Periodic Safety Review for Seismic Qualification of Equipment in Korean
Operating Nuclear Power Plants
Kwangho Joo1), Woosang Lim1)
1) PSR Performance Assessment Team, Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co.
ABSTRACT
According to the enforcement decree of Korean Atomic Energy Act, the Periodic Safety Review (PSR) should be
performed for nuclear power plants in operation every 10 years. The scope of PSR applicable to nuclear power plants
operating in Korea is based on 11 safety factors recommended by the IAEA including a review for seismic qualification
of equipment in nuclear power plants. The following units are completed: PSR of Kori unit 1 in May 2000, the PSRs of
Wolsong unit 1, Kori units 2, 3, 4, and Yonggwang units 1, 2, 3, 4. At present, the PSRs of Ulchin units 1, 2 and
Wolsong unit 2 are under processing and the PSRs of Ulchin units 3, 4 and Wolsong units 3, 4 will be started. Over half
of all nuclear power plants operated in Korea have been reviewed and lots of experience have been accumulated through
the PSRs. The purpose of PSR is to assure the safety of the nuclear power plants. In this paper, the present status of
seismic PSR in Korea is introduced including corrective actions for safety improvements
INTRODUCTION
The equipment related to the safety of nuclear power plant must be designed and manufactured so that its safety
function does not malfunction during normal operation and even when natural disasters such as earthquake occur.
Therefore, we have checked whether the seismic qualification has been adequately performed for the nuclear power plant
according to the PSR legal requirements. The seismic qualification safety factors required for the PSR are evaluated for
the purpose of checking if the safety related equipment of nuclear power plant adequately performs the intended function
during its service life and especially during the design basis earthquakes.
The enforcement regulation requires the evaluation of six (6) items in relation to equipment qualification of the
environmental qualification and the seismic qualification[1]. The PSR guide prepared by the IAEA also defines how the
equipment qualification evaluation works[2,3]. They are to check and evaluate whether the equipment qualification
master list and its administrative procedures of the equipment qualification plans are available, equipment qualification
method and quality assurance activities are appropriate, analysis of the impacts of equipment functional failure on the
qualification is sound, countermeasure plans to protect the qualified equipment from harsh environment are available,
physical condition and functionality are appropriate and qualification documents prepared when the equipment was
installed or operated are appropriately kept in a place or maintained up to date.
In this regard, we have checked all the technical standards in the Final Safety Analysis Report (FSAR) applicable
to the nuclear power plants under operation, and surveyed the site-specific technical standards such as administrative
actions and regulatory actions, taken by the regulatory body, and the owner's commitments. Because the applied technical
standards and all the detailed technical standards, related to the performance of seismic qualification, should be effective
and valid for the PSR of seismic qualification. We have also evaluated if the equipment, classified as seismic category I
class, is safe against earthquakes and adequately performs the intended function based on these effective technical
power plants. In addition, we have reviewed the qualification documents, performed the walk-down and prepared for
safety improvement plans required for assuring the seismic safety of each nuclear power plant.
SCOPE
The equipment to be evaluated for the seismic qualification must be normally operated during or after earthquakes.
The details of safety requirements for classifying, selecting and designing the system and equipment belonging to seismic
category I class are stated in the chapters 3.2, 3.9, 3.10 and 3.11 of FSAR.
The items required for the seismic qualification of equipment are stipulated as follows in the clause 19.2.3 'details
of periodic safety review' of enforcement regulation of Korean Atomic Energy Act:
Master list and administrative procedures of qualified equipment ●
Method of equipment qualification and quality assurance ●
● Analysis of equipment failures influencing the qualification
Monitoring the environmental condition of qualified equipment ●
Physical condition and functionality of qualified equipment ●
Maintenance records of qualified equipment ●
METHODOLOGY
The evaluation goals and methodology applicable to six (6) detailed evaluation items required by the
enforcement regulation of Korean Atomic Energy Act are as follows:
Master List And Administrative Procedures of Qualified Equipment
Check if the master list of equipment to be qualified, in the seismic qualification plans, is available. In addition,
evaluate if the list of systematic administrative procedures applicable to the equipment including the list of equipment
replaced during the operation is prepared. Also, check if the technical basis applied when classifying the equipment used
for the seismic qualification is appropriate.
Method of Equipment Qualification and Quality Assurance
Review if the seismic qualification method used when preparing the seismic qualification plans is appropriate and
evaluate if the seismic qualification works are actually properly performed. Review the seismic qualification documents,
evaluate if the applied seismic qualification technical standards are sufficiently met. Next, check if the quality control
procedures are suitable. Then compare the seismic qualification technical standards applied on the design of nuclear
power plant with the latest regulatory requirements.
Analysis of Equipment Failures Influencing the Qualification
Analyze both the periodic monitoring procedures, required for maintaining the optimal condition of equipment, and
equipment failure influencing the qualification results. Check if the appropriate actions are taken to assure the
qualification performance of equipment due to maintenance and replacement of equipment.
Monitoring the Environmental Condition of Qualified Equipment
Access if the environmental conditions, considered upon seismic qualification, are appropriately maintained.
environmental conditions do not meet their requirements. Then check if the countermeasure plans intended to protect the
equipment in the seismic qualification plans are prepared.
Physical Condition and Functionality of Qualified Equipment
Evaluate the physical condition and functionality of equipment used for the seismic qualification. Review if the
equipment is appropriately and safely installed. Perform the walk-down to check if the equipment is appropriately and
safely installed. Access if there are any factors influencing the seismic safety of equipment through visual inspection and
then provide recommendations for the improvement of seismic safety of equipment.
Maintenance Records of Qualified Equipment
Check if the equipment qualification records including seismic qualification documents are stored and managed
under auditable conditions. These documents are essential to earthquake-proof qualification and evaluation.
CODE AND STANDARDS
The nuclear power plants operated in Korea may be classified into Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) and
Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) of four (4) groups as shown in the table 1.
Table 1. PSR Status of Seismic Qualification Performed for Korean Operating NPPs
Items GroupⅠ GroupⅡ GroupⅢ Others
Reference
years Before 1975 1975~1989 After 1989 PHWR
License basis
Housner type spectrum IEEE 344-1971 SRP 3.7(Rev. 2) is not applied
Reg. Guide 1.60 IEEE 344-1975 SRP 3.7(Rev.2) is not applied
Reg. Guide 1.60 IEEE 344-1987 SRP 3.7(Rev. 2) is applied
Canadian spectrum
NPPs
Kori 1 Kori 2
Kori 3, 4
Yonggwang 1, 2, 3, 4 Ulchin 1, 2
Ulchin 3, 4, 5, 6 Yonggwang 5, 6
Wolsong 1 Wolsong 2, 3, 4
Seismic issues
USI A-46 USI A-40 USI A-17
USI A-40
Updated license basis is
owned
-PSR status
Completely done (K 1: life extension is
under processing)
K 3, 4 / Y 1, 2, 3, 4: Completely done U 1, 2: Under review
To be performed
W 1: Completely done W 2: Under
processing W 3,4: To be
performed
The operating license of each group is permitted based on different standards. Therefore, different seismic
qualification and evaluation standards are applied to each group. The license basis is classified into legal requirements
commonly applied to all the nuclear power plants operating in Korea and detailed technical requirements prepared in
consideration of characteristics of specific power plant. The structures of technical requirements commonly applied to the
Codes and standards development organizations
ASME ●
IEEE ●
ANS ●
NRC Code of Federal Regulation (CFR) applicable to Nuclear Power (law)
10CFR50.49 ●
10CFR21 ●
10CFR50 Appendix A ●
NRC and research organizations
NUREGs ●
Branch technical ●
positions Research results ●
Codes, standards, and other documents cited by
10CFRXX ASME Sec. III
ASME Sec. XI IEEE 279-71 IEEE 323-74
DOR guidelines NUREG-0588
Codes, standards, and other documents applicable per plant-specific requirements (commitments)
FSAR ●
NRC order ●
Utility commitment ●
IEEE 344 IEEE 382
RG 1.97 SRP(NUREG -0800)
Other codes and standards used to develop/implement plant procedures and practices (nonmandatory) IEEE 334
IEEE 323-83
IE Notices NRC research report EPRI reports Utility, manufacturer, and
contractor policies, programs, procedures, and practices
Figure 1. Hierarchy of Equipment Qualification Requirements, Standards, and Practices
Legal Requirements
The legal requirements of evaluating if the seismic qualification of equipment installed in the nuclear power plant
under operation is appropriate are as follows:
Clause 42.4 of Enforcement Decree of Korean Atomic Energy Act ●
(Periodic safety review method and standards)
Clause 19.3 of Enforcement Regulation of Korean Atomic Energy Act ●
(Periodic safety review standards)
Ministry of Science and Technology Decree No. 30 ●
(Rule on technical code and standards such as radiation safety control)
Ministry of Science and Technology Decree No. 31 ●
(Rule on technical code and standards such as nuclear reactor)
Ministry of Science and Technology Notice No. 2000-8 ●
Ministry of Science and Technology Notice No. 2002-5 ●
(Regulation on initial periodic safety review of electricity generating reactor)
Ministry of Science and Technology Notice No. 2002-21 ●
(Regulation on safety class of nuclear reactor and standards of each class)
Detailed Technical Requirements
Check the design data, administrative actions and regulatory actions, taken by the regulatory body, and the owner's
commitment in order to evaluate if the technical standards and methodology applied to the seismic qualification of
nuclear power plant are effective and valid. The nuclear power plants operating in Korea are classified into Combustion
Engineering type, Westinghouse type, CANDU type, and Korean standard type. The detailed technical standards, used
upon design, are in the FSAR. The seismic qualification and evaluation are performed in consideration of nuclear power
plant operation experience and study results. The representative technical standards of each nuclear power plant
stipulated in the FSAR are as follows: We evaluate the technical standards after comparing with IEEE 344-1987
standards[5].
Methodology for Qualifying Westinghouse WRD Supplied NSSS Safety-Related Electrical ●
Equipment, WCAP-8587
Seismic Qualification of C-E Instrumentation Equipment, CENPD-182 ●
Seismic Qualification, AECL Safety Design Guides 86-03650-SDG-002 ●
UTE C 20-420, Guide for Equipment Seismic Testing Procedures ●
EVALUATION RESULTS
The evaluation results show that most of the nuclear power plants meet the requirements for the evaluation
standards, methods and procedures except for the nuclear power plants of group I of Table 1. Furthermore, the evaluation
items applied to each nuclear power plant are required to be partially complemented (refer to the Table 2).
Evaluation Results of Each Item
From the results of evaluating the master list and administrative procedures of qualified equipment, the seismic
categories of Nuclear Steam Supply System (NSSS) and Balance of Plant (BOP) are appropriately classified according to
Regulatory Guide 1.29[6]. The lists of equipment and qualification report are specified in chapters 3.10 and 3.11 of the
FSAR. However, the seismic qualification documents are not kept for nuclear power plants belonging to Group I.
From the results of evaluating the method of equipment qualification and quality assurance, the quality assurance
activity has performed appropriately in each of the nuclear power plant. Also, the results of comparing the seismic input
motion, response spectrum analysis procedures, seismic qualification method, excitation direction of input motion,
waveform of input motion and functionality monitoring as per IEEE 344 standards show that the nuclear power plants,
designed by versions prepared before 1975, partially meet the technical standard requirements.
From the results of evaluating the analysis of equipment failures influencing qualification, each nuclear power
plant takes the appropriate actions required for analysis of the failure according to standard technical administrative
procedures.
The results from evaluating the environmental condition of qualified equipment show that each nuclear power
enable the equipment to keep its seismic performance during the service life of nuclear power plant under any
circumstance. The results also show that each nuclear power plant meets the requirements for the technical standards by
monitoring potential earthquakes using the earthquake monitoring system.
The results from evaluating the installation condition of the seismically qualified equipment and functional items
show that each nuclear power plant appropriately prepares countermeasure plans against earthquakes by checking the
ruggedness of equipment anchor and the interference between surrounding equipment by means of site survey or
walk-down during the overhaul period. Each nuclear power plant records the required information after completing the
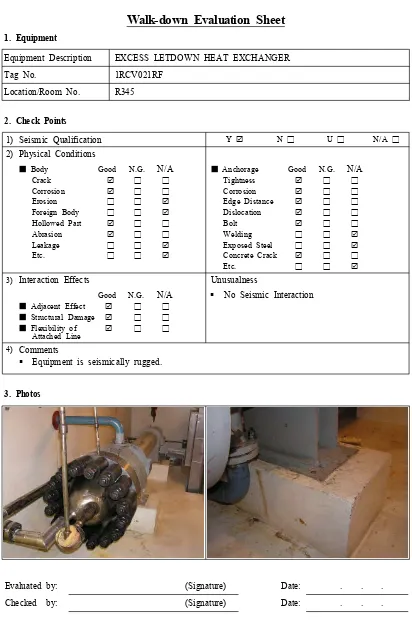
walk-down evaluation sheet for each equipment (refer to the table 3).
Also, the results from evaluating the maintenance records and administrative procedures of qualified equipment
show that all power plants do not adequately prepare records maintenance and control procedures required for seismic
qualification.
In this regard, we have identified the items to be supplemented and prepared performance plans to meet the
requirements. At the stage, we are undertaking the required works by following the performance plans.
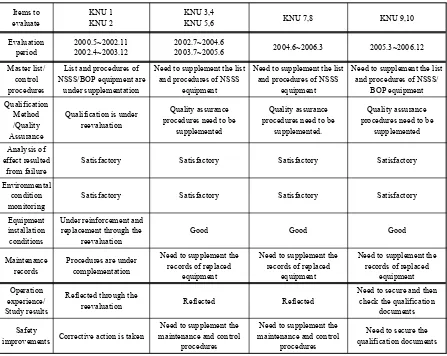
Table 2. Summary of PSR Results Acquired from the Seismic Qualification Performed for Korean Operating NPPs
Items to evaluate
KNU 1 KNU 2
KNU 3,4
KNU 5,6 KNU 7,8 KNU 9,10
Evaluation period
2000.5~2002.11 2002.4~2003.12
2002.7~2004.6
2003.7~2005.6 2004.6~2006.3 2005.3~2006.12
Master list/ control procedures
List and procedures of NSSS/BOP equipment are
under supplementation
Need to supplement the list and procedures of NSSS
equipment
Need to supplement the list and procedures of NSSS
equipment
Need to supplement the list and procedures of NSSS/
BOP equipment
Qualification Method /Quality Assurance
Qualification is under reevaluation
Quality assurance procedures need to be
supplemented
Quality assurance procedures need to be
supplemented.
Quality assurance procedures need to be
supplemented
Analysis of effect resulted
from failure
Satisfactory Satisfactory Satisfactory Satisfactory
Environmental condition monitoring
Satisfactory Satisfactory Satisfactory Satisfactory
Equipment installation conditions
Under reinforcement and replacement through the
reevaluation
Good Good Good
Maintenance records
Procedures are under complementation
Need to supplement the records of replaced
equipment
Need to supplement the records of replaced
equipment
Need to supplement the records of replaced
equipment
Operation experience/ Study results
Reflected through the
reevaluation Reflected Reflected
Need to secure and then check the qualification
documents
Safety
improvements Corrective action is taken
Need to supplement the maintenance and control
procedures
Need to supplement the maintenance and control
procedures
Safety Improvement Items
All actions such as seismic qualification, design change and equipment replacement and repair history are
appropriately maintained and controlled through the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System and procedures.
However, the systematic administrative procedures of seismic qualification need to be prepared and supplemented for the
improvement of seismic safety. We plan to supplement the insufficient items found in the nuclear power plants after
preparing for performance plans.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The seismic qualification and evaluation are performed for the equipment operating in the Korean nuclear power
plants in order to check or evaluate if the equipments belong to seismic category I class of NSSS and BOP according to
clause 19.2.3 of enforcement regulation of Korean Atomic Energy Act, ‘details of periodic safety review.’ We have
found out how to improve the seismic safety by reviewing or referring to the technical standards in the FSAR, applicable
technical standards and updated technical standards.
From evaluation results, most of the nuclear power plants except those plants belonging to group 1 meet the
requirements for the seismic qualification.
The systematic maintenance and administrative procedures need to be prepared and supplemented in order to meet
the requirements for the enforcement regulation of Korean Atomic Energy Act and updated IEEE 344 Standards and
improve the seismic safety. We are currently making every effort to accomplish it.
REFERENCES
1. Enforcement Regulation of the Korean Atomic Energy Act, “Periodic Safety Review of Operating Nuclear Power
Plants,” Ministry of Science and Technology, Korea, 2001.
2. IAEA Safety Series No. 50-SG-O12, “Periodic Safety Review of Operational Nuclear Power Plants,” IAEA, Vienna,
1994.
3. IAEA Safety Standards Series No. NS-G2.10, “Periodic Safety Review for Nuclear Power Plants,” IAEA, Vienna,
2003.
4. EPRI TR-100516, “Nuclear Power Plant Equipment Qualification Referenced Manual,” EPRI, 1992.
5. IEEE Std 344-1987, “IEEE Recommended Practice for Seismic Qualification of Class 1E Equipment for Nuclear
Power Generating Stations,” IEEE, New York, NY.
Table 3. Sample of Walk-down Evaluation Sheet
Seismic PSR NPP Unit ○○ ○
Walk-down Evaluation Sheet
1. Equipment
Equipment Description EXCESS LETDOWN HEAT EXCHANGER
Tag No. 1RCV021RF
Location/Room No. R345
2. Check Points
1) Seismic Qualification Y N □ U □ N/A □
2) Physical Conditions
Body Good N.G.
■ N/A
Crack □ □
Corrosion □ □
Erosion □ □
Foreign Body □ □ Hollowed Part □ □
Abrasion □ □
Leakage □ □
Etc. □ □
Anchorage Good N.G.
■ N/A
Tightness □ □
Corrosion □ □
Edge Distance □ □
Dislocation □ □
Bolt □ □
Welding □ □
Exposed Steel □ □ Concrete Crack □ □
Etc. □ □
3) Interaction Effects Unusualness
Good N.G. N/A Adjacent Effect
■ □ □
Structural Damage
■ □ □
Flexibility of
■ □ □
Attached Line
No Seismic Interaction
4) Comments
Equipment is seismically rugged.
3. Photos
Evaluated by: (Signature) Date: . . .
Checked by: (Signature) Date: . . .