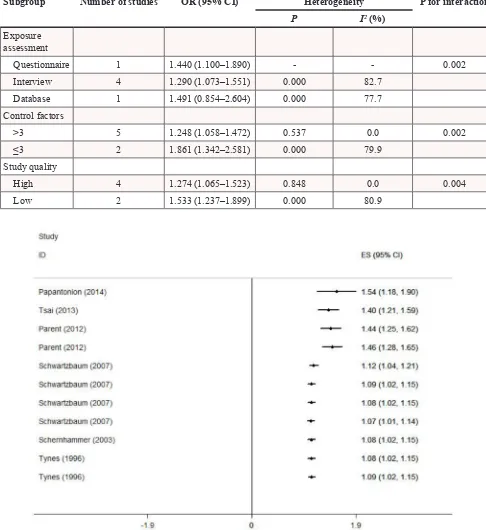
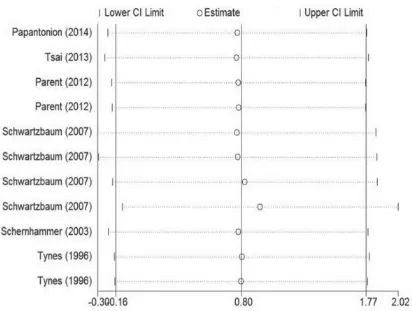
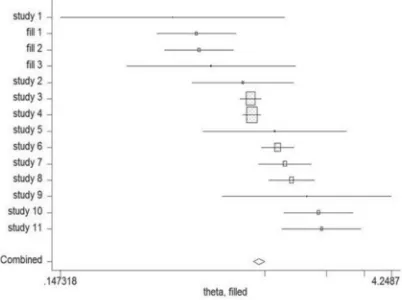
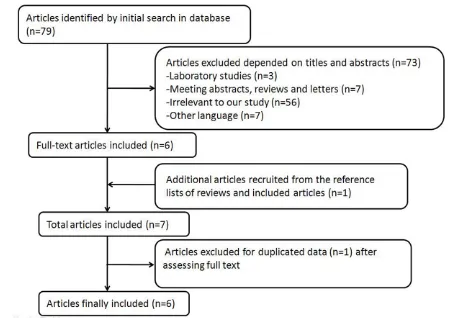
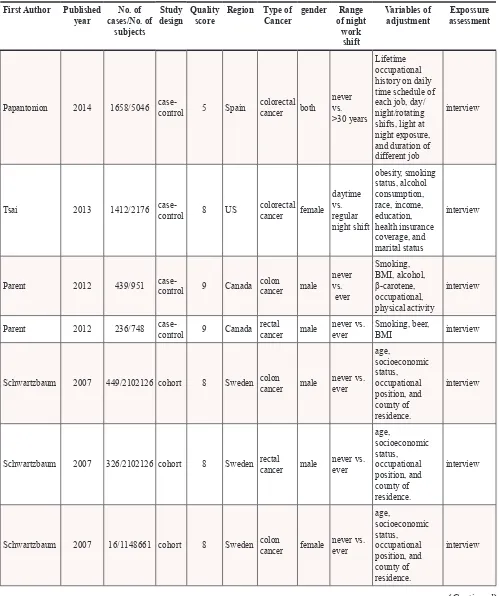
A meta-analysis including dose-response relationship between night shift work and the risk of colorectal cancer
Full text
Figure


Related documents
The lower elevations in postprandial insulin levels in T allele carriers observed in our study, associated with comparable blood glucose and similar weight reduction after
Social entrepreneurship can change the face of society in India, there have been many such examples and projects. which run under the banner of social entrepreneurship and proved to
This paper also describes a distributed framework designed to enable law enforcement agents to crack encrypted archives and applications in an efficient and cost-effective
A one-piece composite drive shaft for rear wheel drive automobile has been designed for E-Glass/ Epoxy, High Strength Carbon/Epoxy and High Modulus Carbon/Epoxy composites with
Environmental Center, designed to achieve net-zero energy usage, at Choate Rosemary Hall in Wallingford, Connecticut; the Chestnut Square student residences, a mixed-use development
We have proposed ICA algorithm (in the framework of fast ICA) where the self-adaptive nonlinear function is derived using k-distribution density model for the probability
drivers of deforestation and forest degradation, emissions reduction potential and estimates.. of
the aims of this study were (1) to quantify the contribution of early life factors to 7-year language outcomes, specifically receptive and expressive language scores and