Original Article Gender differences of risk factors for early gastric cancer with lymph node metastasis
Full text
Figure

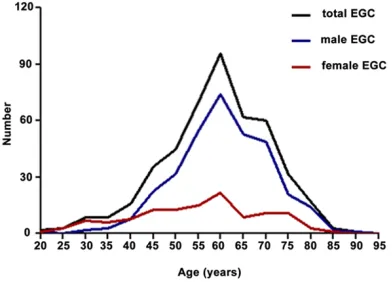
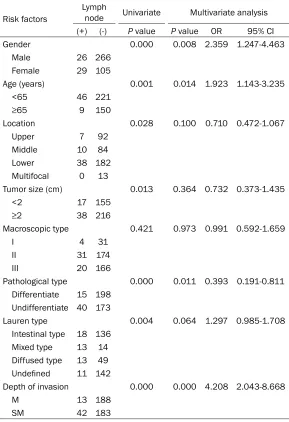

Related documents
In the study by Viale et al., multivariate analysis also showed that tumor size, the number of tumors and SLN positive rates were independent risk factors for axillary
Age <45 years, larger tumor (>5 mm) and multifocality were predictors of LNM; age <45 years, larger tumor size and absence of concomitant thyroiditis were associated
In conclusion, our results show that miR-378 is frequently downregulated, and decreased expression of miR-378 is associated with de- ep tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis,
Univariate prognostic factor analysis focusing on this group of 156 NEN cases revealed that the prognostic factors included tumor stage, grade, depth of invasion, tumor
Univariate analysis showed that there was statistically significant difference ( P < 0.05) in terms of postoperative survival condition for patients with LNM of thoracic ESCC
Abstract: This study aims to study the values of computed tomography (CT) perfusion enhancement parameters (CT-PEPs) in predicting lymph node metastasis (LNM) of lung cancer.. A
A: Gender; B: Lauren type; C: Tumor differentiation; D: Lymph node metastasis; E: TNM stage; F: OS in GC patients... Sensitivity analyses in
Age, tumor location, lymph node status and positive levels of the neuroendo- crine marker CgA are independent risk factors that affect the prognosis of