Reverse immunodynamics : a new method for identifying targets of protective immunity
Full text
Figure
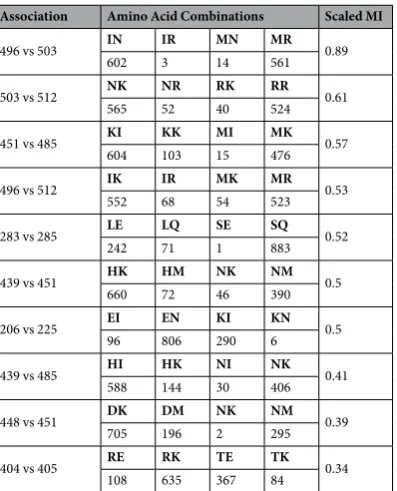
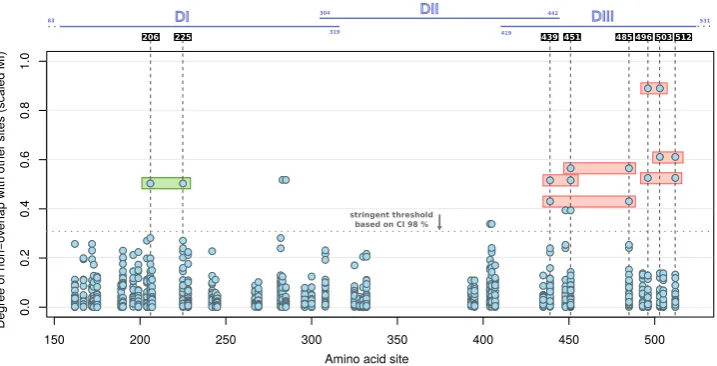


Related documents
Thus the proposed decision – making function can be formulated as follows: a variable of state representing a decision taken by a manager of an international enterprise is
“Development of Sequence Characterized Amplified Region (SCAR) markers for the identification of popularly used five bark drugs ‘ Panchavalkala ’
The narrow and uniform pore size of mesoporous transition metal oxide materials. (M = Ti, Nb, Ta) with variable oxidation states and high surface area holds
If we assume that the R1 stock possessed many hereditary factors with potentiality for resistance and for susceptibility as well, as evidenced in part by the
Results: The HR programmed cell death initiated by a bacterial type III secretion system dependent proteinaceous elicitor harpin (from Erwinia amylovora ) can be reversed till
Testing the hypothesis: We applied our previously published mathematical heterogeneity model to decipher tumor heterogeneity through the analysis of genetic copy number
Objective: bPeaks is a peak calling program to detect protein DNA-binding sites from ChIPseq data in small eukary- otic genomes.. The simplicity of the bPeaks method is
Using a MALDI-TOF score cut off value of ≥ 1.700 and top three results matching for species level identifica- tion gave reliable organism identifications from 72% of