Feeding studies of radiation sterilization ready to eat foods on sprague dawley rats: In vivo
Full text
Figure


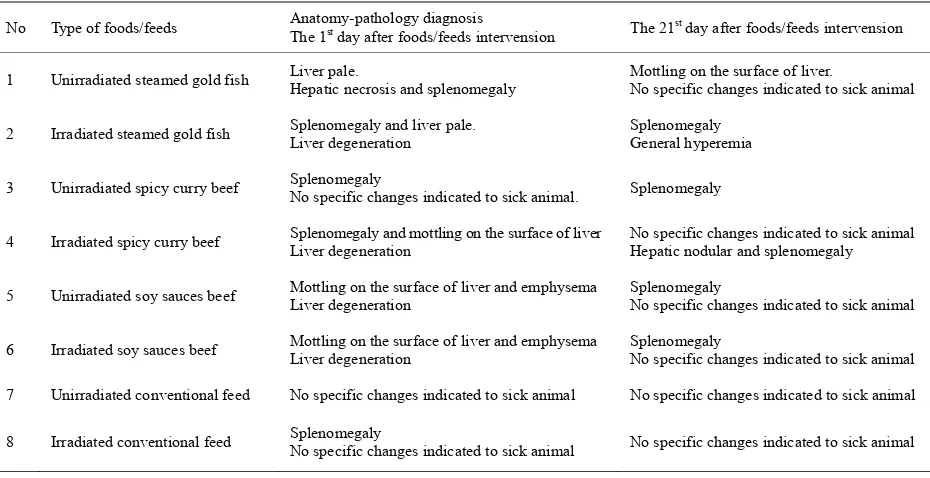
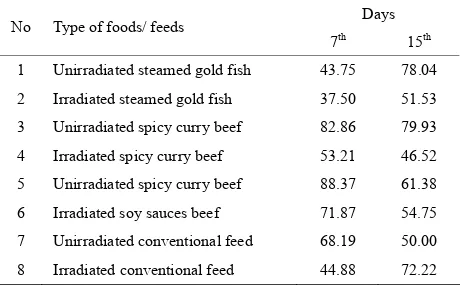
Related documents
The dummy variable’s coefficient is positive and statistically significant at 5%, suggesting that the global financial crisis had a positive impact on short-term debt levels used
On the Saudi Gulf coast the major environmental effects of coastal and marine use.. are concentrated in and around, Jubayl and
From this point on the approximation error can still be reduced by increasing the sampling density, but this is attributed to the fact that the random sampling errors
This work has been used to determine Plasma levels of Haptoglobin, Complement C3 and C4 in Plasmodium infected children presenting with hypoglycemia which revealed
Those with children with attenuated phenotypes reported limited impact on breathing, hearing or mobility into adoles- cence whilst those with more severe Hurler ’ s phenotypes
significantly increased BS/BV and Tb.Sp in rats from the CSD group compared with those of the CON group ( P < 0.05), suggesting that rats from the CSD group had lower bone mass
In summary, the present study showed that goal-directed transfusion protocol via TEG was feasible in patients with abdominal trauma, and was better than conventional trans-
In the MetaPlus study, immune-modulating high-pro- tein (IMHP) enteral feeding enriched with glutamine, fish oil and antioxidants was compared with standard high- protein (HP)