COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS
OF SHORT NEUROPEPTIDE F FROM
TRIBOLIUM CASTANEUM.
*Somnath Waghmare1, Manjit Singh Arora1, Anant Sherkhane2 and Viren Gomase2
1
Department of Zoology, Nowrosjee Wadia College of Arts and Science, Pune-411001, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
2
The Global Open University, Nagaland.
ABSTRACT
In the present study annotating and analysing the function of neuropeptide F from Tribolium castaneum is done. The Tribolium castaneum which is a cosmopolitan pest of stored products. Sequence
of Neuropeptide F protein was retrieved from Uniprot and analysed for their structural and functional characteristics by using various bioinformatics tools and database. Subcellular localization prediction suggested that it is a cytoplasmic protein. Furthermore, it was discovered that Neuropeptides and neuro hormones are among the more diverse and functionally important classes of cell-to-cell signaling molecules involved in animal development and behavior. Less is known about the hormones and neuropeptides F of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum, than many other insects. The secondary structural prediction of those proteins has been done which would be useful for further analysis of this protein.
KEYWORDS: Tribolium, Neuropeptide F, Secondary structure, etc.
INTRODUCTION
For the stored product the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) is a cosmopolitan pest. By feeding externally on both grains and processed food both the larvae and the adults cause the devastating damage. Adult beetles produce a foul odour from secreted quinones and hydrocarbons and turn flour light pink. The viscosity
and elasticity of flour can be adversely affected by enormous infestation. Tribolium
Volume 3, Issue 10, 1235-1244. Research Article ISSN 2277– 7105
Article Received on 10 October 2014,
Revised on 02 Nov 2014, Accepted on 25 Nov 2014
*Correspondence for
Author
Dr.Somnath Waghmare
Department of Zoology,
Nowrosjee Wadia
College of Arts and
Science, Pune-411001,
Savitribai Phule Pune
University, Pune,
infestation can also cause contamination in the form of dead animals and exuviae and depletion of the nutritive value of the medium (Aftab Hussain 1994).
An important role in the physiology of insects is played by neuropeptides, protein hormones, biogenic amines and their G protein ‐coupled receptors (GPCRs), because they steer central processes, such as feeding, reproduction, and development. Nearly 50 neuropeptide and protein hormone genes have presents in the insects. The wide range of behaviors and
physiological functions of insects are affected by neuropeptides and hormones which are the signalling molecules; for example, in arthropods the molting process, which is essential for the growth and maturation of the organism is modulated by these neuropeptides and hormones (Hesterlee 1996). While in platyhelminthes nervous systems Neuropeptide F (NPF) protein is an abundantly expressed neuropeptide and exhibits a moderate,myogenic effect on muscle preparations of parasitic flatworms. (Gomase et.al., 2009)
The peptides of the sNPF family appear to be implicated in a wide range of processes, including locomotor activity [Kahsai 2010] and circadian rhythms [Johard 2009], their main function appears to lie in the regulation of feeding behaviour.
Methodology
Protein retrieval and sequence analysis: The protein sequence of Triboliun castenium short
neuropeptide F protein (101 AA) was retrieved from Uniprot Knowledgebase database using accession No. D6X455. Physiochemical properties of the protein were computed by ProtParam tool (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/). The parameters computed by ProtParam included the molecular weight, theoretical pI, amino acid composition, atomic composition, extinction coefficient, estimated half-life, instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY). Subcellular localization of any protein is important understanding protein function. Prediction of subcellular localization of protein was carried out by CELLO v.2.5 [Yu C. S. 2006, 2004].
Secondary structure prediction
PredictProtein tool was employed for computing and analyzing the secondary structural
& Roux used to calculate profile of Neuropeptide F . Secondery structure prediction also predicted using GOR method
Seq2Logo is a web-based sequence logo method for construction and visualization of amino acid binding motifs and sequence profiles including sequence weighting, pseudo counts and two-sided representation of amino acid enrichment and depletion (Martin Christen, 2012).
Prediction of transmembrane proteins
SOSUI server is used to characterize whether the protein is soluble or transmembrane in nature (Web)
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In present study was to perform sequence and structure analysis of Triboliun castenium (Fig 1) short neuropeptide F protein (101 aa) (Fig. 2) was retrieved from Uniprot Knowledgebase database using accession No. D6X455.
Protein sequence analysis
ProtParam was used to find out the physiochemical properties from protein sequence. The hypothetical protein was predicted to have 101 amino acids, with molecular weight of
11273.9 Daltons and theoretical isoelectric point (PI) of 7.74. Total number of negatively harged residues (Asp + Glu): 11, Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 12
The instability index (II) is computed to be 55.32. This classifies the protein as unstable. The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met). The estimated half-life is: 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro) >20 hours (yeast, in vivo) >10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo). The negative Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) of -0.246 indicates that the
protein is hydrophilic and soluble in nature.
The study of subcellular localization is important for elucidating of the protein functions
Fig. 1. Larva and Adult of Triboluim castenium
Fig. 2. short neuropeptide F protein Triboluim castenium
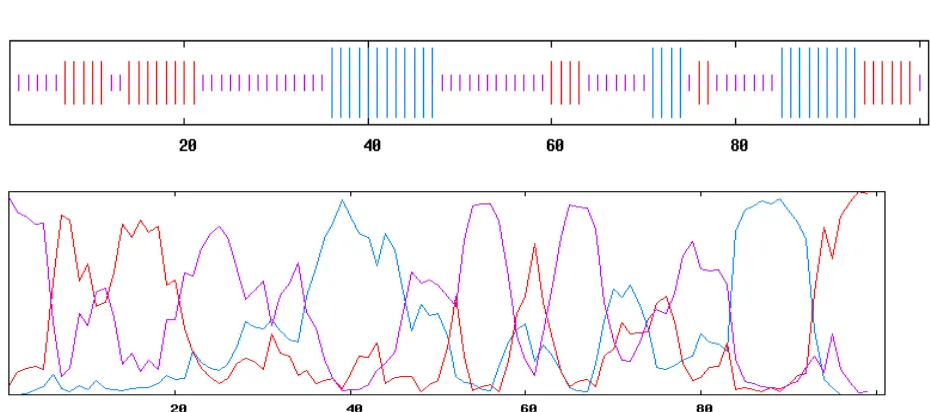
[image:4.595.148.444.518.690.2]Fig.4.ProtScale Hphob. / Abraham & Leo profile of Neuropeptide F
Fig.5 ProtScale alpha-helix / Deleage & Roux profile of Neuropeptide F
Fig.7 ProtScale beta-sheet / Deleage & Roux profile of Neuropeptide F
Fig.8 ProtScale Coil / Deleage & Roux profile of Neuropeptide F
Sequence length : 101 GOR4 :
Alpha helix (Hh) : 25 is 24.75% 310 helix (Gg) : 0 is 0.00%
Other states : 0 is 0.00%
Fig. 9 GOR analysis of short neuropeptide F from Tribolium castenium
This amino acid sequence is of a MEMBRANE PROTEIN which have 1 transmembrane helix. 6 N terminal transmembrane region AMKCLCAVTCIMIVVATVTSAAP while C terminal 28 type Primary length 23. Average of hydrophobicity : -0.245545
DISCUSSION
The physicochemical properties of neuropeptide F were calculated. The calculated isoelectric point (pI) will be useful because at pI, solubility is least and mobility in an electro focusing system is zero. Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the surface of protein is covered with charge but net charge of protein is zero. At pI, proteins are stable and compact. The computed isoelectricpoint (pI) will be useful for developing buffer system for purification by isoelectric focusing method. Although Expasy’s Protparam computes the extinction coefficient for 276,
278, 279, 280 and 282 nm wavelengths, 280 nm is favored because proteins absorb light strongly there while other substances commonly in protein solutions do not. Extinction coefficient of Neuropeptide F proteins homologue at 280 nm is 10095 assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines.
The high extinction coefficient of Neuropeptide F indicates presence of high concentration of Cys, The computed extinction coefficients help in the quantitative study of protein–protein
method assigns a weight value of instability.Using these weight values it is possible to compute an instability index (II). A protein whose instability index is smaller than 40 is predicted as stable, a value above 40 predicts that the protein may be unstable [18]. The instability index value for the neuropeptide F proteins was found to be 55.32.Hence the protein neuropeptide F is unstable.
The aliphatic index (AI) which is defined as the relative volume of a protein occupied by aliphatic side chains (A, V, I and L) is regarded as a positive factor for the increase of thermal stability of globular proteins. Aliphatic index for the neuropeptide F proteins sequencesis 68.71.The very high aliphatic index of the protein sequences indicates that these proteins may be stable for a wide temperature range. The lower thermal stability of proteins was indicative of a more flexible structure when compared to other protein. The Grand Average hydropathy (GRAVY) value for a neuropeptide F is calculated as the sum of hydropathy values of all the amino acids, divided by the number of residues in the sequence. GRAVY indices of hypothetical proteins is -0.246. This low range of value indicates the possibility of better interaction with water.
Functional analysis of these proteins includes protein domains and family prediction and prediction of trans-membrane regions. The neuropeptide F was found to be extracellular in nature in this study.
For the conformational and structural analysis we also determined solvent accessible surface activity of short neuropeptide F from Tribolium castenium (Fig. 3-8)
The GOR method is based on information theory GOR IV, uses all possible pair frequencies within a window of 17 amino acid residues. The results of GOR shows H=helix, E=extended or beta strand and C=coil; the second gives the probability values for each secondary structure at each amino acid position. The predicted secondary structure is the one of highest probability compatible with a predicted helix segment of at least four residues and a predicted extended segment of at least two residues (Fig.9)
CONCLUSION
database and characterized its physicochemical properties and identified domains and families using various bioinformatics tools and databases. This also would provide useful solution for drug discovery for neuropeptide F proteins which were involved in central processes, such as feeding, reproduction, and development of harmful insect Tribolium castenium.
REFERENCES
1. Aftab Husain (1994) Chemical ecology of tribolium castaneum herbst (coleoptera: tenebrionidae): factors affecting biology and application of pheromone. By aftab hussain a thesis submitted to oregon state university june 1994.
2. Hesterlee S, Morton DB. Insect physiology: the emerging story of ecdysis. Curr Biol 1996; 6: 648–50. [PubMed: 8793284.
3. Kahsai L, Martin JR, Winther AME (2010) Neuropeptides in the Drosophila central complex in modulation of locomotor behavior. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2010; 213: 2256–2265. [PubMed]
4. Johard HAD, Yoishii T, Dircksen H, Cusumano P, Rouyer F, et al. (2009) Peptidergic Clock Neurons in Drosophila: Ion Transport Peptide and Short Neuropeptide F in Subsets of Dorsal and Ventral Lateral Neurons. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2009; 516:
59–73. [PubMed]
5. Martin Christen, Frolund Thomsen, Morten Nielsen (2012) Seq2logo: a method for construction and visualization of amino acid binding motifs and sequence profiles including sequence weighting, pseudo counts and two-sided representation of amino acids enrichment and depletion., Nucleic Acid Research doi:10.1093/nar/gks 649.
6. Yu C. S., C. J. Lin, J. K. Hwang (2006). Predicting Subcellular Localization of Proteins for Gram-negative Bacteria by Support Vector Machines based on n-peptide Compositions, Protein Science, 2006; 13: 1402-1406.
7. Yu C. S., Y. C. Chen, C. H. Lu, J. K. Hwang (2004). Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization, Proteins: Structure, Function and Bioinformatics, 2004; 64: 643-651. 8. Rost B., G. Yachdav, J. Liu (2004). The PredictProtein Server, Nucleic Acids Research,
32(Web Server issue), W321-W326.
10.Virendra S Gomase, Somnath B Waghmare, Baba Jadhav, Karbhari V Kale. (2009):- Functional analysis of the binding ability of Neuropeptide F (NPF) from Moniezia expansa. Gene Therapy and Molecular Biology. [Imp Factor- 2.704], Vol. 13. 64-70 11.J. Garnier, J.-F. Gibrat, B. Robson- GOR secondary structure prediction method version
IV, , Methods in Enzymology,R.F. Doolittle Ed., Vol 266, 540-553, (1Q1ED996)