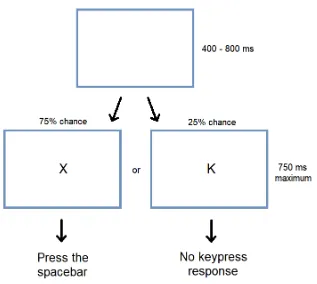
Dopaminergic Medication Decreases Motor Impulsivity on the Go/No-go Task in Parkinson's Disease
Full text
Figure

Related documents
The model/method integrates the Modular Open Systems Approach (MOSA) with two powerful mathematical models, namely the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Goal
In order to ensure that post-discharged COVID-19 patients were appropriately monitored and provided with the required input, a group of clinicians with clinical expertise
Purposive sampling technique was employed to select one hundred respondents from the Faculties of Education and social Sciences in the University of Ibadan who were using the library
As Eisler (1987) points out, this gendered division between men and women has particularly deep historical roots that perhaps do not exist in relation to other oppressed groups,
Automated reasoning tools are a collection of GeoGebra features and commands that allow to conjecture, discover, adjust and prove geometric statements in a dynamic geometric
However, recent research has arrived at a more nuanced understanding of mind wandering, demonstrating that overall mind wandering can be decomposed into spontaneous
Linkage between multiple sclerosis natural history data, trial outcomes, and cost and qual- ity of life data was through the expanded disability status scale (EDSS).. As this is
- The student is able to identify significant theological, ministerial, and pastoral issues; develop a thesis that draws upon relevant scholarly research in