The Evolution of lipid Metabolism in Iraqi Children with Nephrotic Syndrome
Full text
Figure

Related documents
MDD: major depressive disorder; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDL-c: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c: low-density lipoprotein choles- terol; BMI: body
MetS: metabolic syndrome; TSP: textured soy protein; TC: cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; HDL‑C: high density lipoprotein; LDL‑C: low density lipoprotein; VLDL‑C: very low
CVD: cardiovascular disease; CAD: coronary artery disease; TC: total cholesterol; HDL-c: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c: low density lipoprotein cholesterol;
There was a marked decrease in body weight, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDL‑C: high‑density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL‑C: low‑density lipoprotein
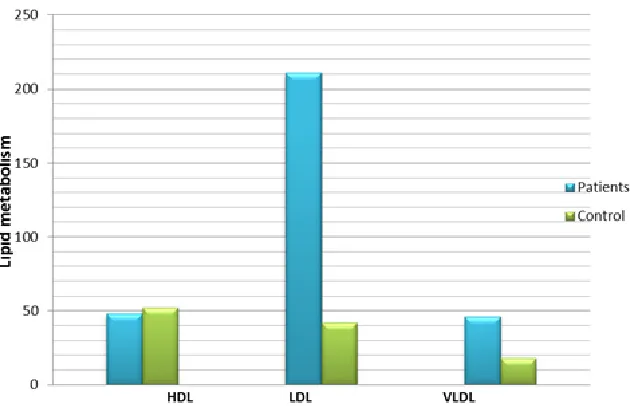
Serum total cholesterol, Low density lipoprotein (LDL), High density lipoprotein (HDL), Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), Triglycerides and Atherogenic index, and
Results: The significant increase of blood glucose level, serum total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low- density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and very
Results: A statistically significant higher serum total cholesterol, very low density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides