Our Neural Machine Translation Systems for WAT 2019
Full text
Figure
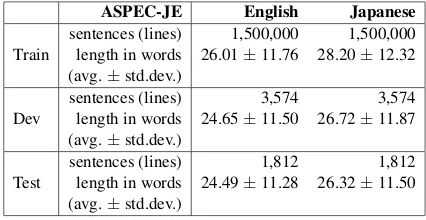
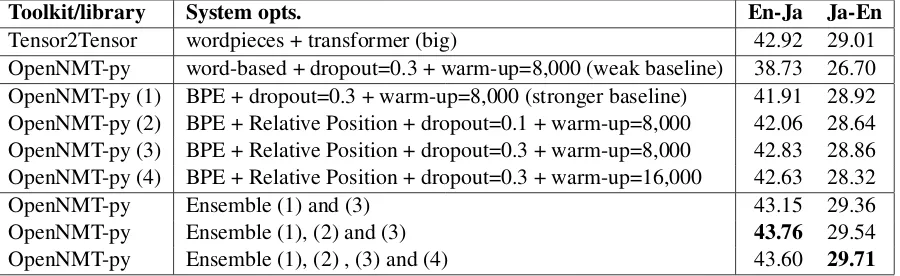
Related documents
We train LSTM-based Chinese and English language mod- els on these monolingual data sets, as well as a big Transformer-based Chinese → English transla- tion model on the 18.9M
In the case of Japanese → English task with JIJI Corpus and Equivalent-JIJI Corpus, the origin of the target-side English sentences differs between the two corpora (JIji Press news
2 A trustable baseline for neural GEC In this section, we combine insights from Junczys- Dowmunt and Grundkiewicz (2016) for grammati- cal error correction by phrase-based
(2015) that combining the baseline features with those obtained from external sources of bilingual information provide a noticeable im- provement, in this case, not only for
On the English-Italian data from the IWSLT 2017 shared task (Cettolo et al., 2017), the best of our models achieves a 2.3% increase in BLEU score over a baseline Transformer
We report the accuracy on each individual test set, including the following comparison scores: a baseline of the most frequent class; a bag-of-vectors baseline obtained by