CT of parotid tumors
Full text
Figure

Related documents
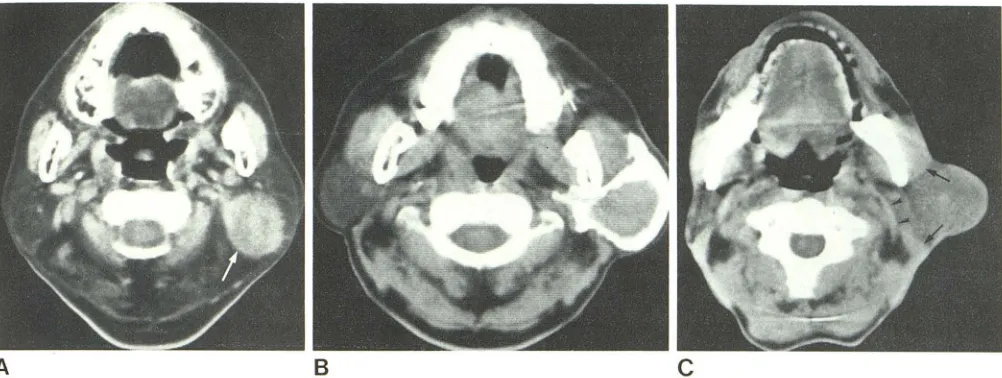
The CT features of parotid oncocytomas in the largest imaging series of this rare but important benign lesion include a well-defined enhancing tumor with a “deform- able”
L.: Relations of Superficial and Deep Lobes of Parotid Gland to Duct and Facial Nerve. Fine-needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of parotid lesions,
Primary malignant melanomas of parotid gland (PMMP) are relatively unusual, representing 0.68% of all malignant neoplasms of parotid gland, despite the fact that 25% to 35% of
Therefore, mean ADC could be used to distin- guish between the parotid tumor-like BLEL and parotid MALT lymphoma and other primary benign parotid gland tumors.. However, at b =
malignancies. Treatment of malignant neoplasms of the parotid gland. Management of the neck in parotid carcinoma. Conservation parotidectomy by the peripheral app-.
In the case of accessory parotid tumor, Stensen’s duct tumor, intramasseter hemangioma, the anterior extension of main parotid gland tumor, sialolithiasis and heterotopic salivary
Conclusions: Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common parotid gland tumor and superficial parotidectomy with preservation of the facial nerve is the most common and appropriate
Classic literature has tended to suggest that benign tumours are more common than malignant tumours, particularly when referring to primary salivary gland tumours of the