International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
121
Triple Secured Hybrid Authentication Scheme
Salim Istyaq
Assistant Professor, Computer Engineering, University Polytechnic, Faculty of Engineering & Technology, A.M.U. Aligarh-202002, U.P.-India
Abstract—The use of password is to provide security and
protection to the user’s information. Graphical password authentication has been proposed as a possible alternative solution to text-based authentication, motivated particularly by the fact that humans can remember images better than text. In recent years, many networks computer systems and internet based environments try to use graphical authentication technique for their user’s authentication. Graphical passwords have two different aspects which are usability and security. In this paper, we have proposed a new hybrid graphical password based system, which is a combination of recognition and recall based techniques that offers many advantages over the existing systems and may be more convenient for the user. Our scheme is resistant to shoulder surfing and many other attacks on graphical passwords.
Keywords— Graphical Password, Authentication, Hybrid,
Biometric, and OTP.
I. INTRODUCTION
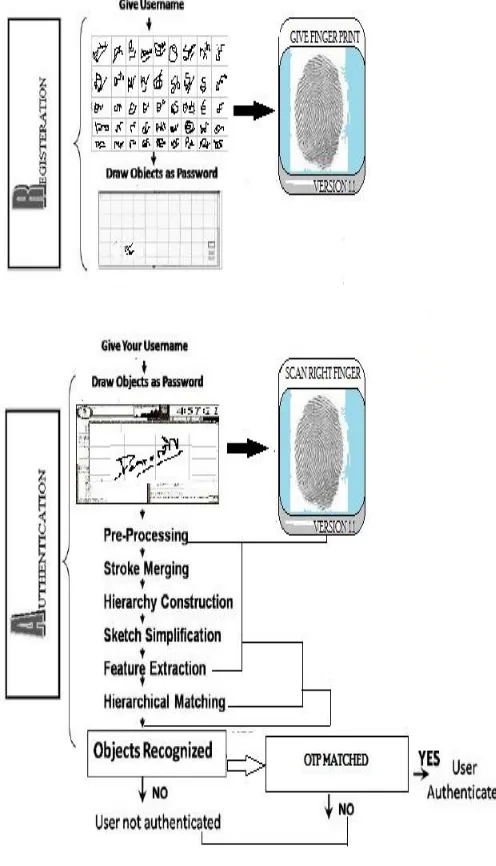
Graphical passwords [2] which are composed of pictures and are partially motivated by the fact that human can remember pictures more easily than a string of characters. The beginning of graphical password was introduced by Greg Bonder in 1996 [4]. Besides several advantages, there was a problem for the user through shoulder surfing as the onlooker can easily recognise the user password track and there will be a long duration to input in graphical sequence [5]. Sometimes the process of authentication in graphical passwords is slow which causes frustration in short tempered user [6]. In this paper, considering the problems of text based password systems and low security protection in small graphical schemes. We have proposed a new graphical password scheme which has desirable usability. Our proposed system has composition of hybrid technology that comprises (Biometric authentication, Graphical sketch Authentication, OTP recognition along with alphanumeric password) which is based on recall and recognition based technique and consisting of two phases. Registration phase, it comprises the registration of the user, the user is asked to give his/her username and password with mobile number which is used to identify the correct OTP at last step.
Afterwards the signature window is displayed, the users have to insert their signature template [7] along with biometric scan of finger, and this information is now saved on database. At the time of login phase the users now give their username along with passwords and then they draw the signature and scan their finger. If one of the identities is not matched then user has to be unauthorised for next process. After the matching of both the sketch and biometric, the proposed system generate the OTP and this OTP is recognised further through right users mobile and email id [8].
A.Methods of Authentication
The following are main methods of authentication:
a. Token based authentication. b. Biometrics based authentication. c. Knowledge based authentication.
Key cards, bank cards and smart cards are widely used as a token based authentication. They also use knowledge based techniques to enhance security [1]. For example, ATM cards are generally used together with a PIN number. Biometric based authentication techniques, such as fingerprints, iris scan, or facial recognition has been developed due to uniqueness properties of biometrics. These systems are the most secure way of authentication. The major disadvantage of this approach is that such systems can be expensive, and the recognition phase can be slow and often not dominant. Knowledge based techniques which are used mostly in all aspects mostly that include both text-based and picture-based passwords. The picture based techniques can be divided into two categories: recognition based and recall based techniques. Using recognition based techniques, a user is presented with a set of images and the user recognizing and identifying the images as he or she has already selected during the registration stage. Using recall based techniques, a user is asked to reproduce something that he or she created or selected earlier during the registration stage.
B.Classification of graphical password system
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
122 Recognition based techniques involve identifying whether one has seen an image before. It totally depends on the user presence of mind or the ability of thinking. The user must only be able to recognize previously seen images. Second is Pure Recall based systems which are also known as drawn metric Systems. In pure recall based methods the user has to enter some pattern that he/she enters in earlier phase (registration). Third is Cued Recall based systems which are also termed as Iconmetric Systems. In cued recall based methods a user is provided by a hint. Fourth is Hybrid systems which are typically the combination of two or more schemes. Like recognition and recall based or textual with graphical password [3] schemes.
Why Graphical Password?
Today, authentication [13] technology is the main measure to fulfill the protection in information security, and the most common and relevant authentication process is alphanumeric initials. GUA is a promising way to replace the existing trend of alphanumeric password. The main motivation lies with the fact that the human brain is capable of remembering graphical or pictorial objects better than texts, even psychological studies support such assumptions.
II. RELATED WORK
Graphical passwords were originally described by Blonder [4]. In their theory a screen is showing some image and the user have to click on some major regions that are correct. If the user is established to make the link with picture then the user is authenticated.
Graphical approach is a type of authentication module that works by having the user input on the image, on a correct order, presented in a graphical user interface (GUI) [10]. For this, the authentication approach in which photos or images are used as a key is generally known as graphical user authentication (GUA). Many techniques have been proposed in this field, since 1996.
Jansen [6] proposed a graphical system, which is good for mobile and small devices. During the registration time, a user choose a image that are composed of sea, cat, etc. which consists of tiles of photos and then registers a sequence of images as a password. For login in the system the user have to enter the images in the right sequence. Disadvantage of this technique is that, since the number of tiles is not extending to 30, the password space is little. Each tile image is given as a numerical set, and the sequence of choosing will generate a same numerical set.
Passface technique[9] as the name depicted that it is the technique which is basically worked on the recognition of faces from the set of the grids , here the grids contain the faces in which the correct face should be chosen in order to login on the system through this approach.
Syukri, et al. [7] proposed a first system which uses users signature for login on system. The user have to register his/her signature on a 2 d grid where it is saved on the database at the time of login the users draw their signature via mouse or by stylus. In the verification process the users input signature is matched with the signature in database by some geometrical distance etc.
Dhamija and Perrig [12] proposed a graphical authentication system which is based on the Hash Visualization technique. In their authentication system, user selects some images from a program that produce random pictures. In order to authenticate in the system he or she would have to identify the preselected images. One disadvantage of their system is that the server needs to store the seeds of the selected images of each user in plain text and it are also some time consuming to select the image from database.
III. PROPOSED WORK
Our proposed system works on the basis of following steps:
Step 1: The first step is to type the username and a textual password with correct mobile number and email id (in order to accept OTP), which is stored in the database. During authentication the user has to give the specific username and textual password in order to login.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
123 So, in this way the total combinations of each password
will be 2
n
–1, ‗n‘ being the number of objects selected by the user as password during the registration phase. But we just go ahead with 1 in our proposed system.
Step 3: At the time of authentication, the users make their signature as his password on a touch sensitive screen (or according to the environment) with a mouse or a pointer and scan their finger.
Step 4: The system performs preprocessing is occurred in this step.
Step 5: In this step the system gets input from the user as signature and merges the stroke in the users input.
Step 6: The system construct hierarchy after above steps taken successfully.
Step 7: At the end of the hierarchy construction, simplification of sketch is done.
Step 8: In the eighth step three types of features are extracted from the sketch drawn by the user.
Step 9: After that hierarchical matching is to be performed.
Step 10: The 10th step is to generate one time password on user email/mobile number.
Step 11: The last step is to enter the correct OTP.
[image:3.612.340.588.141.574.2]Graphical Representation of our proposed system is shown in Figure 1.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
124 At the time of registration the user enters the username and textual password and choose the given set of signatures as passwords (the length of password P=6). This password also contains the numbers, alphabets and symbols. After this, system shows signature on the screen to set as a graphical password [14]. We have to choose the signature, the system is also asked to scan any of the fingers at the same time, this scanned finger print goes to the biometric database also, along with the universal information of the user, and then the user draws the signatures on a screen with a mouse. Flow chart of registration phase is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Registration phase
During authentication process, the user has to first give his initials i.e. username and textual password. Afterwards draw the selected signature, the signature is now matched with the template of all the signatures stored in the database. At the same time the users have to scan their finger on the biometric which will parallel processed as signature with the stored finger scan of the particular user. The authentication system phases like the preprocessing, stroke merging, hierarchy construction, sketch simplification, feature extraction, and hierarchical matching are the steps proposed by wing ho leung and tushan chen [11]. The user will be authenticated if the drawn signature is matched successfully with the selected signature template stored in the database along with right biometric scan and right OTP entered. This hybrid system [15] is a mixture of both recognition and recall based schemes. Our proposed system is an approach towards more reliable, secure, user-friendly, and robust authentication, by giving the 3 ways more hybridized security methods i.e. by using biometric, hand drawn sketches and OTP. We have also reduced the shoulder surfing problem to some extent.
We have introduced some methods for noise reduction in our paper this is because when we draw the signature there will be some extended humps and elongated lines. These cause noise in actual template. Various techniques exist to reduce the noise like as smoothing, filtering etc. In our paper, we approach the Gaussian smoothing to reduce noise that comes in drawing on touch sensitive screen.
Or in 2-D.
r= BLUR RADIUS (r2 = u2 + v2)
σ =STANDARD DEVIATION. (Gaussian distribution)
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
[image:5.612.333.562.134.516.2]125 Figure 3: 3- phases of biometric
The steps that come in our process are further discussed below:
Stroke merging: In this phase broken stroke in sketch (signature) are fixed at the end points, .if the end points in a sketch are not too close then they are considered as open stroke.
Hierarchy construction in this phase strokes are presented in hierarchy for other phases for simplification and make it meaningful.
Sketch simplification in this step single hyper stroke is done for shaded region.
At the end, feature extraction takes place in which three types of feature extraction phases are placed Bi-stroke, stroke, and hyper stroke features. Finally, hierarchical matching of all the phases are calculated and simplified at the end of biometric scan and signature matched successfully, the system send the OTP to the legal user‘s phone and user can easily type the OTP and authorize in system.
[image:5.612.71.260.144.312.2]Figure 4: Authentication Phase
IV. COMPARISON OF PROPOSED SYSTEM WITH EXISTING
SCHEMES
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
126 There is no harm from online and offline attacks as we are using mouse to draw our signature. According to Van Oorschot‘s approach, our system is resistant to attack by hackers as we use graphical (signature) passwords [16]. Therefore, it is more difficult to crack. If it is possible in any situation, the user now has challenge to pass with biometric and then with OTP which will send again on verified user phone or email. As compared to all graphical based systems, our system will also be slow. The normalization and matching will take time. An important issue of our system is that it is somewhat user dependent during authentication. It depends upon the user‘s drawing ability.
V. RESULT ANALYSIS
At the time of login on the system, the user can draw his own signature template in the same order as he chooses at registration time, therefore total combinations of each password will be (2^n -1).
Where n = number of signature template selected by the user as password.
Results show that graphical authentication has a high accuracy and it is mostly likely to replace text-based methods in the upcoming time. Even today, we can observe in latest OS versions and software, graphical password is too common. We also recognize in android, windows or apple based mobile phones some type of swipe or pattern password takes place in these devices. So, with the advancement in technology mainly in touch based technology, graphical authentication plays a very promising role for various authentications in such devices or gadgets. Graphical based passwords are less vulnerable to all these possible attacks than text based passwords and they believe that it is more difficult to break graphical passwords using these traditional attack methods. Our System is resistant to almost all the possible attacks on graphical passwords. The comparison of our system to existing schemes and systems in resisting attacks on graphical passwords as shown in figure 5.
VI. CONCLUSION
The basic aim of the computational trust is identity. Currently there are many password schemes running all around the world but all have some advantages and loop holes. There is a growing interest in using pictures as passwords rather than text passwords but very little research has been done on graphical based passwords so far.
[image:6.612.340.547.289.515.2]In view of the above, we have proposed authentication system which is based on very complex and very secured schemes that provide major security and protection through the means of 3 ways security i.e. 1-Graphical Password 2- Biometric 3-OTP generates alphanumeric password. Although our system aims to reduce the problems with existing graphical based password schemes but it has also some limitations and issues like all the other graphical based password techniques. To conclude, we need our authentication systems to be more secure, reliable and some other important things regarding the performance of our system will be investigated like User Adoptability, Usability and Security of our system.
Figure 5: Different system vulnerabilities
REFERENCES
[1] William Stallings and Lawrie Brown. ―Computer Security: Principle and Practices." Pearson Education, 2008.
[2] L.Sobrado and J.C. Birget, ―Graphical Passwords‖, The Rutgers Schloar, An Electronic Bulletin for Undergraduate Research,Vol 4, 2002,http://rutgersscholar.rutgers.edu/volume04/sobrbirg/ sobrbirg. htm.
[3] Patric Elftmann, Diploma Thesis, ―Secure Alternatives to Password-Based Authentication Mechanisms‖ Aachen, Germany October 2006.
[4] G. E. Blonder, "Graphical passwords," in Lucent Technologies, Inc., Murray Hill, NJ, U. S. Patent, Ed. United States, 1996.
[5] Xiayuan Suo, Ying Zhu, G. Scott. Owen, ―Graphical Passwords: A Survey‖, in Proceedings of Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, 2005.
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering
Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN 2250-2459, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016)
127 [7] A. F. Syukri, E. Okamoto, and M. Mambo, "A User Identification
System Using Signature Written with Mouse", in Third Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy (ACISP): Springer Verlag Lecture Notes in Computer Science (1438), 1998, pp. 403-441.
[8] Salim Istyaq and Lovish agrawal ―A New Technique For User authentication Using Numeric One Time Password Scheme‖ in International Journal Of Computer Sciences and Engineering (IJCSE), Volume-4, Issue-5, E-ISSN: 2347-2693 on 31 May-2016, pp. 163-165.
[9] Passfaces Corporation, The Science behind Passfaces, White paper, http://www.passfaces.com/enterprise/resources/white papers.htm. [10] Sannella, M. J. 1994 Constraint Satisfaction and Debugging for
Interactive User Interfaces. Doctoral Thesis. UMI Order Number: UMI Order No. GAX95-09398., University of Washington. [11] Wing Ho Leung and Tsuhan Chen, User-independent Retrieval of
free-form hand-drawn sketches. In proc. of the IEEE ICASSP ‘02, volume 2, pages 2029-2032, Orlando, Florida, USA, May 2002, IEEE Press.
[12] Rachna Dhamija and Adrian Perrig, ―Deja Vu: A User Study. Using Images for Authentication‖ in Proceedings of the 9th USENIX Security Symposium, August 2000.
[13] Mohammad Sarosh Umar and Mohammad Qasim Rafiq, ―A Novel Graphical Interface for User Authentication on Mobile Phones and Handheld Devices‖, International Journal On Advances in Intelligent Systems, volume 4, numbers 3 and 4, pp 380 to 387, 2011 (IARIA Journals) Publication Date April 30, 2012.
[14] Salim Istyaq, ―A New approach of Graphical Password with Integration of Audio Signature Combination of Recall and recognition‖ in International Journal of Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology Research (IJCSEITR), ISSN(P): 2249-6831; ISSN(E): 2249-7943 Vol. 6, Issue 4, Aug 2016, 45-50.
[15] Wazir Zada Khan, Mohammed Y Aalsalem and Yang Xiang, ―A Graphical Password Based System for Small Mobile Devices‖ in IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 8, Issue 5, No 2, September 2011 ISSN (Online): 1694-0814. [16] Partha Pratim Ray, ―Ray‘s Scheme: Graphical Password Based