Dynamic interferometric measurement with extended unambiguity range in flow measurement
Full text
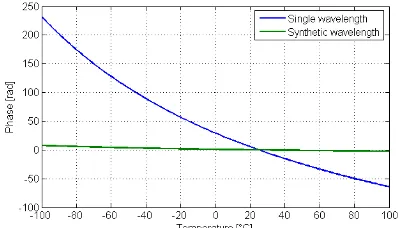
Figure


Related documents
An important question in managing patients with prior anti- NMDAR encephalitis concerns the duration of long-term monitoring after the initial episode to facilitate early
This study aimed to assess the prevalence of anxiety and depression and to identify their associated factors including metabolic components among people with type 2 diabetes..
However, it is unclear to what extent researchers contribute to these presumptions, and how often these relationships are thoroughly delineated within the context of
The aim of this study was to determine the an- tibacterial activity of two traditionally used herbs in Iranian medicine, Anacyclus pyrethrum and Pistacia lentiscus L., on
Because of the importance and sensitivity of CA1 area of hippocampus and the pathophysiological mechanisms of cerebral ischemia, this study provided the novel thera- peutic window
In conclusion, the finding of the current study indicat- ed that a BSA based nanocurcumin in doses of 15 and 20 mg/kg -the doses which natural curcumin has no ef- fect-
Although formal hunting status is found significant when individually entered, the variation it explains is not significant enough (or unique enough) to be included in the
Rather than focusing exclusively on incentives and expectations about the base rate of errors, the field interview study examines payoffs of error detection more broadly by