,‖ IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett., vol. 29, no. 18, pp. 1588– 1591, 2017.Continuous Spectrum of Nonlinear Optical Fibers,‖ J. Light. Technol., vol. 35, no. 11, pp. 2086– 2097, 2017.
[11] Vigneswaran and A. Mahendran, ―Study on 20 and 50 Gbps soliton transmission in conventional single mode
[12] S. M. Hosseini-Jenab and F. fiber (SMF),‖ 2014 Int. Conf. Control. Spanier, ―Kinetic Simulation Study of Electron Holes Dynamics during Collisions of Ion-Acoustic Solitons,‖ IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., vol. 45, no. 8, pp. 2182–2190, 2017.
[13] A. Sharma, ―Performance Analysis of 4 × 10Gb / s DWDM Soliton System Using Different Parameters,‖ pp. 17–24, 2016.
[14] B. Pamukti, ―Non-linear Effects of High Rate Soliton Transmission on DWDM Optical Fiber Communication System,‖ no. 1, pp. 26–30, 2016.
[15] S. K. Pavan, B. Mumey, and R. S. Wolff, ―Performance Evaluation of Soliton-Based and Non-Soliton All-Optical Wdm Systems.‖
[16] G. Borgese, S. Vena, P. Pantano, C. Pace, and E. Bilotta, ―Simulation, modeling, and analysis of soliton waves interaction and propagation in CNN transmission lines for innovative data communication and processing,‖ Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc., vol. 2015, 2015.
[17] I. Tavakkolnia and M. Safari, ―Capacity Analysis of Signaling on the Instrumentation, Commun. Comput. Technol. ICCICCT 2014, pp. 850–855, 2014.
[18] S. Bala, A. Sheetal, R. Campus, and R. Campus, ―SOLITONS : NOVEL APPROACH FOR
DISPERSION MANAGEMENT,‖ pp. 411–418, 2015.
[19] M. Singh and H. S. Saini, ―High Performance Soliton WDM Optical Communication System,‖ 2014 Fourth Int. Conf. Adv. Comput. Commun., no. 1834, pp. 20– 24, 2014.
[20] A. Y. Fattah and S. S. Madlool, ―Soliton Transmission in DWDM Network,‖ vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 28–36, 2017.
[21] N. Badraoui, T. Berceli, and S. Singh, ―Distortion
cancellation for solitons carrying high speed information in WDM systems,‖ Int. Conf. Transparent Opt. Networks, pp. 3–6, 2017.