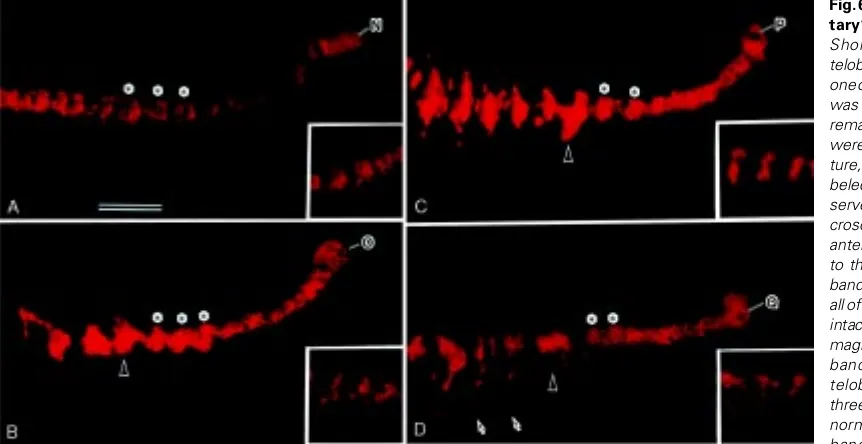
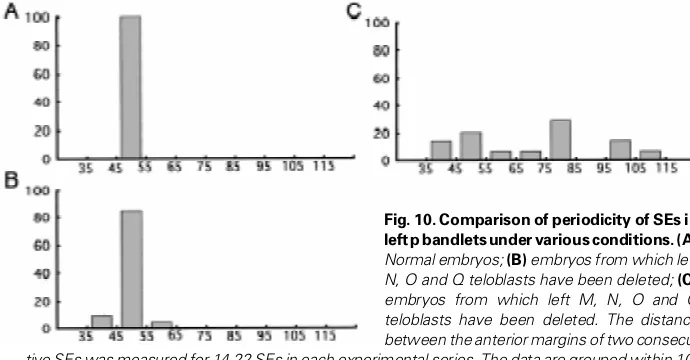
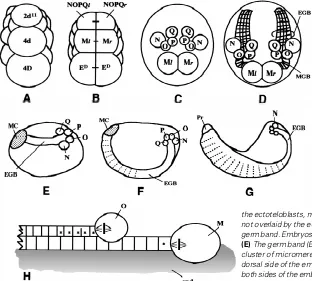
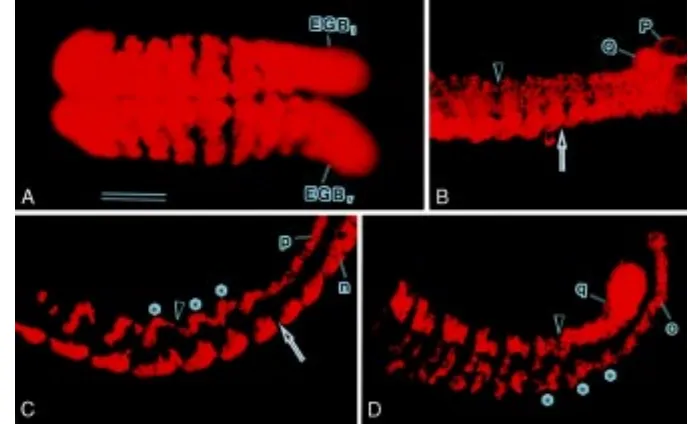
Cell lineage analysis of pattern formation in the Tubifex embryo II Segmentation in the ectoderm
Full text
Figure
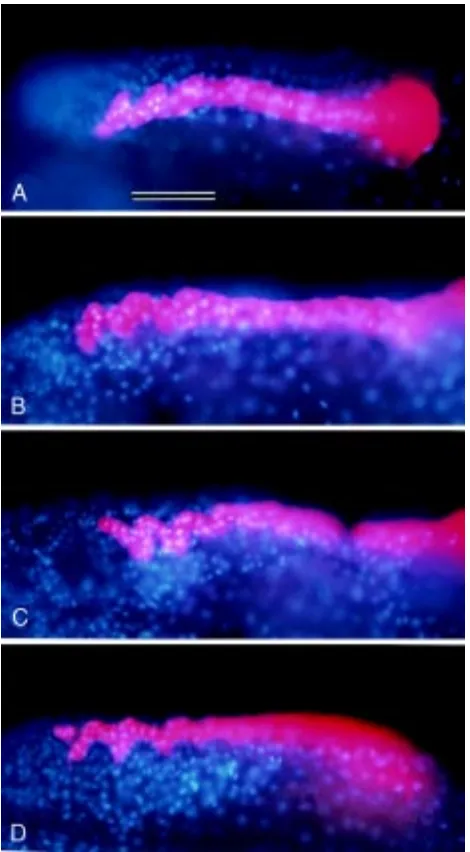
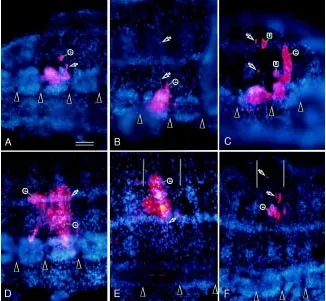
Related documents
También líderes liberales de menos poder (por ejemplo Muñoz 1903) así como varios jefes conservadores (Folíaco 1903; Villamizar 1903; González 1904), publicaron relatos en que
In our system, Support Vector Regression (SVR) model is employed to find out the importance of every sentence in an exceedingly paper, so integer linear programming
Analysing the connection of the grade 11 boys’ physical development parameters with such functional parameters as breath hold-up during the inhalation (s), the param- eters of the
faecalis E1Sol PIP EF and the variable region of V583 PIP EF show that the PIP EF variable region determines phage tropism (pLZEV).. faecalis V583 is indicated by
The realization of European Economic and Monetary Union has made it obvious that certain fundamental principles of the EC Treaty have be- come part of Germany's
(c) Expression of rtxBDE is induced by zebrafish larva coloniza- tion. Results of a  -galactosidase assay done using lysates of bacterial cells growing planktonically in E3 medium
Dynamics of fungal invasion, epithelial damage, and loss of epithelial barrier integrity during translocation of Candida albicans through intestinal epithelial layers.. A combination